
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms and coined many terms in biology, including ecology, phylum, phylogeny, and Protista. Haeckel promoted and popularised Charles Darwin's work in Germany and developed the influential but no longer widely held recapitulation theory claiming that an individual organism's biological development, or ontogeny, parallels and summarises its species' evolutionary development, or phylogeny.

Tobias Barreto de Meneses was a Brazilian poet, philosopher, jurist and literary critic. He is famous for creating the "Condorism" and revolutionizing Brazilian Romanticism and poetry. He is patron of the 38th chair of the Brazilian Academy of Letters.

Richard Wilhelm Karl Theodor Ritter von Hertwig, also Richard Hertwig or Richard von Hertwig, was a German zoologist and professor of 50 years, notable as the first to describe zygote formation as the fusing of spermatozoa inside the membrane of an egg cell during fertilization. Richard Hertwig was the younger brother of Oscar Hertwig, who also analyzed zygote formation.
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, conceptual model, and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species (1859).
The affinities of all the beings of the same class have sometimes been represented by a great tree. I believe this simile largely speaks the truth.

Solmissus, or dinner plate jellyfish, is a genus of hydrozoans. Its species are unique among cnidarians in that they actively hunt for prey as opposed to passively waiting for plankton to pass by. They are found in the deep waters of Monterey Bay, California. They are most likely to be found in the deep sea, mid water. They grow to be 20 cm (7.9 in) in diameter. These hydrozoans feed on gelatinous zooplankton, including salps and doliolids, ctenophores, jellyfish, and copepods. However, Solmissus may be limited to feeding on soft-bodied prey by the type of nematocysts on their tentacles (Mills).
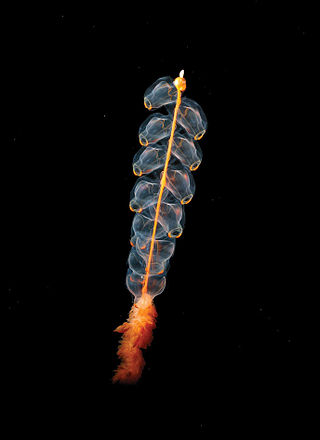
Agalmatidae, or Agalmidae, is a family of siphonophores.

Pandeidae is a family of hydroids in the class Hydrozoa. Like other jellyfish there is usually a mature medusa form which is pelagic and reproduces sexually and a hydroid or polyp form which is often benthic and reproduces asexually by budding.

Aeginidae is a family of hydrozoans in the order Narcomedusae. The family comprises 6 genera and 8 species.
Solmarisidae is a family of hydrozoans in the order Narcomedusae. The name is sometimes spelled "Solmaridae".

Corynidae is a family of hydrozoans in the order Anthomedusae.

Filifera is a suborder of hydrozoans in the order Anthoathecata. They are found in marine, brackish and freshwater habitats.

Aeginura is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Aeginidae.

Aglantha is a genus of deep-sea hydrozoans of the family Rhopalonematidae.

Eirenidae is a family of hydrozoans.
Mitrocomidae is an accepted family in the order Leptothecata.
Mitrocomium is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Lovenellidae.
Laodiceidae is a family of cnidarians belonging to the order Leptomedusae.
Codonium is a genus of hydrozoans belonging to the family Corynidae.
Staurodiscus is a genus of hydrozoans belonging to the family Hebellidae.












