Related Research Articles

The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally they have the form of small amoebae, with branching cytoplasmic extensions that capture prey and connect the cells together, forming a net. They may also form flagellate zoospores, which characteristically have a single subapical flagellum that spirals backwards around the cell body, and walled coccoid cells.

Buddleja is a genus comprising over 140 species of flowering plants endemic to Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The generic name bestowed by Linnaeus posthumously honoured the Reverend Adam Buddle (1662–1715), an English botanist and rector, at the suggestion of Dr. William Houstoun. Houstoun sent the first plants to become known to science as buddleja to England from the Caribbean about 15 years after Buddle's death.

Malassezia is a genus of fungi. Malassezia is naturally found on the skin surfaces of many animals, including humans. In occasional opportunistic infections, some species can cause hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation on the trunk and other locations in humans. Allergy tests for this fungus are available.

Gomphrena is a genus of plants in the family Amaranthaceae. They are known as the globe amaranths.

Gomphrena globosa, commonly known as globe amaranth, makhmali, and vadamalli, is an edible plant from the family Amaranthaceae. The round-shaped flower inflorescences are a visually dominant feature and cultivars have been propagated to exhibit shades of magenta, purple, red, orange, white, pink, and lilac. Within the flowerheads, the true flowers are small and inconspicuous.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Globosa' was first described in the Späth nursery catalogue of 1892–93. Considered "probably Ulmus carpinifolia " by Green
Anisophyllea globosa is a tree of Borneo in the family Anisophylleaceae. The specific epithet globosa is from the Latin meaning "round", referring to the fruits.

Myristica globosa is a species of plant in the family Myristicaceae. It is found in Papua New Guinea the Solomon Islands and Australia.

Buddleja globosa, also known as the orange-ball-tree, orange ball buddleja, and matico is a species of flowering plant endemic to Chile and Argentina, where it grows in dry and moist forest, from sea level to 2,000 m. The species was first described and named by Hope in 1782

Janthina is a genus of small to medium-sized pelagic or planktonic sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Epitoniidae.

Traunsteinera, the round headed orchid, or globe orchid, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. There are two known species, native to Europe, Turkey and the Caucasus.

Grevillea globosa is a shrub in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia, occurring in the northern wheatbelt.
Eua globosa is a species of tropical air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Partulidae. It is endemic to the island of 'Eua, Tonga.

Wolffia globosa is a species of flowering plant known by the common names Asian watermeal and duckweed. It is native to Asia and is found in parts of the Americas, where it may be native or naturalized. It grows in mats on the surface of calm, freshwater bodies, such as ponds, lakes, and marshes. It is a very tiny, oval-shaped plant with no leaves, stems, or roots. The body of the plant, a transparent green frond, is less than a millimeter wide. In one human experiment, processed W globosa was reported to provide dietary protein and vitamin B12.
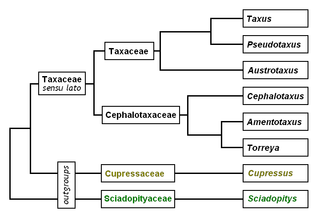
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.

Pterolophia is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Tsukubea is a monotypic class of excavates that contains a single species, Tsukubamonas globosaYabuki et al. 2011. T. globosa is a free-living flagellate that was isolated from a pond in the University of Tsukuba, Japan.

Scotoplanes globosa, commonly known as the sea pig, is a species of sea cucumber that lives in the deep sea. It was first described by Hjalmar Théel, a Swedish scientist. Scotoplanes globosa, along with numerous other sea cucumbers were discovered by Théel during an expedition on the HMS Challenger between the years of 1873-1876. Scotoplanes globosa was officially described in 1882, 6 to 9 years after its first sighting. Scotoplanes globosa is most closely related to the genus Peniagone.

Pila globosa is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Ampullariidae, the apple snails.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Pterolophia globosa. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.