Related Research Articles

A motor neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. "Medulla" is from Latin, ‘pith or marrow’. And "oblongata" is from Latin, ‘lengthened or longish or elongated'.

The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that connects the forebrain with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.

The grey columns are three regions of the somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. These regions present as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are visible in cross-section of the spinal cord.

The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal) and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body.

The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) (also known as the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception from the skin and joints. It transmits this information to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus in the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus, tracts that make up the dorsal columns. The dorsal columns are carried in the white matter of the posterior funiculus of the spinal cord. At the level of the medulla oblongata, the fibers of the tracts decussate and are continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.
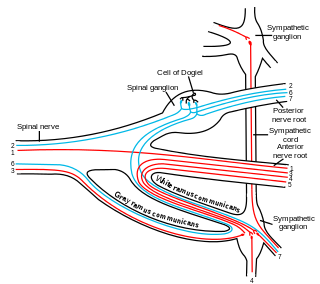
The white ramus communicans from Latin ramus (branch) and communicans (communicating) is the preganglionic sympathetic outflow nerve tract from the spinal cord.

The anterior corticospinal tract is a small bundle of descending fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts are pathways by which motor signals are sent from upper motor neurons in the brain to lower motor neurons which then directly innervate muscle to produce movement. The anterior corticospinal tract is usually small, varying inversely in size with the lateral corticospinal tract, which is the main part of the corticospinal tract.

The Rexed laminae comprise a system of ten layers of grey matter (I–X), identified in the early 1950s by Bror Rexed to label portions of the grey columns of the spinal cord.

The spinotectal tract and/or spinomesencephalic tract is one of the ascending tracts in the anterolateral system of the spinal cord that is involved in processing of pain and visceral sensations. The tract is involved in the processing of pain sensation, and reflex turning of the head and trunk in the direction of painful stimuli. It projects contralaterally to the midbrain tectum.
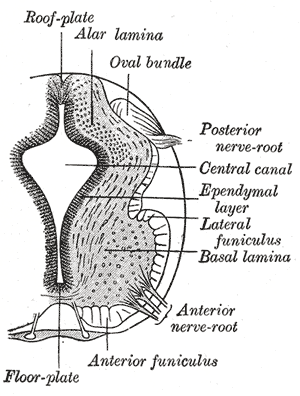
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.

In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussate).
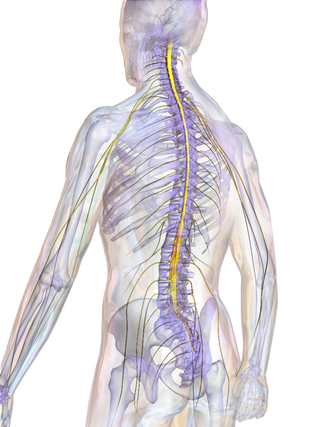
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
Anterolateral corticospinal tract is a subdivision of the corticospinal tract in the spinal cord. It is formed by approximately 2% of the corticospinal fibers that do not cross to the opposite side of the brainstem in the pyramidal decussation. This tract descends in the lateral white column anterior to the lateral corticospinal tract.
Ventral propriospinal tract is a collection of nerve fibers, ascending, descending, crossed and uncrossed, that interconnect various levels of the spinal cord. It is a component of the white anterior columns. The fibers are largely myelinated and run close to the spinal central gray for the length of the cord. Shorter fibers are closer to, longer fibers further from the gray. Other prominent components of the anterior columns are the medial longitudinal fasciculus of the spinal cord, the anterior spinothalamic tract of the spinal cord and the lateral vestibulospinal tract of the spinal cord. The ventral propriospinal tract is one of three propriospinal tracts in which most pathways intrinsic to the spinal cord are located. The others are the dorsal propriospinal tract and the lateral propriospinal tract.,
Lateral propriospinal tract is a collection of nerve fibers, ascending, descending, crossed and uncrossed, that interconnect various levels of the spinal cord. Its fibers are largely myelinated. It is a component of the white lateral columns. Most prominent in the cervical and lumbar regions, it is located close to the spinal central gray. Shorter fibers are closer to, longer fibers further from the gray The tract is one of three propriospinal tracts in which most pathways intrinsic to the spinal cord are located. The others are the ventral propriospinal tract and the dorsal propriospinal tract.
The dorsal propriospinal tract is a collection of nerve fibers, ascending, descending, crossed and uncrossed, that interconnect various levels of the spinal cord. It is a component of the white posterior column. Myelinated fibers are located adjacent to the spinal central gray. Shorter fibers are closer to, longer fibers further from the gray. Some fibers are unmyelinated and scattered through the posterior column. The tract is one of three propriospinal tracts in which most pathways intrinsic to the spinal cord are located. The others are the ventral propriospinal tract and the lateral propriospinal tract.
The raphespinal tract is an unmyelinated descending serotonergic tract involved in pain modulation. It is a descending pain-inhibiting pathway; it is a component of the reticulospinal tract.
References
- ↑ Carpenter MB; Sutin J (1983). Human Neuroanatomy. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Co. OCLC 8346573.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Jastrow H (2007). Histologischer Atlas im Internet http://www.uni-mainz.de/FB/Medizin/Anatomie/workshop/Histology/RM.html
- ↑ Schoenen J, Grant G (2004). "8:Spinal Cord: Connections". In Paxinos G, Mai JK (eds.). The Human Nervous System (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. OCLC 54767534.