
Montes Haemus is a mountain range that forms the southwestern edge of the Mare Serenitatis basin on the Moon. They form a less prominent mirror image of the Montes Apenninus range to the west, and curve up to nearly join at the northern end. The eastern edge terminates with the Promontorium Archerusia, to the northwest of the crater Plinius. This end reaches a gap where the Mare Serenitatis to the north joins the Mare Tranquillitatis to the south.

Ching-Te is a small lunar impact crater located in a mountainous area to the east of the Mare Serenitatis. It is a circular, bowl-shaped formation with no distinguishing features.

Fahrenheit is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of the Mare Crisium. This area of the surface is nearly devoid of impact features of interest. To the east are the Dorsa Harker wrinkle ridges, and beyond them is Promontorium Agarum at the edge of the mare. The landing site of the Soviet Luna 24 probe is located about 15 kilometers to the southeast.

Aratus is a small lunar impact crater located on the highland to the south and east of the rugged Montes Apenninus range. It is a circular, cup-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo. It was named after Greek astronomer Aratus of Soli. To the east is the Mare Serenitatis, and to the southwest is the somewhat larger crater Conon. North-northeast of Aratus is the landing site of the Apollo 15 mission, just beyond Mons Hadley Delta.

Von Kármán is a large lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. The crater is about 180 km (110 mi) in diameter and lies within an immense impact crater known as the South Pole–Aitken basin of roughly 2,500 km (1,600 mi) in diameter and 13 km (8.1 mi) deep. Von Kármán is the site of the first soft-landing on the lunar far side by the Chinese Chang'e 4 spacecraft on 3 January 2019.

Montes Alpes is a mountain range in the northern part of the Moon's near side. It was named after the Alps in Europe; the name was confirmed by the International Astronomical Union in 1935. It lies between the selenographic coordinates latitudes 52.81°N and 42.04°N, and longitudes 5.6°W and 3.22°E. The range thus crosses the lunar prime meridian, and is partially illuminated and partially in shadow during first and last quarters. The center of the range is at 48.36°N, 0.58°W, and has a diameter of 334 km.

Santos-Dumont is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern end of the Montes Apenninus range at the eastern edge of the Mare Imbrium. It is located about 30 kilometers to the northeast of Mons Hadley, a mountain massif.

Mons Hadley is a massif in the northern portion of the Montes Apenninus, a range in the northern hemisphere of the Moon. It has a height of 4.5 km (2.8 mi) 14,764 ft (4,500 m) above the adjacent plain and a maximum diameter of 25 km at the base.

Mons Esam is a small, isolated mountain in the northern part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is located to the southeast of the crater Vitruvius and to the west-northwest of Lyell. To the northeast of this ridge is the bay called Sinus Amoris.

Mons La Hire is a solitary lunar mountain in the western Mare Imbrium. It is located to the northeast of the crater Euler, and to the west-northwest of Lambert.

Sinus Iridum is a plain of basaltic lava that forms a northwestern extension to the Mare Imbrium on Earth's moon. It is surrounded from the northeast to the southwest by the Montes Jura range. The protruding part of the range at the southwest end is named Promontorium Heraclides, while that at the northeast end is called Promontorium Laplace. This bay and the surrounding mountains is considered one of the most beautiful features on the Moon, and is a favorite among lunar observers.

Cassini is a lunar impact crater that is located in the Palus Nebularum, at the eastern end of Mare Imbrium. The crater was named after astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Jacques Cassini. To the northeast is the Promontorium Agassiz, the southern tip of the Montes Alpes mountain range. South by south-east of Cassini is the crater Theaetetus. To the northwest is the lone peak Mons Piton.
Alexander Pavlovich Vinogradov was a Soviet geochemist, academician (1953), and Hero of Socialist Labour.

Promontorium Laplace is a raised mountainous cape situated at the end of Montes Jura in Mare Imbrium on the near side of the Moon. Its selenographic coordinates are 46.8° N, 25.5° W and it is 2600 meters high. It forms the northeast boundary of the bay of Sinus Iridum.
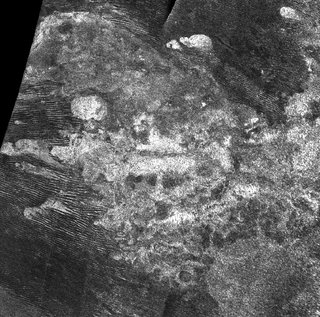
Erebor Mons is a mountain on Titan, the largest moon of the planet Saturn. It is located near Titan's equator, between 4-5° south and 35-36° west, centered on 4.97°S 36.23°W, in the western part of Quivira region. It is 40 km across, more than 1 km high and has lobate flow features to its north and east. It is probably a cryovolcano. Erebor Mons is situated about 470 km to the north-northeast of a larger cryovolcanic construct, Doom Mons.
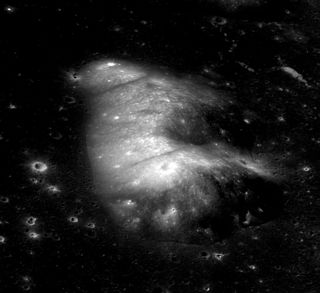
Mons Usov is a small lunar mountain that is located in the southeastern part of the Mare Crisium, to the north of the crater Firmicus, west of Concorcet crater, and northwest of Promontorium Agarum. It is essentially a part of the mountainous rim of the Crisium basin but appears somewhat isolated because of flooding of the basin by mare basalt.

Vogel is an impact crater in the Argyre quadrangle of Mars, located at 36.8°S latitude and 13.4°W longitude, and is inside Noachis Terra. It measures approximately 121 kilometres (75 mi) in diameter and was named after German astronomer Hermann Carl Vogel. The name was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1973.

Heaviside is an impact crater in the Mare Australe quadrangle of Mars. It is 83.28 km in diameter. It was named after British physicist Oliver Heaviside; the name was approved in 1973 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Agassiz is an impact crater on Mars, named in honor of geologist Louis Agassiz (1807–1873). The name was approved in 1973 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN).

Promontorium Deville is a mountainous cape situated on the northeast margin of Mare Imbrium on the near side of the Moon. Its selenographic coordinates are 43.31° N, 1.14° E. It is located north of Promontorium Agassiz, south of Mont Blanc, northeast of Mons Piton, and northwest of Cassini crater.




















