
Runaway Train is a 1985 American independent action thriller film directed by Andrei Konchalovsky and starring Jon Voight, Eric Roberts, Rebecca De Mornay and John P. Ryan. The screenplay by Djordje Milicevic, Paul Zindel and Edward Bunker was based on an original screenplay by Akira Kurosawa, with uncredited contributions by frequent Kurosawa collaborators Hideo Oguni and Ryūzō Kikushima. The film was also the feature debuts of Danny Trejo and Tommy "Tiny" Lister, who both proceeded to successful careers as "tough guy" character actors.

The Soo Line Railroad is the primary United States railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway, one of seven U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CP subsidiaries: The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway, and the Wisconsin Central Railway. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line Railroad and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, CP's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway. Most equipment has been repainted into the CP scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all of CP's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are located in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

The EMD GP30 is a 2,250 hp (1,680 kW) four-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division of La Grange, Illinois between July 1961 and November 1963. A total of 948 units were built for railroads in the United States and Canada, including 40 cabless B units for the Union Pacific Railroad.

The Iowa, Chicago and Eastern Railroad (IC&E) was a Class II railroad operating in the north central United States. It has been controlled by the Canadian Pacific Railway and operated as a part of its system since October 30, 2008. Formerly, the IC&E was jointly owned with the Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad by Cedar American Rail Holdings (CARH), making the combined system the largest class II railroad in the United States. Created by the purchase of I&M Rail Link, IC&E commenced operations on July 30, 2002. The 1,400-mile (2,300 km) line, based in Davenport, Iowa, serves the states of Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Minnesota and Wisconsin. Principal commodities include chemicals, coal, steel, automobiles, and agricultural products. Train dispatching is performed at a joint DM&E/IC&E facility in Sioux Falls, South Dakota. On December 26, 2008, the IC&E was merged into parent CARH, which immediately merged into the DM&E.

The EMD SD90MAC is a 6,000 hp (4,470 kW) C-C diesel-electric locomotive produced by General Motors Electro-Motive Division. It is, with the SD80MAC, one of the largest single-engined locomotives produced by EMD, surpassed only by the dual-engined DDA40X.

Carrizo Gorge Railway, Inc. was a railroad operator on the San Diego and Arizona Eastern Railway (SD&AE) from Tijuana, Mexico to Plaster City, California.

An EMD GP38AC is a 4-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between February 1970 and December 1971. It was basically a GP38 with an AR10 alternator instead of the GP38's normal generator.

An EMD GP20 is a 4-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division between November 1959 and April 1962. Power was provided by an EMD 567D2 16-cylinder turbocharged engine which generated 2,000 horsepower (1,500 kW). EMD was initially hesitant to turbocharge their 567-series diesel engine, but was spurred on to do so following successful tests made by Union Pacific in the form of UP's experimental Omaha GP20 units. 260 examples of EMD's production locomotive model were built for American railroads.

The Denver Rock Island Railroad, formerly known as the Denver Terminal Railroad, is a Class III terminal railroad in Commerce City, Colorado. The DRIR works around Denver's stock yards and many industries in that area.

The Central Illinois Railroad is a shortline railroad in Illinois. The switching and terminal railroad operates trackage near Peoria, Illinois. The Central Illinois Railroad was established in 2000, operating on track leased from the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway (BNSF).

The Indiana Railway Museum is a railroad museum located in French Lick, Indiana, United States, dedicated to preserving and displaying artifacts related to the history of railroads in Indiana.

The Willamette Valley Railway is a short-line railroad that operates in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. It leased a line from Woodburn to Stayton from the Southern Pacific Transportation Company in February 1993, as well as a branch from Geer west to Salem, and purchased the property in 1996. The company also leased a line between Albany and Mill City in 1993, but transferred the lease to the Albany and Eastern Railroad in October 2000.

The Arizona Eastern Railway is a Class III railroad that operates 265 miles (426 km) of railroad between Clifton, Arizona, and Miami, Arizona, in the United States. This includes trackage rights over the Union Pacific Railroad between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Bowie, Arizona. The railroad serves the copper mining region of southeastern Arizona, and the agricultural Gila River Valley. Primary commodities are sulfuric acid, copper concentrate, copper anode and cathode, and copper rod and other copper processing materials. AZER also handles minerals, chemicals, building supplies and lumber. The railroad offers a transload location for lumber, building materials and other consumer commodities at Globe, Arizona.
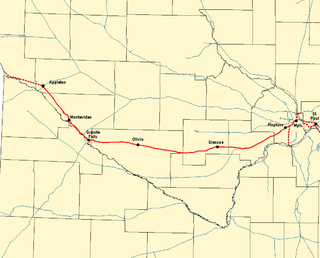
The Twin Cities and Western Railroad is a railroad operating in the U.S. state of Minnesota which started operations on July 27, 1991. Trackage includes the former Soo Line Railroad "Ortonville Line", originally built as the first part of the Pacific extension of the Milwaukee Road. This main line extends from Hopkins, Minnesota to Appleton, Minnesota. The line was originally built between Hopkins and Cologne, Minnesota in 1876 by Hastings and Dakota Railroad. In 1913, the Milwaukee Road rerouted it, reducing the curves. The line was eventually extended to the Pacific.

An EMD GP49 is a 4-axle diesel locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division. Power was provided by an EMD 645F3B 12-cylinder engine which generated 2,800 horsepower (2.09 MW). The GP49 was marketed as one of four models in the 50 series introduced in 1979. The 50 series includes GP/SD49 and GP/SD50. Both the GP and SD50 was relatively popular with a total of 278 GP50s and 427 SD50s built. The SD49 was advertised but never built and a total of 9 GP49s were built.
The Terre Haute, Brazil and Eastern Railroad was a short-line railroad that was incorporated May 1, 1987 and began operations on October 15, 1987. The TBER operated over 30 miles of the Pennsylvania Railroad's St. Louis-Indianapolis-Pittsburgh Line, which had been abandoned by Conrail in 1984 in favor of the former New York Central-Big Four St. Louis Line subdivision. The line extended from Terre Haute to Limedale and included a seven-mile branch line to the Amax Coal Company's Chinook Mine south of Brazil.

Included in this list of Soo Line locomotives are those of the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad, as well as those of the Wisconsin Central Railway, which it inherited on its lease in 1909. The M.St.P.&S.Ste.M. finally merged the WC and the Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway on December 30, 1961 to form the Soo Line Railroad. The Soo Line later acquired the Milwaukee Road and became part of the Canadian Pacific Railway.

The Escanaba & Lake Superior Railroad is a Class III shortline railroad that operates 347 miles (558 km) of track in Northeastern Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Its main line runs 208 miles (335 km) from Rockland, Michigan, to Green Bay, Wisconsin, and it also owns various branch lines and out-of-service track.

The Squaw Creek Southern Railroad is a Class III railroad subsidiary of Respondek Railroad operating in the southern portion of the State of Indiana. Originally, the Squaw Creek Southern started operating 21 miles of former Yankeetown Dock Corporation/Peabody Coal trackage owned by Norfolk Southern, but has since started servicing Foresight Energy's Sitran Coal Terminal near Evansville, Indiana and SABIC's Innovative Plastics plant in Mount Vernon, Indiana.

A B unit, in railroad terminology, is a locomotive unit which does not have a control cab or crew compartment, and must therefore be operated in tandem with another coupled locomotive with a cab. The terms booster unit and cabless are also used. The concept is largely confined to North America. Elsewhere, locomotives without driving cabs are rare.




















