
The Araceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in which flowers are borne on a type of inflorescence called a spadix. The spadix is usually accompanied by, and sometimes partially enclosed in, a spathe. Also known as the arum family, members are often colloquially known as aroids. This family of 114 genera and about 3,750 known species is most diverse in the New World tropics, although also distributed in the Old World tropics and northern temperate regions.

Heinrich Wilhelm Schott was an Austrian botanist. He is known for his extensive work on aroids (Araceae).

Anthurium is a genus of about 1,000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, pigtail plant, and laceleaf.

Lysichiton is a genus in the family Araceae. These plants are known commonly as skunk cabbage or less often as swamp lantern. The spelling Lysichitum is also found. The genus has two species, one found in north-east Asia, the other in north-west America.

Rhaphidophora is a genus in the family Araceae, occurring from tropical Africa eastwards through Malesia and Australasia to the Western Pacific. The genus consists of approximately 100 species.

Homalomena is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. Homalomena are native to tropical Asia and China. Many Homalomena have a strong smell of anise. The name derives apparently from a mistranslated Malayan vernacular name, translated as homalos, meaning flat, and mene = moon.

Asterostigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Brazil and Argentina. The leaves are pinnate and the plant is tuberous.
- Asterostigma cryptostylumBogner - Brasília, Goiás, Minas Gerais
- Asterostigma cubense(A.Rich.) K.Krause ex Bogner - São Paulo
- Asterostigma lividum(G.Lodd.) Engl. - southern Brazil; Misiones Province of Argentina
- Asterostigma lombardiiE.G.Gonç. - Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo
- Asterostigma luschnathianumSchott - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma reticulatumE.G.Gonç - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma riedelianum(Schott) Kuntze - eastern Brazil
- Asterostigma tweedieanumSchott - Santa Catarina in southern Brazil

Biarum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is composed of plants that are native to the Middle East, southern Europe, and North Africa. Biarum are often found growing in rock crevices and graveled soil composed largely of limestone.

Aroideae is a subfamily of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is the largest subfamily in Araceae and consists of about 72 different genera, and 2,300 species. Many Aroideae have spiny pollen grains without a sporopollenin outer exine layer and lacking an aperture.
Amydrium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that is native to Southeast Asia, southern China, and New Guinea.
Anadendrum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to China and Southeast Asia.

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of 11 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.

Lagenandra is a genus of aquatic flowering plants in the aroid family, Araceae, endemic to the Indian Subcontinent. The genus has gradually become more known through the aquascaping and aquarium hobby, in which several related Araceae genera are already highly prized and grown on a large scale ; Lagenandra, however, is still relatively rare in cultivation or private collections.

Eminium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus ranges from Turkey and Egypt east to Central Asia. Usually they can be found growing in barren areas in sand or stony soil. The foliage of Eminium resembles Helicodiceros and its inflorescence and fruit resembles those of Biarum.
- Eminium albertii(Regel) Engl. - Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan
- Eminium heterophyllum(Blume) Schott - Iran, Iraq, Turkey
- Eminium intortum(Banks & Sol.) Kuntze - Turkey, Syria
- Eminium jaegeriBogner & P.C.Boyce - Iran
- Eminium koenenianumLobin & P.C.Boyce - Turkey
- Eminium lehmannii(Bunge) Kuntze - Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan
- Eminium rauwolffii(Blume) Schott - Turkey, Syria
- Eminium regeliiVved. - Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan
- Eminium spiculatum(Blume) Schott - Egypt, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, Iran
Gorgonidium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to South America. The spathes tend to be purple and the fruits are black.
- Gorgonidium beckianumBogner - Bolivia
- Gorgonidium bulbostylumBogner & E.G.Gonç - Bolivia
- Gorgonidium cardenasianum(Bogner) E.G.Gonç - Bolivia
- Gorgonidium intermedium(Bogner) E.G.Gonç - Peru
- Gorgonidium mirabileSchott - Bolivia
- Gorgonidium striatumHett., Ibisch & E.G.Gonç
- Gorgonidium vargasiiBogner & Nicolson - Peru
- Gorgonidium vermicidum(Speg.) Bogner & Nicolson - Bolivia, northern Argentina
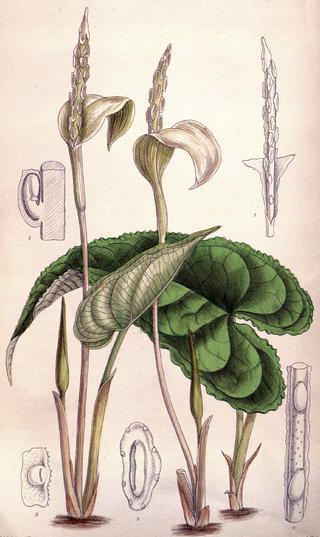
Hapaline is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It contains 7 species that are found from southern China to Borneo.
Scaphispatha gracilis is a species in the family Araceae. This species is native to Brazil and Bolivia, and has peltate leaves that resembles those in the genus Caladium. The species was described by Heinrich Wilhelm Schott in 1860 after he received an inflorescence of the plant. He had not however seen the plant itself and it was not rediscovered until 1976 when Josef Bogner collected tubers from the plant and successfully flowered them at the Munich Botanic Garden. Upon seeing the inflorescence it was realized that this was the plant Schott had originally described.

Philodendron verrucosum is a species of flowering plant in the family Araceae. It is native to Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, and is a hemiepiphyte climbing plant. This Philodendron is kept by houseplant collectors for its unique appearance, with foliage that has slightly wavy edges, white veins, and flushes of reddish hues, as well as hairy bristles along its petioles.

Montrichardia arborescens, the yautia madera, or moco-moco, is a tropical plant grows along river banks, swamps, or creeks to a maximum height of 9'. They consist of arrow shaped leaves that are food sources for animal species. The plant produces inflorescences which then leave a fruit of Montrichardia arborescens which is edible and can be cooked. Its fruiting spadices produces large infructescences, which contain about 80 edible yellow fruits.















