Related Research Articles

The Mon are an ethnic group who inhabit Lower Myanmar's Mon State, Kayin State, Kayah State, Tanintharyi Region, Bago Region, the Irrawaddy Delta, and several areas in Thailand. The native language is Mon, which belongs to the Monic branch of the Austroasiatic language family and shares a common origin with the Nyah Kur language, which is spoken by the people of the same name that live in Northeastern Thailand. A number of languages in Mainland Southeast Asia are influenced by the Mon language, which is also in turn influenced by those languages.
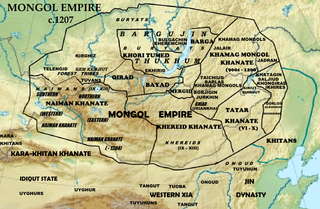
A Borjigin is a member of the Mongol sub-clan that started with Bodonchar Munkhag of the Kiyat clan. Yesugei's descendants were thus said to be Kiyat-Borjigin. The senior Borjigids provided ruling princes for Mongolia and Inner Mongolia until the 20th century. The clan formed the ruling class among the Mongols and some other peoples of Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Today, the Borjigid are found in most of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia and Xinjiang, and genetic research has shown that descent from Genghis Khan and Timur is common throughout Central Asia and other regions.
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Deg Xinag is a Northern Athabaskan language spoken by the Deg Hitʼan peoples of the GASH region. The GASH region consists of the villages of Grayling, Anvik, Shageluk, and Holy Cross along the lower Yukon River in Interior Alaska. The language is severely endangered; out of an ethnic population of approximately 250 people, only 2 people still speak the language.
Basaa, or Mbene, is a Bantu language spoken in Cameroon by the Basaa people. It is spoken by about 300,000 people in the Centre and Littoral regions.

Tamilakam is the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, Lakshadweep and southern parts of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. Traditional accounts and the Tolkāppiyam referred to these territories as a single cultural area, where Tamil was the natural language and permeated the culture of all its inhabitants. The ancient Tamil country was divided into kingdoms. The best known among them were the Cheras, Cholas, Pandyans and Pallavas. During the Sangam period, Tamil culture began to spread outside Tamilakam. Ancient Tamil settlements were also established in Sri Lanka and the Maldives (Giravarus).

Ghana is a multilingual country in which about eighty languages are spoken. Of these, English, which was inherited from the colonial era, is the official language and lingua franca. Of the languages indigenous to Ghana, Akan is the most widely spoken in the south. Dagbani is most widely spoken in the north.
Anguthimri is an extinct Paman language formerly spoken on the Cape York Peninsula of Queensland, Australia, by the Anguthimri people who lived in the area from the mouth of the Mission River north to Pennefather River and west to Duyfken Point. It is unknown when it became extinct.
Nedebang is a Papuan language spoken in the villages of Balungada and Baulang in the eastern district of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. There are also Nedebang speakers in Air Panas, administratively part of Balungada but located 1 km from the main village.
Mwanga, or Namwanga (Nyamwanga), is a Bantu language spoken by the Mwanga people in the Northern Province of Zambia and in Mbeya Region, Tanzania. The 2010 Zambian census found 140,000 speakers. The current number in Tanzania is unknown; Ethnologue cites a figure from 1987 of 87,000.

Arabi Malayalam is the traditional Dravidian language of the Mappila Muslim community. It is spoken by several thousand people, predominantly in the Malabar Coast of Kerala state, southern India. The form can be classified as a regional dialect in northern Kerala, or as a class or occupational dialect of the Mappila community. It can also be called a vernacular in general, or as a provincial patois, with the latter label being increasingly applicable in Colonial times. All the forms of the Malayalam language, including Mappila, are mutually intelligible.
Larteh is a language of southeastern Ghana. It belongs to the Guang subgroup of the Niger-Congo languages and is spoken by about 74,000 people.
The Oti–Volta languages form a subgroup of the Gur languages, comprising about 30 languages of northern Ghana, Benin, and Burkina Faso spoken by twelve million people. The most populous language is Mooré, the national language of Burkina Faso, spoken by over 55% of Burkina Faso’s 20 million population and an additional 1 million in neighboring countries such as Ghana, Ivory Coast, Niger, and Mali.
The Guan languages are languages of the Kwa language family spoken by the Guan people in Ghana and Togo:
The Guan or Guang people are an ethnic group found almost in all parts of Ghana, including the Krachi people, language-Kaakye people Nkonya tribe, the Gonja, Anum, Larteh, Akposo, Nawuri and Ntsumburu. The Guan are believed to have been the first settlers in modern day Ghana, migrating from the Mossi region of modern Burkina around 1000 A.D.
Chamba Leko is one of two languages spoken by the Chamba people, the other being Chamba Daka. It is a member of the Leko branch of Savanna languages, and is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
The Mampruli language is a Gur language spoken in northern Ghana, Northern Togo, Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali by the Mamprusi people. It is partially mutually intelligible with Dagbani. The Mamprusi language is spoken in a broad belt across the northern parts of the Northern Region of Ghana, stretching west to east from Yizeesi to Nakpanduri and centred on the towns of Gambaga, Nalerigu and Walewale.
Nawuri is a Guang language of Ghana. It is nearly intelligible with Kyode.
Of the populated places in the Eastern region of Ghana, Larteh Akuapem is the capital of the Benkum Division of the Akuapem Traditional Council. It lies on the east of the ridge on the Akonnobepow.

Northern Alta is a distinctive Aeta language of the mountains of the Sierra Madre in Aurora province, Northern Philippines. Linguist Lawrence Reid reports two different Alta languages, Northern and Southern Alta, which form one of the high nodes of the Northern Luzon languages, together with the South-Central Cordilleran subgroup. Although the Alta languages are genetically related, they have a low level of mutual intelligibility.
References
- ↑ Gua at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)