
Calisthenics or callisthenics is a form of strength training that utilizes an individual's body weight as resistance to perform multi-joint, compound movements with little or no equipment.

The latissimus dorsi is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline.

The push-up is a common calisthenics exercise beginning from the prone position. By raising and lowering the body using the arms, push-ups exercise the pectoral muscles, triceps, and anterior deltoids, with ancillary benefits to the rest of the deltoids, serratus anterior, coracobrachialis and the midsection as a whole. Push-ups are a basic exercise used in civilian athletic training or physical education and commonly in military physical training. They are also a common form of punishment used in the military, school sport, and some martial arts disciplines to humiliate and its absence of use for equipment. Variations of push-ups, such as wide-arm push-ups, diamond push-ups target specific muscle groups and provide further challenges.

The sit-up is an abdominal endurance training exercise to strengthen, tighten and tone the abdominal muscles. It is similar to a curl-up, but sit-ups have a fuller range of motion and condition additional muscles.

An aponeurosis is a flattened tendon by which muscle attaches to bone or fascia. Aponeuroses exhibit an ordered arrangement of collagen fibres, thus attaining high tensile strength in a particular direction while being vulnerable to tensional or shear forces in other directions. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections. The primary regions with thick aponeuroses are in the ventral abdominal region, the dorsal lumbar region, the ventriculus in birds, and the palmar (palms) and plantar (soles) regions.

A dip bar is a piece of fitness equipment that consists of a U-shaped bar, usually about 25 mm (1 in) in diameter, which surrounds the user's body at the waist. It is designed for the performance of, and named after, the dip exercise.
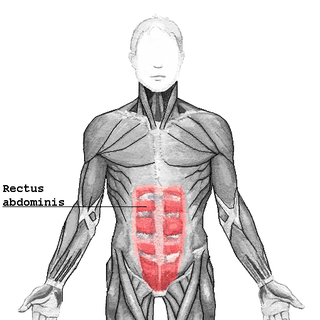
The rectus abdominis muscle, also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline by a band of dense connective tissue called the linea alba, and the connective tissue defining each lateral margin of the rectus abdominus is the linea semilunaris. The muscle extends from the pubic symphysis, pubic crest and pubic tubercle inferiorly, to the xiphoid process and costal cartilages of the 5th–7th ribs superiorly.

The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral abdominal wall, deep to the internal oblique muscle. It serves to compress and retain the contents of the abdomen as well as assist in exhalation.

The lying triceps extension, also known as skull crusher and French extension or French press, is a strength exercise used in many different forms of strength training. It is one of the most stimulating exercises to the entire triceps muscle group in the upper arm, and works the triceps from the elbow all the way to the latissimus dorsi. Due to its full use of the triceps muscle group, the lying triceps extensions are used by many as part of their training regimen.
Abdominal exercises are a type of strength exercise that affect the abdominal muscles. Human abdominal consist of four muscles which are the rectus abdomens, internal oblique, external oblique, and transversus abdominis. When performing abdominal exercises it is important to understand the effects, functions, the types of exercises, and think about how to perform this exercise safely.
A bent-over row is a weight training exercise that targets a variety of back muscles depending on the form used. It is often used for both bodybuilding and powerlifting.

The pull-down exercise is a strength training exercise designed to develop the latissimus dorsi muscle. It performs the functions of downward rotation and depression of the scapulae combined with adduction and extension of the shoulder joint.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to exercise:

A pull-up is an upper-body strength exercise. The pull-up is a closed-chain movement where the body is suspended by the hands, gripping a bar or other implement at a distance typically wider than shoulder-width, and pulled up. As this happens, the elbows flex and the shoulders adduct and extend to bring the elbows to the torso.
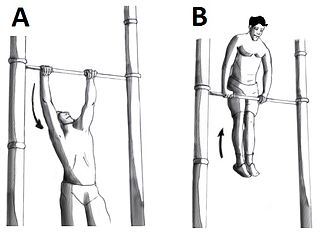
The muscle-up is an intermediate strength training exercise within the domain of calisthenics. It is a combination routine of a radial pull-up followed by a dip. Variations exist for the rings as well as the bar.
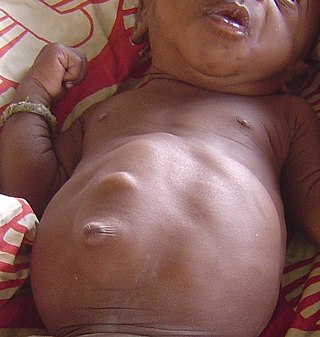
Diastasis recti, or rectus abdominis diastasis, is an increased gap between the right and left rectus abdominis muscles. The increased distance between the muscles is created by the stretching of the linea alba, a connective collagen sheath created by the aponeurosis insertions of the transverse abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique. This condition has no associated morbidity or mortality. Physical therapy is often required to repair this separation and surgery is an option for more severe cases. Standard exercise rarely results in complete healing of the separated muscles.

The inverted row is an exercise in calisthenics. It primarily works the muscles of the upper back—the trapezius and latissimus dorsi—as well as the biceps as a secondary muscle group. The supine row is normally carried out in three to five sets, but repetitions depend on the type of training a lifter is using to make their required gains. This exercise is lighter on the joints compared to weighted rows. The exercise can also be performed with mixed, underhand, or overhand grips with either wide or narrow hand placement. The exercise is also known under various names such as supine row, bodyweight row, Australian pull up or "horizontal pull-up".

The leg raise is a strength training exercise which targets the iliopsoas. Because the abdominal muscles are used isometrically to stabilize the body during the motion, leg raises are also often used to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle and the internal and external oblique muscles.

Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.

















