Related Research Articles

Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of 114,763 square kilometres (44,310 sq mi) and its population in 2021 was estimated to be approximately 13 million. It is a tropical nation, dependent on agriculture, and is an exporter of palm oil and cotton. Some employment and income arise from subsistence farming.

Cotonou is a city in Benin. Its official population count was 761,137 inhabitants in 2006; however, some estimates indicate its population to be as high as 2.4 million.

Porto-Novo, also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe, is the capital of Benin. The commune covers an area of 110 square kilometres (42 sq mi) and as of 2002 had a population of 223,552 people.

Benin City is the capital and largest city of Edo State, Nigeria. It is the fourth-largest city in Nigeria according to the 2006 census, after Lagos, Kano, and Ibadan, with a population estimate of about 3,500,000 as of 2022. It is situated approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of the Benin River and 320 kilometres (200 mi) by road east of Lagos. Benin City is the centre of Nigeria's rubber industry, and oil production is also a significant industry.

Alibori is the largest and northernmost department of Benin. Externally the department borders the countries of Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria, and internally the departments of Atakora and Borgou. The department of Alibori was created in 1999 when it was split off from Borgou Department and is named after the Alibori River.
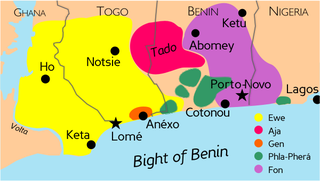
Fon is spoken in Benin, Nigeria, Togo, Ghana and Gabon by approximately 1.7 million speakers, and is the language of the Fon people. Like the other Gbe languages, Fon is an isolating language with an SVO basic word order.

Edo, commonly known as Edo State, is a state located in the South-South geopolitical zone of Nigeria. As of 2006 National population census, the state was ranked as the 24th populated state (3,233,366) in Nigeria, However there was controversy over the population census figures, for example this same state that was ranked 24, population wise in 2006, was number 16 in terms of voters registration in the country in 2019, That shows strongly that the census conducted in 2006 is not a testament of reality on ground. The state population figures is expected to be about 8,000,000 in 2022. Edo State is the 22nd largest State by landmass in Nigeria. The state's capital and city, Benin City, is the fourth largest city in Nigeria, and the centre of the country's rubber industry. Created in 1991 from the former Bendel State, is also known as the heart beat of the nation. Edo State borders Kogi State to the northeast, Anambra State to the east, Delta State to the southeast and southsouth and Ondo State to the west.
The Edoid languages are a few dozen languages spoken in Southern Nigeria, predominantly in the former Bendel State. The name Edoid derives from its most widely spoken member, Edo, the language of Benin City, which has 25 million native and secondary speakers.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language of Nigeria is English, the language of former colonial British Nigeria. As reported in 2003, Nigerian Pidgin was spoken as a second language by 60 million people in Nigeria.
Bissa, is a Mande ethnic group of south-central Burkina Faso, northeastern Ghana and the northernmost tip of Togo. Their language, Bissa, is a Mande language that is related to, but not the same as, a cluster of languages in the old Borgu Kingdom area of Northeast Benin and Northwest Nigeria, including Busa, Boko, and Kyenga. An alternate name for the Bissa is Busansi or Busanga which is used by the Mossi people.
Isoko is an Edoid language, one of the languages in Delta State spoken by the Isoko people in Isoko South, North and part of Ndokwa East Local Government Areas of Delta State, Southern part of Nigeria in Niger Delta region. It is also spoken in some part of Bayelsa. The Isoko language has close similarities between them and Edo people with other Edoid language because it is an Edoid language,the Isoko people are “an ethnic nationality made up of people and their ancestral roots can be traced through history to the Benin (Aka) kingdom, attested to by the linguistic and cultural similarities that exist between the Isoko people and the Benin (Aka)people” although a few of the Isoko communities or clans have their origins attached to the Ibo language and Urhobo language. Some 750,000 people consider themselves Isoko. Language is a mark of identity and plays an all-important role in the life of a people. The Isoko language however, is being threatened with extinction as reported by Idudhe (2002), as a result of neglect in teaching, learning and use. The Isoko language has about 20 to 21 dialects, but the Aviara/Uzere dialect is the standard dialect of the language.
Busa, or Bisã, is the Mande language of the former Borgu Emirate in northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin. It is called Busanci in Hausa, and has also been called Zugweya.

Gun is a language in the Gbe languages group. It is spoken by the Ogu people in Benin, as well as in south-western Nigeria. Gun is part of the Fon cluster of languages inside the Eastern Gbe languages; it is close to Fon, especially its Agbome and Kpase varieties, as well as to the Maxi and Weme (Ouémé) languages. It is used in some schools in the Ouémé Department of Benin.
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as the Edo Kingdom, or the Benin Empire was a kingdom within what is now south-south Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th century until 1975. The Kingdom of Benin's capital was Edo, now known as Benin City in Edo State, Nigeria. The Benin Kingdom was "one of the oldest and most developed states in the coastal hinterland of West Africa". It grew out of the previous Edo Kingdom of Igodomigodo around the 11th century AD, and lasted until it was annexed by the British Empire in 1897.
The Itsekiri language is a major branch of the Yoruboid group of languages, which as a group, is a key member of the Volta–Niger sub-family of the Niger–Congo family of African languages. Itsekiri is spoken by nearly 900,000 people in Nigeria as a first language and by many others as an additional language notably in the Niger Delta and in parts of Edo and Ondo states of Nigeria. The other key members of the Yoruboid group are Yoruba and Igala along with the various Yoruba dialects spoken in Benin and Togo.
Bariba, also known as Baatonum, is the language of the Bariba people of Benin and Nigeria and was the language of the state of Borgu.
Boko, or Boo, is a Mande language of Benin and Nigeria.
Foodo is a Guang language spoken in and around the town of Sèmèrè in the north of Benin. There are approximately 37,000 speakers. A large proportion of the population live beyond the homeland in other parts of Benin, as well as in neighboring Togo, Nigeria, and Ghana. There may be as many as 1,000 living in Ghana.
The Eastern Mande languages are a branch of the Mande languages spoken in six areas: northwest Burkina Faso, the border region of northern Benin and Nigeria, and one language, Bissa, also spoken in Ghana, Togo, and Ivory Coast.
References
- ↑ Kyenga at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.