Related Research Articles

An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. Women begin puberty with about 400,000 follicles, each with the potential to release an egg cell (ovum) at ovulation for fertilization. These eggs are developed once every menstrual cycle.

The corpus albicans is the regressed form of the corpus luteum. As the corpus luteum is being broken down by macrophages, fibroblasts lay down type I collagen, forming the corpus albicans. This process is called "luteolysis". The remains of the corpus albicans may persist as a scar on the surface of the ovary.

Granulosa cell tumours are tumours that arise from granulosa cells. They are estrogen secreting tumors and present as large, complex, ovarian masses. These tumours are part of the sex cord-gonadal stromal tumour or non-epithelial group of tumours. Although granulosa cells normally occur only in the ovary, granulosa cell tumours occur in both ovaries and testicles. These tumours should be considered malignant and treated in the same way as other malignant tumours of ovary. The ovarian disease has two forms, juvenile and adult, both characterized by indolent growth, and therefore has high recovery rates. The staging system for these tumours is the same as for epithelial tumours and most present as stage I. The peak age at which they occur is 50–55 years, but they may occur at any age.

Sex cord–gonadal stromal tumour is a group of tumors derived from the stromal component of the ovary and testis, which comprises the granulosa, thecal cells and fibrocytes. In contrast, the epithelial cells originate from the outer epithelial lining surrounding the gonad while the germ cell tumors arise from the precursor cells of the gametes, hence the name germ cell. In humans, this group accounts for 8% of ovarian cancers and under 5% of testicular cancers. Their diagnosis is histological: only a biopsy of the tumour can make an exact diagnosis. They are often suspected of being malignant prior to operation, being solid ovarian tumours that tend to occur most commonly in post menopausal women.

A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete in the ovary of mammals.

In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte. Folliculogenesis describes the progression of a number of small primordial follicles into large preovulatory follicles that occurs in part during the menstrual cycle.

The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.

The follicular phase, also known as the preovulatory phase or proliferative phase, is the phase of the estrous cycle during which follicles in the ovary mature from primary follicle to a fully mature graafian follicle. It ends with ovulation. The main hormones controlling this stage are secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone which are follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone. They are released by pulsatile secretion.

The corona radiata is the innermost layer of the cells of the cumulus oophorus and is directly adjacent to the zona pellucida, the inner protective glycoprotein layer of the ovum. Its main purpose in many animals is to supply vital proteins to the cell. It is formed by follicle cells adhering to the oocyte before it leaves the ovarian follicle, and originates from the squamous granulosa cells present at the primordial stage of follicular development. The corona radiata is formed when the granulosa cells enlarge and become cuboidal, which occurs during the transition from the primordial to primary stage. These cuboidal granulosa cells, also known as the granulosa radiata, form more layers throughout the maturation process, and remain attached to the zona pellucida after the ovulation of the Graafian follicle. For fertilization to occur, sperm cells rely on hyaluronidase to disperse the corona radiata from the zona pellucida of the secondary (ovulated) oocyte, thus permitting entry into the perivitelline space and allowing contact between the sperm cell and the nucleus of the oocyte.
Follicular atresia is the breakdown of the ovarian follicles, which consist of an oocyte surrounded by granulosa cells and internal and external theca cells. It occurs continually throughout a woman’s life, as they are born with millions of follicles but will only ovulate around 400 times in their lifetime. Typically around 20 follicles mature each month but only a single follicle is ovulated; the follicle from which the oocyte was released becomes the corpus luteum. The rest undergo atresia.

Bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP-15) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP15 gene. It is involved in folliculogenesis, the process in which primordial follicles develop into pre-ovulatory follicles.

Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II or BMPR2 is a serine/threonine receptor kinase. It binds Bone morphogenetic proteins, members of the TGF beta superfamily of ligands, which are involved in paracrine signalling. BMPs are involved in a host of cellular functions including osteogenesis, cell growth and cell differentiation. Signaling in the BMP pathway begins with the binding of a BMP to the type II receptor. This causes the recruitment of a BMP type I receptor, which it phosphorylates. The Type I receptor phosphorylates an R-SMAD a transcriptional regulator.
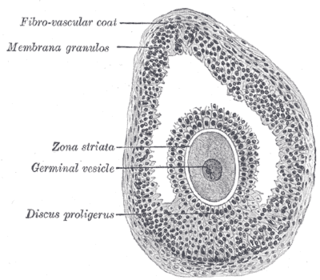
The larger ovarian follicles consist of an external fibrovascular coat, connected with the surrounding stroma of the ovary by a network of blood vessels, and an internal coat, which consists of several layers of nucleated cells, called the membrana granulosa. It contains numerous granulosa cells.
The theca folliculi comprise a layer of the ovarian follicles. They appear as the follicles become secondary follicles.

Rhinella granulosa, also known as granular toad and common lesser toad, is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. The species was redelimited in 2009 and is now considered endemic to Brazil.
TOX high mobility group box family member 2, also known as TOX2, is a human gene.

miR-224 is a family of microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. The ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA sequence is excised from the precursor hairpin by the enzyme Dicer.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) insensitivity, or ovarian insensitivity to FSH in females, also referable to as ovarian follicle hypoplasia or granulosa cell hypoplasia in females, is a rare autosomal recessive genetic and endocrine syndrome affecting both females and males, with the former presenting with much greater severity of symptomatology. It is characterized by a resistance or complete insensitivity to the effects of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), a gonadotropin which is normally responsible for the stimulation of estrogen production by the ovaries in females and maintenance of fertility in both sexes. The condition manifests itself as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism, reduced or absent puberty, amenorrhea, and infertility in females, whereas males present merely with varying degrees of infertility and associated symptoms.

Grevillea granulosa is a shrub of the family Proteaceae native to Western Australia.

Pterolophia is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Pterolophia granulosa. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.