
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark. It is one of two dialect groups, the other being East Low German.
Cuyonon is a regional Bisayan language spoken on the coast of Palawan and the Cuyo Islands in the Philippines. Cuyonon had been the lingua franca of the province of Palawan until recently when migration flow into the region rapidly increased. Forty-three percent of the total population of Palawan during the late 1980s spoke and used Cuyonon as a language. Later studies showed a significant decrease in the number of speakers due to an increase of Tagalog-speaking immigrants from Luzon.
Sirionó is a Tupian language spoken by about 400 Sirionó people and 120 Yuqui in eastern Bolivia in the village of Ibiato (Eviato) and along the Río Blanco in farms and ranches.

Giimbiyu is an extinct Aboriginal Australian language isolate once spoken by the Giimbiyu people of northern Australia.
Maninka, or more precisely Eastern Maninka, is the name of several closely related languages and dialects of the southeastern Manding subgroup of the Mande language family. It is the mother tongue of the Malinké people in Guinea, where it is spoken by 3.1 million people and is the main language in the Upper Guinea region, and in Mali, where the closely related Bambara is a national language, as well as in Liberia, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Ivory Coast, where it has no official status. It was the language of court and government during the Mali Empire.
Aghu, or Central Awyu, is a Papuan language of South Papua, Indonesia. It may actually be two languages, depending on one's criteria for a 'language'. The two varieties are: Mappi River Awyu (Aghu) and Pasue River Awyu.

Shumashti – also known as Shumasht – is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in eastern Afghanistan. It is spoken in parts of Kunar Province: on the western side of the Kunar Valley between Jalalabad and the Pech Valley. The number of speakers was estimated at 1,000 in 1994.
Subtiaba is an extinct Oto-Manguean language which was spoken on the Pacific slope of Nicaragua, especially in the Subtiaba district of León. Edward Sapir established a connection between Subtiaba and Tlapanec. When Lehmann wrote about it in 1909 it was already very endangered or moribund.

Spanish is the language that is predominantly understood and spoken as a first, or second language by nearly all of the population of Argentina. According to the latest estimations, the population is currently greater than 45 million.
The Ngbandi language is a dialect continuum of the Ubangian family spoken by a half-million or so people in the Democratic Republic of Congo and in the Central African Republic. It is primarily spoken by the Ngbandi people, which included the dictator of what was then known as Zaire, Mobutu Sese Seko.
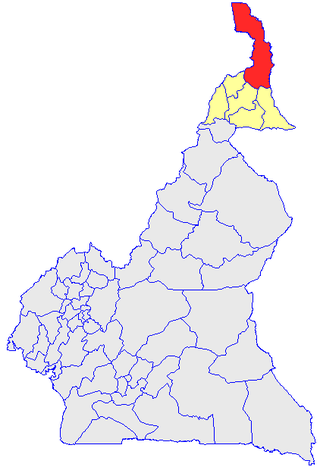
Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 12,133 km2 and at the 2005 Census had a total population of 486,997. The capital of the department is at Kousséri. Most inhabitants of this department speak Chadian Arabic.

Sámi languages, in English also rendered as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.
Asu is a Nupoid language spoken in Niger State in Western Nigeria. The Asu live in about ten villages southeast of Kontagora.
Phowa is a dialect cluster of Loloish languages spoken by the Phula people of China. There are three principal varieties, Hlepho, Ani, and Labo, which may be considered distinct languages. Hlepho may be closer to Phukha than it is to Labo and Ani. Usage is decreasing, with about two-thirds of Phowa speaking their language.
Zemba or Dhimba is a Bantu language spoken mainly in Angola where the language has about 18,000 speakers, and also in Namibia with some 7,000. It is closely related to Herero, and is often considered a dialect of that language, especially as the Zemba are ethnically Herero.
Central Teke is a member of the Teke languages dialect continuum of the Congolese plateau. Central Teke dialects are Ngungwel and Mpu (Mpumpum), Boo, and Nzikou (Njyunjyu/Ndzindziu). They are spoken in the Malebo Pool region of the Republic of Congo, with an unknown number of Boo speakers in DRC.
Bala (Lobala) is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. According to Maho (2009), it includes Boko (Iboko).
Alto Pativilca–Alto Marañón–Alto Huallaga Quechua is a dialect cluster of Quechua languages spoken in the Peruvian provinces of Huánuco, Lauricocha, Cajatambo and neighboring areas. The best-known dialect within the Huánuco cluster is Huallaga Quechua.
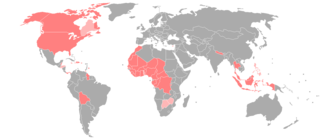
American Sign Language (ASL) developed in the United States and Canada, but has spread around the world. Local varieties have developed in many countries, but there is little research on which should be considered dialects of ASL and which have diverged to the point of being distinct languages.






