
The politics of Puerto Rico take place in the framework of a democratic republic form of government that is under the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United States Congress as an organized unincorporated territory. Since the 1898 invasion of Puerto Rico by the United States during the Spanish–American War, politics in Puerto Rico have been significantly shaped by its status as territory of the United States. The nature of Puerto Rico's political relationship with the United States is the subject of ongoing debate in Puerto Rico, in the United States, the United Nations and the international community, with all major political parties in the archipelago calling it a colonial relationship.

The New Progressive Party is a political party in Puerto Rico that advocates statehood. The PNP is one of the two major parties in Puerto Rico with significant political strength and currently holds both the seat of the governor and of the resident commissioner.
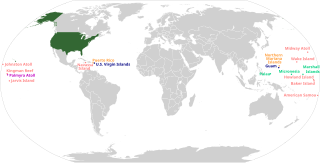
The 51st state in American political discourse refers to the concept of granting statehood to one of the United States' territories, splitting one or more of the existing states up to form a new state, or granting statehood to the District of Columbia, thereby increasing the number of states in the Union from 50 to 51.
Commonwealth is a term used by two unincorporated territories of the United States in their full official names, which are the Northern Mariana Islands, whose full name is Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and Puerto Rico, which is named Commonwealth of Puerto Rico in English and Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico in Spanish, translating to "Free Associated State of Puerto Rico." The term was also used by the Philippines during most of its period under U.S. sovereignty, when it was officially called the Commonwealth of the Philippines.
Throughout the history of Puerto Rico, its inhabitants have initiated several movements to obtain independence for the island, first from the Spanish Empire from 1493 to 1898 and since then from the United States.
The United States-Puerto Rico Political Status Act (1998) was a bill proposed in the United States Congress to help refine the political status of Puerto Rico. The senior sponsor of the bill was Representative Don Young, Republican of Alaska. While a version was approved in the House, it failed to reach a vote in the Senate.

Pedro Rafael Pierluisi Urrutia is a Puerto Rican politician and lawyer currently serving as governor of Puerto Rico since 2021. He has previously served as secretary of justice, resident commissioner, acting secretary of state, de facto governor of Puerto Rico and as private attorney for Puerto Rico's fiscal oversight board under the Puerto Rico Oversight, Management, and Economic Stability Act.
The Puerto Rico Statehood Students Association (PRSSA) —Spanish: Asociación de Estudiantes Estadistas de Puerto Rico— is a Puerto Rican non-profit student organization dedicated to promoting statehood for Puerto Rico. It was founded in 1979, and remained active for two years, becoming inactive 1981–1993, active again 1993 to 1997, inactive once more 1997 to 2007, when it was reactivated once again.

The Puerto Rico statehood movement aims to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. Puerto Rico is an unincorporated territorial possession of the United States acquired in 1898 following the Spanish–American War, making it "the oldest colony in the modern world". As of 2023, the population of Puerto Rico is 3.2 million, around half the average state population and higher than that of 19 U.S. states. Statehood is one of several competing options for the future political status of Puerto Rico, including: maintaining its current status, becoming fully independent, or becoming a freely associated state. Puerto Rico has held six referendums on the topic. These are non-binding, as the power to grant statehood lies with the US Congress. The most recent referendum was in November 2020, with a majority (52.52%) of those who voted opting for statehood.

The political status of Puerto Rico is that of an unincorporated territory of the United States officially known as the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. As such, the island of Puerto Rico is neither a sovereign nation nor a U.S. state.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on November 6, 2012. It was the fourth referendum on status to be held in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has been an unincorporated territory of the United States since the Spanish–American War in 1898.
There are differing points of view on whether Puerto Rico's current political status as a territory of the United States should change. Four major viewpoints emerge in principle: that Puerto Rico maintains its current status, becomes a US state, becomes fully independent, or becomes a freely associated state.

The free association movement in Puerto Rico refers to initiatives throughout the history of Puerto Rico aimed at changing the current political status of Puerto Rico to that of a sovereign freely associated state. Locally, the term soberanista refers to someone that seeks to redefine the relationship between Puerto Rico and the United States to that of a compact with full sovereignty. The term is mostly used in reference to those that support a compact of free association or a variation of this formula, commonly known as Estado Libre Asociado (ELA) Soberano, between Puerto Rico and the United States. Members of the independence movement that are willing to pursue alliances with this ideology are occasionally referred to as such, but are mostly known as independentistas. Consequently, soberanismo then became the local name for the free association movement.

The status quo movement in Puerto Rico refers to initiatives throughout the history of Puerto Rico aimed at maintaining the current political status of Puerto Rico, that of a commonwealth of the United States.

Puerto Rico is an unincorporated territory within the United States. As such, the island is neither a U.S. state or a sovereign nation. Due to the territory's ambiguous status, there are ongoing disputes regarding how Puerto Rico should be governed. Both major United States political parties,, have expressed their support for the U.S. citizens in Puerto Rico to exercise their right to self-determination, with the Republican Party platform explicitly mentioning support for right to statehood and the Democratic Party platform voicing broader support for right to self-determination. Puerto Rico has been under U.S. sovereignty for over a century and Puerto Ricans have been U.S. citizens since 1917, but the island's ultimate status still has not been determined and its 3.9 million residents do not have voting representation in their national government.
Three main alternatives are generally presented to Puerto Rican voters during a Puerto Rico political status plebiscite: full independence, maintenance or enhancement of the current commonwealth status, and full statehood into the American Union. The exact expectations for each of these status formulas are a matter of debate by a given position's adherents and detractors. Puerto Ricans have proposed positions that modify the three alternatives above, such as (a) indemnified independence with phased-out US subsidy, (b) expanded political but not fiscal autonomy, and (c) statehood with a gradual phasing out of federal tax exemption.
The Territories Clause of the United States Constitution allows for Congress to "dispose of" Puerto Rico and allow it to become independent of the U.S. or, under the authority of the Admissions Clause for it to be admitted as a state of the United States.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on June 11, 2017. The referendum had three options: becoming a state of the United States, independence/free association, or maintaining the current territorial status. Those who voted overwhelmingly chose statehood by 97%. This figure is attributed to a boycott led by the pro-status quo PPD party, which resulted in a 22.93% turnout.
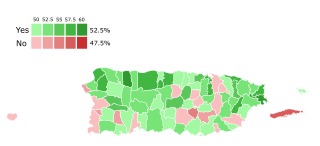
A referendum of the status of Puerto Rico was held on November 3, 2020, concurrently with the general election. The Referendum was announced by Puerto Rico Governor Wanda Vázquez Garced on May 16, 2020. This was the sixth referendum held on the status of Puerto Rico, with the previous one having taken place in 2017. This was the first referendum with a simple yes-or-no question, with voters having the option of voting for or against becoming a U.S. state. The New Progressive Party (PNP), of whom Vázquez is a member, supports statehood, while the opposition Popular Democratic Party (PDP) and Puerto Rican Independence Party (PIP) oppose it.

The Puerto Rico Statehood Admission Act, H.R. 4901, was a bill introduced during the 116th United States Congress. The intention of the bill is to grant Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States, admission into the Union as a state. The bill was originally introduced in the 116th Congress and was reintroduced as H.R. 1522, on March 2, 2021, in the 117th Congress. It was referred to the House Committee on Natural Resources with last action taken on June 16.








