
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about nine million people in India, Bangladesh and Nepal. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages.

Birsa Munda was an Indian tribal independence activist, and folk hero who belonged to the Munda tribe. He spearheaded a tribal religious millenarian movement that arose in the Bengal Presidency in the late 19th century, during the British Raj, thereby making him an important figure in the history of the Indian independence movement. The revolt mainly concentrated in the Munda belt of Khunti, Tamar, Sarwada and Bandgaon.

The Munda people are an Austroasiatic-speaking ethnic group of the Indian subcontinent. They speak Mundari as their native language, which belongs to the Munda subgroup of Austroasiatic languages. The Munda are found mainly concentrated in the south and East Chhotanagpur Plateau region of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. The Munda also reside in adjacent areas of Madhya Pradesh as well as in portions of Bangladesh, Nepal, and the state of Tripura. They are one of India's largest scheduled tribes. Munda people in Tripura are also known as Mura.

Agrotis munda, the brown cutworm or pink cutworm, is a noctuid moth. It is endemic to Australia. It is present in New Zealand.
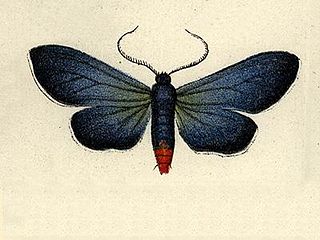
Uranophora is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1831.

Pseudosphex is a genus of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1818. These moths are mimics of a variety of Hymenoptera. The prefix pseudo means "false", and Sphex is a genus of wasps.
Torocca is a genus of flies in the family Tachinidae.
Pseudosphex aequalis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1864. It is found in Tefé, Brazil.
Pseudosphex consobrina is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found in the Amazon region.

Pseudosphex leovazquezae is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Pérez and Sánchez in 1986. It is found in southern Texas, Mexico and Guatemala.
Pseudosphex postica is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in the Amazon region.
Pseudosphex singularis is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Pará, Brazil.
Uranophora munda is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856. It is found on Haiti.

The Euchromiina are a subtribe of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876. Many species in the subtribe are mimics of wasps. Euchromiina have always been considered closely related to the subtribe Ctenuchina due to their similarity to moths and wasps. These two subtribes make up around 3,000 valid species, the majority of which occur in the Neotropics.

Gyna, also called porcelain roaches, are a genus of cockroaches native to Africa.
Torocca munda is a species of fly in the family Tachinidae.







