Related Research Articles
The Central Tano or Akan languages are a pair of dialect clusters of the Niger-Congo family spoken in Ghana and Ivory Coast by the Akan people.

The modern Mfantsefo or Fante confederacy is a combination of Akan people and aboriginal Guan people. The Fante people are mainly located in the Central and Western regions of Ghana, occupying the forest and coastal areas. Their land stretches from the eastern part of western region in the west to Gomoa in the east. The Fante can be broadly categorized into two groups - the Borbor/Boka Fante(Akan ancestry) and the Etsii Fante(Guan ancestry). Over the last half century, Fante communities have been established as far as Gambia, Liberia, and even Angola due to fishing expeditions. Major Fante cities in modern Ghana include Oguaa, Edina (Elmina), Sekondi Takoradi, Agona Swedru, Mankessim, Saltpond,Winneba,Shama, Komenda, Tarkwa, Kasoa and Anomabo.

Akan is the largest language of Ghana, and the principal native language of the Akan people, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population speak Akan as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. Akan is also spoken across the border in parts of Côte d'Ivoire.
The Akan people are a Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak languages within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi, Ashanti, Baoulé, Bono, Chakosi, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta, and Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal matrilineal descent in the inheritance of property, and for succession to high political office. All Akans are considered royals in status, but not all are in royal succession or hold titles.
Kofi is an Akan masculine given name among the Akan people in Ghana that is given to a boy born on Friday. Traditionally in Ghana, a child would receive their Akan day name during their Outdooring, eight days after birth.
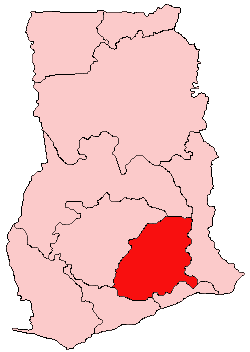
Kwahu or Kwawu is an area and group of people that live in Ghana and are part of the Twi-speaking Akan group. The region has been dubbed Asaase Aban, or the Natural Fortress, given its position as the highest habitable elevation in the country. Kwahu lies in the Eastern Region of Ghana, on the west shore of Lake Volta. The Kwahus share the Eastern Region with the Akyem and Akuapem, as well as the Adangbe-Krobos. Among Kwahu lands, a significant migrant population works as traders, farm-hands, fisherfolk, and caretakers in the fertile waterfront 'melting pot' of Afram plains. These migrants are mostly from the Northern and Volta Regions, as well as, some indigenous Guans from the bordering Oti and Brong-Ahafo regions live in the Afram Plains area. Kwahus are traditionally known to be wealthy traders, owning a significant number of businesses and industries in Ghana.

Fante, also known as Fanti, Fantse, or Mfantse, is one of the three literary dialects of the Akan language, along with Asante and Akuapem, with which it is mutually intelligible. It is principally spoken in the central and southern regions of Ghana as well as in settlements in other regions in western Ghana, Ivory Coast, as well as in Liberia, Gambia and Angola.

Adinkra are symbols from Ghana that represent concepts or aphorisms. Adinkra are used extensively in fabrics, logos and pottery. They are incorporated into walls and other architectural features. Adinkra symbols appear on some traditional Akan goldweights. The symbols are also carved on stools for domestic and ritual use. Tourism has led to new departures in the use of symbols in items such as T-shirts and jewellery.

Ghana is a multilingual country in which about eighty languages are spoken. Of these, English, which was inherited from the colonial era, is the official language and lingua franca. Of the languages indigenous to Ghana, Akan is the most widely spoken in the south. Dagbani, Dagare, Sisaala, Waale, and Gonja are among the most widely spoken in the northern part of the country.
This is a list of rulers and office-holders of Ghana.
The Mankessim Kingdom (1252–1844) was a pre-colonial African state in modern-day Ghana. It is regarded as the heartland of the Fante people, and operated as capital of the Fante Confederacy in the 19th century. The town of Mankessim still exists, and is located in the Central Region of Ghana, about an hour and a half drive west of Accra. The Mankessim Kingdom's influence was quite vast; it extended to the whole of the Fante people, and at times the entire coast of modern-day Ghana.
Articles related to Ghana include:

The Akyem are an Akan people. The term Akyem is used to describe a group of four states: Asante Akyem, Akyem Abuakwa, Akyem Kotoku, and Akyem Bosome. These nations are located primarily in the eastern region in south Ghana. The term is also used to describe the general area where the Akyem ethnic group clusters. The Akyem ethnic group make up between 3-4 percent of Ghana's population depending on how one defines the group and are very prominent in all aspects of Ghanaian life. The Akyem are a matrilineal people. The history of this ethnic group is that of brave warriors who managed to create a thriving often influential and relatively independent state within modern-day Ghana. When one talks of Ghanaian history, there is often mention of The Big Six. These were six individuals who played a big role in the independence of Ghana. Of the big six, people of Akyem descent made up the majority.

Akropong is a town in South Ghana and is the capital of the Akuapim North District, a district in the Eastern Region of South Ghana. This town is known for producing snails and palm oil. Akropong has a 2013 settlement population of 13,785 people.
Bono, also known as Abron, Brong, and Bono Twi, is a major dialect within the Akan dialect continuum that is spoken by the Bono people. Bono is spoken by approximately 1.2 million people in Ghana, primarily in the Bono Region, Bono East Region, and by over 300,000 in eastern Côte d'Ivoire.

The Asante, also known as Ashanti in English, are part of the Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante people as their native language.
Twi is the common name of the Akan literary dialects of Asante and Akuapem. Effectively, it is a synonym for 'Akan' that is not used by the Fante people. It is not a linguistic grouping, as Akuapem Twi is more closely related to Fante dialect than it is to Asante Twi. Twi generally subsumes the following Akan dialects: Ahafo, Akuapem, Akyem, Asante, Asen, Dankyira and Kwawu, which have about 4.4 million speakers in southern and central Ghana.
Akuapem, also known as Akuapim, Akwapem Twi, and Akwapi, is one of the literary dialects of the Akan language, along with Asante and Fante, with which it is mutually intelligible. There are 626,000 speakers of Akuapem, mainly concentrated in Ghana and southeastern Cote D'Ivoire. It is the historical literary and prestige dialect of Akan, having been chosen as the basis of the Akan translation of the Bible.
Kwadwo/Kwadjo/Kojo is an Akan masculine given name originating from the Akan people, meaning born on a Monday. As an Akan given name, with the Akans being a large ethnic group consisting of various tribes such as the Fante, Asante, Akuapem among others, Kwadwo/Kwadjo is sometimes written as "Kojo", Kwadwo or Kwadjo and is also used less frequently as a family name. People born on particular days are supposed to exhibit the characteristics or attributes and philosophy, associated with the days. Kwadwo has the appellation Okoto or Asera meaning peace. Thus, males named Kwodwo tend to be peaceful.

Johann Gottlieb Christaller was a German missionary, clergyman, ethnolinguist, translator and philologist who served with the Basel Mission. He was devoted to the study of the Twi language in what was then the Gold Coast, now Ghana. He was instrumental, together with African colleagues, Akan linguists, David Asante, Theophilus Opoku, Jonathan Palmer Bekoe, and Paul Keteku in the translation of the Bible into the Akuapem dialect of Twi. Christaller was also the first editor of the Christian Messenger, the official news publication of the Basel Mission, serving from 1883 to 1895. He is recognised in some circles as the "founder of scientific linguistic research in West Africa".
References
- ↑ Akan at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)

- 1 2 "Akan". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2019-12-25.
- ↑ Schacter, Paul; Fromkin, Victoria (1968). A Phonology of Akan: Akuapem, Asante, Fante. Los Angeles: University of California Press. p. 3.
- ↑ Arhin, Kwame (1979). A Profile of Brong Kyempim: Essays on the Archaeology, History, Language and Politics of the Brong Peoples of Ghana. Afram.