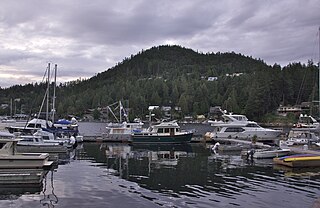The Lower Mainland is a geographic and cultural region of the mainland coast of British Columbia that generally comprises the regional districts of Metro Vancouver and the Fraser Valley. Home to approximately 3.05 million people as of the 2021 Canadian census, the Lower Mainland contains sixteen of the province's 30 most populous municipalities and approximately 60% of the province's total population.

The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for 1,375 kilometres (854 mi), into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. The river's annual discharge at its mouth is 112 cubic kilometres (27 cu mi) or 3,550 cubic metres per second (125,000 cu ft/s), and each year it discharges about 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean.
Campbell River is a city in the Sayward Land District of British Columbia, Canada, on the east coast of Vancouver Island at the south end of Discovery Passage, which lies along the 50th parallel north along the important Inside Passage shipping route. Campbell River has a population of 35,138 and has long been touted as the "salmon capital of the world." Campbell River and Region are near the communities of Quadra and the Discovery Islands, Sayward, Oyster River, Gold River, Tahsis and Zeballos.

The Okanogan River is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 115 mi (185 km) long, in southern British Columbia and north central Washington. It drains a scenic plateau region called the Okanagan Country east of the Cascade Range and north and west of the Columbia, and also the Okanagan region of British Columbia. The Canadian portion of the river has been channelized since the mid-1950s.

Bennett Lake is a lake in the Province of British Columbia and Yukon Territory in northwestern Canada, at an elevation of 656 m (2,152 ft). It is just north of the border with the United States state of Alaska, near the Alaskan port of Skagway. The lake has an area of either 90.68 or 96.8 km2. The average depth is 61.9 m (203 ft) and the maximum depth is 123 m (404 ft).

Powell River is a city on the northern Sunshine Coast of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Most of its population lives near the eastern shores of Malaspina Strait, which is part of the larger Georgia Strait between Vancouver Island and the Mainland. With two intervening long, steep-sided fjords inhibiting the construction of a contiguous road connection with Vancouver to the south, geographical surroundings explain Powell River's remoteness as a community, despite relative proximity to Vancouver and other populous areas of the BC Coast. The city is the location of the head office of the qathet Regional District.
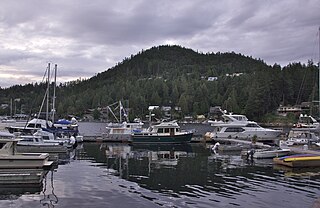
The Sunshine Coast is a geographic subregion of the British Columbia Coast that generally comprises the regional districts of qathet and Sunshine Coast.

The qathet Regional District is a regional district in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Its only incorporated municipality is the City of Powell River, although it includes a number of unincorporated areas. The district encompasses a land area of 5,075.33 square kilometres (1,959.60 sq mi). The district was formerly known as the Powell River Regional District. Because of frequent confusion between the identical names of Powell River district and city, the district's name was changed in 2018 to qathet, from q̓at̓ᶿɛt, meaning "working together, bringing together" in the ʔayʔaǰuθəm language of the ɬəʔamɩn, k̓ómoks, χʷɛmaɬkʷu, & ƛohos Nations.

The Nass River is a river in northern British Columbia, Canada. It flows 380 km (240 mi) from the Coast Mountains southwest to Nass Bay, a sidewater of Portland Inlet, which connects to the North Pacific Ocean via the Dixon Entrance. Nass Bay joins Portland Inlet just south of Observatory Inlet.

Kicking Horse Pass is a high mountain pass across the Continental Divide of the Americas of the Canadian Rockies on the Alberta–British Columbia border, and lying within Yoho and Banff national parks. Divide Creek forks onto both sides of the Continental Divide.

The Nechako River arises on the Nechako Plateau east of the Kitimat Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, and flows north toward Fort Fraser, then east to Prince George where it enters the Fraser River. "Nechako" is an anglicization of netʃa koh, its name in the indigenous Carrier language which means "big river".

Bute Inlet is one of the principal inlets of the British Columbia Coast. It is 80 km (50 mi) long from the estuaries of the Homathko and Southgate Rivers at the head of the inlet, to the mouth, where it is nearly blocked by Stuart Island, and it averages about 4 km (2.5 mi) in width. Bute Inlet is in a spectacular wilderness setting and is one of the most scenic waterways in the world. In the upper reaches of the inlet mountains rise 2,700 m (9,000 ft) feet above sea level. Bute Inlet is a spectacular wilderness that is visited by very few people. In more recent years tourists are travelling from around the world to view grizzly bears in a natural setting and explore the wilderness of Bute Inlet.

Snow Dome is a mountain located on the Continental Divide in the Columbia Icefield, where the boundary of Banff National Park and Jasper National Park meets the border of Alberta and British Columbia in Canada. The summit's elevation is 3,456 m (11,339 ft).
The Taseko River or Dasiqox in the original Chilcotin, is a tributary of British Columbia's Chilko River, a tributary of the Chilcotin River which joins the Fraser near the city of Williams Lake.

The Kettle River is a 281-kilometre (175 mi) tributary of the Columbia River, encompassing a 10,877-square-kilometre (4,200 sq mi) drainage basin, of which 8,228 square kilometres (3,177 sq mi) are in southern British Columbia, Canada and 2,649 square kilometres (1,023 sq mi) in northeastern Washington, US.

The Moyie River is a 92-mile (148 km) long tributary of the Kootenai River in the U.S. state of Idaho and the Canadian province of British Columbia. The Moyie River is part of the Columbia River basin, being a tributary of the Kootenay River, which is a tributary to the Columbia River.

The Pouce Coupe River is a major tributary of the Peace River in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. Its name is officially spelled Pouce Coupé River, but it is commonly written without the acute accent.

The Cariboo River is a tributary of the Quesnel River, one of the main tributaries of the Fraser River, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows through the Cariboo region of the British Columbia Interior, southeast of Prince George. Above Cariboo Lake it was formerly known as the Swamp River. The name was adopted, and replaced the former names, in 1936 in association with Cariboo Lake.

Israel Wood Powell was British Columbia's first superintendent of Indian Affairs and a businessman, politician and doctor. He served in the Legislative Assembly of Vancouver Island from 1863 to 1866.
The Brittain River is a river of the Sunshine Coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It originates in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, and flows about 23 km (14 mi) southeast to the Pacific Ocean at the Princess Royal Reach of Jervis Inlet.