
Regional elections in were held in France on 21 and 28 March 2004. At stake were the presidencies of each of France's 26 regions which, although they do not have legislative powers, manage sizeable budgets. The results were a triumph for the parties of the left, led by the French Socialist Party (PS) in alliance with minor parties, including the French Communist Party (PCF), the Left Radical Party (PRG) and The Greens. The left has usually fared moderately well in regional elections, but this was their best result since the regional system was introduced.

Romania elects on a national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president is elected for a five-year term by the people. The Romanian Parliament has two chambers. The Chamber of Deputies has currently 330 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists. The Senate has currently 136 members, elected for a four-year term by party-list proportional representation on closed lists.

All elections in the Czech Republic are based on the principle of universal suffrage. Any adult citizen who is at least 18 years old can vote, except those who have been stripped of their legal capacities by a court, usually on the basis of mental illness. Elected representatives are elected directly by the citizens without any intermediaries. Election laws are not part of the constitution, but – unlike regular laws – they cannot be changed without the consensus of both houses of the Parliament. The Czech Republic uses a two-round plurality voting system for the presidential and Senate elections and an open party-list proportional representation system for all other elections. The proportional representation system uses the Sainte-Laguë method for allocating seats.
A regional council is the elected assembly of a region of France.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 deputies, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

Legislative elections were held in France on 10 June and 17 June 2007 to elect the 13th National Assembly of the Fifth Republic, a few weeks after the presidential election run-off on 6 May. 7,639 candidates stood for 577 seats, including France's overseas possessions. Early first-round results projected a large majority for President Nicolas Sarkozy's Union for a Popular Movement (UMP) and its allies; however, second-round results showed a closer race and a stronger left. Nevertheless, the right retained its majority from 2002 despite losing some 40 seats to the Socialists.

Parliamentary elections were held in Djibouti on 8 February 2008. There were 65 candidates running for the 65 seats in the National Assembly, with all of the candidates coming from the ruling coalition, the Union for the Presidential Majority (UMP). The opposition boycotted the election, and the UMP won all 65 seats.

Regional elections were held in France on 15 March 1998. At stake were the presidencies of each of France's 26 regions, which, though they don't have legislative autonomy, manage sizeable budgets.

The Politics of Calabria, Italy takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Government is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Regional Government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Regional Council.

The Politics of Abruzzo takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Government is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Regional Government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the Regional Council.
The politics of Brittany, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.

The politics of Rhône-Alpes, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.

The politics of Aquitaine, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.

The Politics of Poitou-Charentes, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.

The politics of Franche-Comté, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.

The Sicilian Regional Assembly is the legislative body of Sicily. While it has a long history as an autonomous entity, the modern Region of Sicily was established by Royal Decree on 15 May 1946, before the Italian Republic. The Regional Assembly has the widest legislative power in Italy and is the only regional assembly to have the title of "parliament" whose members are called "deputies" as are those in Rome. Seventy deputies are elected every five years in the nine provinces.

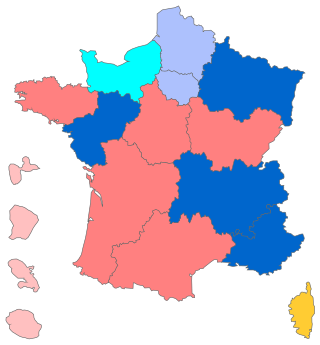
Regional elections were held in France on 6 and 13 December 2015. At stake were the regional councils in metropolitan and overseas France including the Corsican Assembly and inaugural seats in the Assembly of French Guiana and Assembly of Martinique, all for a six-year term. The Departmental Council of Mayotte, which also exercises the powers of a region, was the only region not participating in this election, having already been renewed on 2 April 2015. There were 18 regional presidencies at stake, with 13 in mainland France and Corsica, as well as 5 overseas. Though they do not have legislative autonomy, these territorial collectivities manage sizable budgets. Moreover, regional elections are often taken as a mid-term opinion poll.
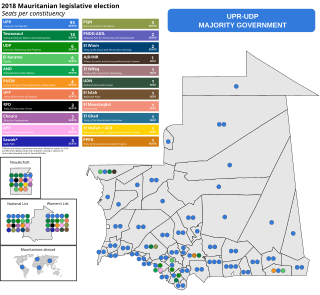
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.

Regional elections were held in France on 20 June and 27 June 2021. At stake were the regional councils in metropolitan and overseas France including the Corsican Assembly, Assembly of French Guiana and Assembly of Martinique, all for a six-year term. The Departmental Council of Mayotte, which also exercises the powers of a region, also participated in this election, because the departmental elections were held at the same time. Eighteen regional presidencies were at stake, with thirteen in mainland France and Corsica, as well as five overseas. Though they do not have legislative autonomy, these territorial collectivities manage sizable budgets. Moreover, regional elections are often perceived as a mid-term opinion poll. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the regional and departmental elections were postponed, first to 13 and 20 June 2021 and then to 20 and 27 June 2021.

The politics of Île-de-France, France takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democracy, whereby the President of Regional Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the regional council.




















