
This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Equatorial Guinea , formerly known as Spanish Guinea .

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Equatorial Guinea , formerly known as Spanish Guinea .

Stamps for the island of Fernando Po were first issued in 1868 by the Spanish colonial authorities in the capital Santa Isabel. [1]

Stamps inscribed "Guinea Continental Española" were issued for the continental enclave of Río Muni from 1902 to 1909. [2] [3]
The colony consisting of the islands of Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, Annobón and Corisco in the Gulf of Guinea issued its own postage stamps between 1903 and 1910. [4]

Stamps inscribed "Territorios Españoles del Golfo de Guinea" (Spanish Territories of the Gulf of Guinea) and later "Guinea Española" (Spanish Guinea) were issued from 1909 to 1959 for Spanish territories in the Guinea region, replacing those of individual colonies. [5]
From 30 July 1959 to 11 October 1968, Fernando Poo and Río Muni were treated as overseas provinces of Spain until they combined to form Equatorial Guinea on 12 October 1968 .
Fernando Poo and Río Muni originally used postage stamps of Spanish Guinea until 1960 when the Spanish government decreed the use of separate issues for Río Muni and Fernando Po.
The first definitive series for Fernando Poo as a province were issued on 25 February 1960. [2]
The first stamps of Río Muni were issued on 27 April 1960. [2] The first definitive series consisted of nine values, 25 c to 10 p, all with the same design showing a missionary and a native boy reading, and inscribed "RÍO MUNI". [6]
Issues from 1961 on added the inscription "ESPAÑA"; typically two to three issues per year, consisting of two to four stamps each, and usually depicting local plants and animals. Another definitive series appeared in 1964, also with nine values. The last issue of Río Muni was a set of three signs of the zodiac issued on 25 April 1968.
Equatorial Guinea became an independent republic on 12 October 1968 and its first stamps as such were issued on that date. [2]
Upon achieving independence from Spain, Francisco Macias Nguema was elected the first president of Equatorial Guinea. By May 1971, Nguema controlled a government that essentially performed no functions except internal security. From 1972 to 1979, the country's main post office was padlocked and completely inoperative. Nonetheless, European agents continued to produce postage stamps for Equatorial Guinea that were promoted by so-called press releases from Madrid, Spain. With the exception of the first four issues and another two from 1973, it is doubtful that any stamps between 1972 and 1979 even reached Equatorial Guinea, much less placed on sale there for postage purposes. Most stamp catalogues do not accept the stamps from this period as being legitimate.
Stamps from this period were of course very colourful and of a topical nature. They proved to be attractive to overseas stamp collectors and were readily available, mostly in packets of stamps.
From 1979 all stamps are designed and printed by the Spanish FNMT, since then a very moderated and decent stamp issuing policy is adopted.

Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of 28,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi). Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location near both the Equator and in the African region of Guinea. As of 2021, the country had a population of 1,468,777, over 85% of whom are members of the Fang people, the country's dominant ethnic group. The Bubi people, indigenous to Bioko, are the second largest group at approximately 6.5% of the population.

The History of Equatorial Guinea is marked by centuries of colonial domination by the Portuguese, British and Spanish colonial empires, and by the local kingdoms.

The Republic of Equatorial Guinea is located in west central Africa. Bioko Island lies about 40 kilometers (24.9 mi) from Cameroon. Annobón Island lies about 595 kilometres (370 mi) southwest of Bioko Island. The larger continental region of Río Muni lies between Cameroon and Gabon on the mainland; it includes the islands of Corisco, Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, and adjacent islets. The total land area is 28,051 km2 (10,831 sq mi). It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 303,509 km2 (117,185 sq mi).
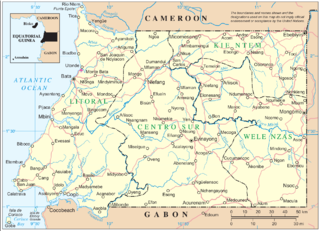
Río Muni is the Continental Region of Equatorial Guinea, and comprises the mainland geographical region, covering 26,017 square kilometres (10,045 sq mi). The name is derived from the Muni River, along which the early Europeans had built the Muni River Settlements.

Spanish Guinea or Spanish Cameroons was a set of insular and continental territories controlled by Spain from 1778 in the Gulf of Guinea and on the Bight of Bonny, in Central Africa. It gained independence in 1968 as Equatorial Guinea.

Elobey, Annobón, and Corisco was a colonial administration of Spanish Africa consisting of the island of Annobón, located southwest of São Tomé and Príncipe in the Gulf of Guinea, and the small islands of Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, and Corisco, located in the Corisco Bay near the mouth of the Mitémélé River in the Muni Estuary.

Elobey, Annobón, and Corisco was a colonial administration of Spanish Africa located in the Gulf of Guinea. The colony consisted of the small islands of Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, Annobón, and Corisco. The capital was Santa Isabel. The islands are presently part of Equatorial Guinea.

Corisco, Mandj, or Mandyi, is a small island of Equatorial Guinea, located 29 km (18 mi) southwest of the Río Muni estuary that defines the border with Gabon. Corisco, whose name derives from the Portuguese word for lightning, has an area of 14 km2 (5 sq mi), and its highest point is 35 m (115 ft) above sea level. The most important settlement on the island is Gobe.

Elobey Grande, or Great Elobey, is an island of Equatorial Guinea, lying at the mouth of the Mitémélé River. It is sparsely inhabited. Elobey Chico is a smaller island offshore, now uninhabited but once the colonial capital of the Río Muni. The island is located in the Gulf of Guinea.

Annobón is a province of Equatorial Guinea. The province consists of the island of Annobón and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea. Annobón is the smallest province of Equatorial Guinea in both area and population. According to the 2015 census, Annobón had 5,314 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and forestry.
Each "article" in this category is a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.

Elobey Chico, or Little Elobey, is a small island off the coast of Equatorial Guinea, lying near the mouth of the Mitémélé River. The island is now uninhabited but was once the de facto colonial capital of the Spanish territory of Río Muni. Officially, the island was associated with Fernando Pó, but the connection seemed to be little more than fiction. The majority of the factories were owned by Hamburg Merchants.

Articles related to Equatorial Guinea include:

Adolfo Obiang Biko is an author, politician and president of the National Liberation Movement of Equatorial Guinea (MONALIGE). He is known as an active participant and a leading freedom fighter in the struggle for independence of Equatorial Guinea from Spain.
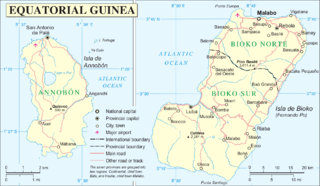
The Insular Region of Equatorial Guinea comprises the former Spanish territory of Fernando Po, together with Annobón island, the latter formerly part of the Spanish territory of Elobey, Annobón, and Corisco, which was located in the Gulf of Guinea and in the Corisco Bay.
According to Article 3 of the Constitution of Equatorial Guinea, the country is divided for administrative and economic purposes into regions, provinces, districts, and municipalities. In practice, the provinces serve as the first-level administrative divisions. Municipalities are subdivided into village councils and neighbourhood communities. Many of the sub-municipal entities are grouped into urban districts, which remain subordinate to municipalities and are distinct from districts proper.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of the Republic of the Congo, a former French colony known as Middle Congo or French Congo, and now often known simply as The Congo.
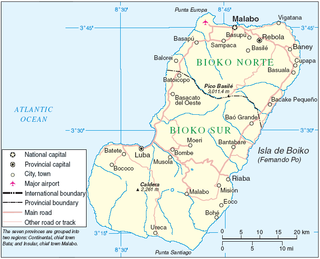
Bioko is an island 32 km (20 mi) south of the coast of Cameroon, and 160 km (99 mi) northwest of the northernmost part of mainland Equatorial Guinea. Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of 2,017 km2 (779 sq mi). The island is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes and is located off the Cameroon coast, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at 3,012 m (9,882 ft).

Equatorial Guinea–Venezuela relations refers to international relations between Equatorial Guinea and Venezuela. In both countries the official language is Spanish and they have an important economic activity based on oil extraction.
The Province of Río Muni was a Spanish province in Africa between 1959 and 1968. It consisted of Río Muni, the continental region of modern-day Equatorial Guinea, plus the islands of Corisco and Elobey. It bordered Gabon to the east and south and Cameroon to the north. Its administrative capital was Bata. It had an area of 26 017 km².