The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, 298.9 Mya. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing" and derives from the Latin words carbō ("coal") and ferō, and was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822.</ref>
The Mississippian is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earliest/lowermost of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi River valley.
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly 323.2 million years ago to 298.9 million years ago Ma. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal-productive beds of this age are widespread.
The Permian is a geologic period and system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period 298.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic period 251.902 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic era; the following Triassic period belongs to the Mesozoic era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the city of Perm.
The PaleozoicEra is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods : the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era.

Graptolithina is a subclass of the class Pterobranchia, the members of which are known as graptolites. These organisms are colonial animals known chiefly as fossils from the Middle Cambrian through the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, Chaunograptus, is known from the Middle Cambrian. One analysis suggests that the pterobranch Rhabdopleura represents extant graptolites. Studies on the tubarium of fossil and living graptolites showed similarities in the basic fusellar construction and it is considered that the group most probably evolved from a Rhabdopleura-like ancestor.

A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain amount of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties. Formations are not defined by the thickness of their rock strata; therefore the thickness of different formations can vary widely.
Romer's gap is an example of an apparent gap in the tetrapod fossil record used in the study of evolutionary biology. Such gaps represent periods from which excavators have not yet found relevant fossils. Romer's gap is named after paleontologist Alfred Romer, who first recognised it. Recent discoveries in Scotland are beginning to close this gap in palaeontological knowledge.

Joggins is a Canadian rural community located in western Cumberland County, Nova Scotia. On July 7, 2008 a 15-km length of the coast constituting the Joggins Fossil Cliffs was officially inscribed on the World Heritage List.
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan.

Carboniferous Limestone is a collective term for the succession of limestones occurring widely throughout Great Britain and Ireland that were deposited during the Dinantian Epoch of the Carboniferous Period. These rocks formed between 363 and 325 million years ago. Within England and Wales, the entire limestone succession, which includes subordinate mudstones and some thin sandstones, is known as the Carboniferous Limestone Supergroup.

Archaeothyris is an extinct genus of ophiacodontid synapsids that lived during the Late Carboniferous and is known from Nova Scotia. Dated to 306 million years ago, Archaeothyris, along with a more poorly known synapsid called Echinerpeton, are the oldest undisputed synapsids known. Protoclepsydrops also from Nova Scotia is slightly older but is known by very fragmentary materials.

Writhlington SSSI is a 0.5 hectare geological Site of Special Scientific Interest near the town of Radstock, Bath and North East Somerset, notified in 1992.

Writhlington is a suburb of Radstock and 6 miles (10 km) north-west of Frome in the Bath and North East Somerset district of Somerset, England.

Adelophthalmus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Adelophthalmus have been discovered in deposits ranging in age from the Early Devonian to the Early Permian, which makes it the longest lived of all known eurypterid genera, with a total temporal range of over 120 million years. Adelopthtalmus was the final genus of the Eurypterina suborder of eurypterids and consisted the only known genus of swimming eurypterids from the Middle Devonian until its extinction during the Permian, after which the few surviving eurypterids were all walking forms of the suborder Stylonurina.

Stenders Quarry is a 2.8-hectare (6.9-acre) biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in the Forest of Dean Gloucestershire, notified in 1966 and renotified in 1990. The site is designated as an SSSI for its important geological features, although there is also a diversity of plants and animals recorded.
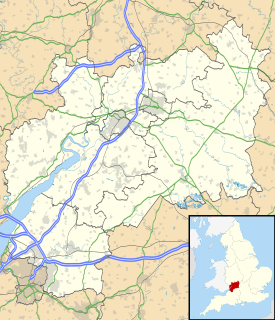
Puddlebrook Quarry is a 0.7-hectare (1.7-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Gloucestershire, near Drybrook notified in 1986. The site is listed in the 'Forest of Dean Local Plan Review' as a Key Wildlife Site (KWS).
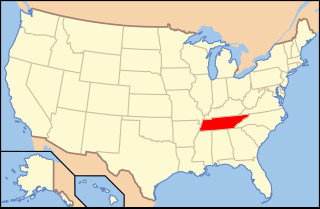
Paleontology in Tennessee refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Tennessee. During the early part of the Paleozoic era, Tennessee was covered by a warm, shallow sea. This sea was home to brachiopods, bryozoans, cephalopods, corals, and trilobites. Tennessee is one of the best sources of Early Devonian fossils in North America. During the mid-to-late Carboniferous, the state became a swampy environment, home to a rich variety of plants including ferns and scale trees. A gap in the local rock record spans from the Permian through the Jurassic. During the Cretaceous, the western part of the state was submerged by seawater. The local waters were home to more fossil gastropods than are known from anywhere else in the world. Mosasaurs and sea turtles also inhabited these waters. On land the state was home to dinosaurs. Western Tennessee was still under the sea during the early part of the Cenozoic. Terrestrial portions of the state were swampy. Climate cooled until the Ice Age, when the state was home to Camelops, horses, mammoths, mastodons, and giant ground sloths. The local Yuchi people told myths of giant lizard monsters that may have been inspired by fossils either local or encountered elsewhere. In 1920, after local fossils became a subject of formal scientific study, a significant discovery of a variety of Pleistocene creatures was made near Nashville. The Cretaceous bivalve Pterotrigonia thoracica is the Tennessee state fossil.

The Joggins Formation is a geologic formation in Nova Scotia. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period, including Hylonomus, the earliest known unquestionable reptile. The Joggins Formation's spectacular coastal exposure, the Joggins Fossil Cliffs, was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2008.


















