
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flatland in North America. The region is located just to the east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include the mixed grass prairie, the tallgrass prairie between the Great Lakes and Appalachian Plateau, and the Taiga Plains and Boreal Plains ecozones in Northern Canada. "Great Plains" or Western Plains also describe the ecoregion of the Great Plains, or alternatively the western portion of the Great Plains.

Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia, and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east.

The sharp-tailed grouse, also known as the sharptail or fire grouse, is a medium-sized prairie grouse. One of three species in the genus Tympanuchus, the sharp-tailed grouse is found throughout Alaska, much of Northern and Western Canada, and parts of the Western and Midwestern United States. The sharp-tailed grouse is the provincial bird of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan.

The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachment of trees, recycling soil nutrients, and facilitating seed dispersal and germination. Prior to widespread use of the steel plow, which enabled large scale conversion to agricultural land use, tallgrass prairies extended throughout the American Midwest and smaller portions of southern central Canada, from the transitional ecotones out of eastern North American forests, west to a climatic threshold based on precipitation and soils, to the southern reaches of the Flint Hills in Oklahoma, to a transition into forest in Manitoba.

The Flint Hills, historically known as Bluestem Pastures or Blue Stem Hills, are a region of hills and prairies that lie mostly in eastern Kansas. It is named for the abundant residual flint eroded from the bedrock that lies near or at the surface. It consists of a band of hills extending from Marshall and Washington Counties in the north to Cowley County, Kansas and Kay and Osage Counties in Oklahoma in the south, to Geary and Shawnee Counties west to east. Oklahomans generally refer to the same geologic formation as the Osage Hills or "the Osage."

Aspen parkland refers to a very large area of transitional biome between prairie and boreal forest in two sections, namely the Peace River Country of northwestern Alberta crossing the border into British Columbia, and a much larger area stretching from central Alberta, all across central Saskatchewan to south central Manitoba and continuing into small parts of the US states of Minnesota and North Dakota. Aspen parkland consists of groves of aspen, poplar and spruce, interspersed with areas of prairie grasslands, also intersected by large stream and river valleys lined with aspen-spruce forests and dense shrubbery. This is the largest boreal-grassland transition zone in the world and is a zone of constant competition and tension as prairie and woodlands struggle to overtake each other within the parkland.

The Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie (MNTP) is a tallgrass prairie reserve and is preserved as United States National Grassland operated by the United States Forest Service. The first national tallgrass prairie ever designated in the United States and the largest conservation site in the Chicago Wilderness region, it is located on the site of the former Joliet Army Ammunition Plant between the towns of Elwood, Manhattan and Wilmington in northeastern Illinois. Since 2015, it has hosted a conservation herd of American bison to study their interaction with prairie restoration and conservation.

Prairie restoration is a conservation effort to restore prairie lands that were destroyed due to industrial, agricultural, commercial, or residential development. The primary aim is to return areas and ecosystems to their previous state before their depletion.
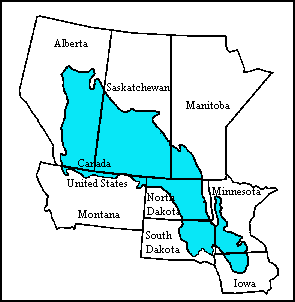
The Prairie Pothole Region is an expansive area of the northern Great Plains that contains thousands of shallow wetlands known as potholes. These potholes are the result of glacier activity in the Wisconsin glaciation, which ended about 10,000 years ago. The decaying ice sheet left behind depressions formed by the uneven deposition of till in ground moraines. These depressions are called potholes, glacial potholes, kettles, or kettle lakes. They fill with water in the spring, creating wetlands, which range in duration from temporary to semi-permanent. The region covers an area of about 800,000 sq. km and expands across three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states. The hydrology of the wetlands is variable, which results in long term productivity and biodiversity. The PPR is a prime spot during breeding and nesting season for millions of migrating waterfowl.

The Osage Plains are a physiographic section of the larger Central Lowland province, which in turn is part of the larger Interior Plains physiographic division. The area is sometimes called the Lower Plains, North Central Plains,or Rolling Plains. The Osage Plains, covering west-central Missouri, the southeastern third of Kansas, most of central Oklahoma, and extending into north-central Texas, is the southernmost of three tallgrass prairie physiographic areas. It grades into savanna and woodland to the east and south, and into shorter, mixed-grass prairie to the west. The Osage Plains consist of three subregions. The Osage Plains proper occupy the northeast segment. Although sharply demarcated from the Ozark uplift, the plains are nonetheless a transitional area across which the boundary between prairie and woodland has shifted over time. In the central portion of the physiographic area lies the second subregion, the Flint Hills, commonly called "the Osage" in Oklahoma. This large remnant core of native tallgrass prairie is a rocky rolling terrain that runs from north to south across Kansas and extends into Oklahoma. To the west and south of these hills are the Blackland Prairies and Cross Timbers. This vegetatively complex region of intermixed prairie and scrubby juniper-mesquite woodland extends into north-central Texas. Bluestem prairies and oak-dominated savannas and woodlands characterize the natural vegetation in the Cross Timbers. Much of the area has been converted to agriculture, although expanses of oak forest and woodland are still scattered throughout the eastern portion of the subregion.

The shortgrass prairie is an ecosystem located in the Great Plains of North America. The two most dominant grasses in the shortgrass prairie are blue grama and buffalograss, the two less dominant grasses in the prairie are greasegrass and sideoats grama. The prairie was formerly maintained by grazing pressure of American bison, which is the keystone species. Due to its semiarid climate, the shortgrass prairie receives on average less precipitation than that of the tall and mixed grass prairies to the east.

The Manitoba Tall Grass Prairie Preserve is located in southeastern Manitoba near Gardenton and Vita, this is about 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Steinbach, Manitoba. It is one of the last remaining stands of tallgrass prairie in Manitoba and is part of the Tallgrass Aspen Parkland conservation area in Manitoba and Minnesota. Several groups and organizations help in land preservation in the Manitoba Tall Grass Prairie such as the Nature Conservancy of Canada, Nature Manitoba, Environment Canada, Manitoba Conservation and the Manitoba Habitat Heritage Corporation.

The Central tall grasslands are a prairie ecoregion of the Midwestern United States, part of the North American Great Plains.
The ecology of the Great Plains is diverse, largely owing to their great size. Differences in rainfall, elevation, and latitude create a variety of habitats including short grass, mixed grass, and tall-grass prairies, and riparian ecosystems.

The Central Great Plains are a prairie ecoregion of the central United States, part of North American Great Plains. The region runs from west-central Texas through west-central Oklahoma, central Kansas, and south-central Nebraska.

The Canadian Aspen Forests and Parklands is one of 844 terrestrial ecoregions defined by One Earth. This ecoregion includes parts of the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, north-central and eastern North Dakota, most of east South Dakota, and north-central Nebraska in the American Great Plains. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) defines this ecoregion as the Northern Glaciated Plains.

A remnant natural area, also known as remnant habitat, is an ecological community containing native flora and fauna that has not been significantly disturbed by destructive activities such as agriculture, logging, pollution, development, fire suppression, or non-native species invasion. The more disturbed an area has been, the less characteristic it becomes of remnant habitat. Remnant areas are also described as "biologically intact" or "ecologically intact."

Dichanthelium leibergii, known as variously as Leiberg's panicum, Leiberg's panicgrass, Leiberg's rosette grass, and prairie panic grass is a species of grass native to North America. It was named for its discoverer, John Bernhard Leiberg (1853-1913), a Swedish-born American botanist active in the western United States.
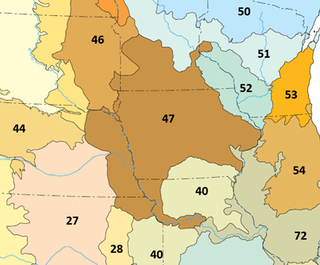
The Western Corn Belt Plains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Iowa.



















