
Pukao are the hat-like structures or topknots formerly placed on top of some moai statues on Easter Island. [1] They were all carved from a very light-red volcanic scoria, which was quarried from a single source at Puna Pau.

Pukao are the hat-like structures or topknots formerly placed on top of some moai statues on Easter Island. [1] They were all carved from a very light-red volcanic scoria, which was quarried from a single source at Puna Pau.
Pukao were not made until the 15th–16th centuries and are later additions to the moai. [2] The reason that pukao were made is not known, though various theories exist. One is that the placing of a pukao on top of the moai was a recognition of the power of the individual represented. This has credibility because such a task at the time was, and even now is, extremely difficult, especially because no evidence has been found of crane technology existing at the time. [3] Another theory is that the pukao serve to distinguish between statues. Those moai with pukao are meant to be shown as more majestic and important. This distinction may have also indicated to islanders those statues at which various rituals should be performed. [4] Pukao are now believed to represent hair [5] because it was the custom for high-ranking men to have long hair tied in a bun on the top of their heads. [2]
Pukao are cylindrical in shape, with a dent on the underside to fit on the head of the moai and a boss or knot on top. They fit onto the moai in such a way that the pukao protrudes forwards. Their size varies in proportion to the moai they were on, but they can be from 6 to 10 feet (1.8 to 3.0 metres) in diameter. [1] Pukao weigh up to 10 tonnes (11 short tons), and the placement of a pukao on top of a moai raised the height of the statues to an average of 11 m (37 ft). [6]
The pukao was balanced as a separate piece on top of the head of a moai. They are believed to have been raised using ramps, possibly requiring only several people. The ring-like indentations along the bottom and edges of the pukao support this theory, as they postulate a ramp made out of logs being used to roll the pukao to the tops of moai statues. In addition, various physicists have made models indicating that this as a possibility, and, given the oblong shape of pukao, the structures would have been easier to roll up the statue than roll back down.[ citation needed ] However, no one theory can be accepted as correct, because virtually any theorized method (such as the use of pulleys) is plausible. [5]
To date, about 100 pukao have been documented archaeologically, but only at Ahu with fallen statues or at the source quarry.

The red-colored topknots were made from reddish scoria, a volcanic rock. [7] The rocks were sourced from a quarry known as Puna Pau, which was located inside the crater of a volcano with the same name, and on its outer lip. After the Pukao were made, they were rolled by hand or on tree logs along an ancient road to the site of the statues. The road was built out of a cement of compressed red scoria dust. [8] Over 70 discarded Pukao have been found along the road and on raised ceremonial platforms. [8] The indents found on the bottom of pukao that reached the statues are not present in those strewn along the path from Puna Pau to the moai, hinting that basic quarrying was done at Puna Pau, as well as moulding the stone into a cylindrical shape easier to transport. Meanwhile, more intricate carvings were made at the site of the moai, immediately prior to the placement of pukao on the statues. [2]

Easter Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, which were created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.

Hanga Roa is the main town, harbour and seat of Easter Island, a municipality of Chile. It is located in the southern part of the island's west coast, in the lowlands between the extinct volcanoes of Terevaka and Rano Kau.

Mu is a lost continent introduced by Augustus Le Plongeon (1825–1908), who identified the "Land of Mu" with Atlantis. The name was subsequently identified with the hypothetical land of Lemuria by James Churchward (1851–1936), who asserted that it was located in the Pacific Ocean before its destruction. The place of Mu in both pseudoscience and fantasy fiction is discussed in detail in Lost Continents by L. Sprague de Camp.

Moai or moʻai are monolithic human figures carved by the Rapa Nui people on Rapa Nui in eastern Polynesia between the years 1250 and 1500. Nearly half are still at Rano Raraku, the main moai quarry, but hundreds were transported from there and set on stone platforms called ahu around the island's perimeter. Almost all moai have overly large heads, which comprise three-eighths the size of the whole statue. They have no legs. The moai are chiefly the living faces of deified ancestors. The statues still gazed inland across their clan lands when Europeans first visited the island in 1722, but all of them had fallen by the latter part of the 19th century. The moai were toppled in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, possibly as a result of European contact or internecine tribal wars.

Scoria is a pyroclastic, highly vesicular, dark-colored volcanic rock formed by ejection from a volcano as a molten blob and cooled in the air to form discrete grains called clasts. It is typically dark in color, and basaltic or andesitic in composition. Scoria has relatively low density, as it is riddled with macroscopic ellipsoidal vesicles, but in contrast to pumice, scoria always has a specific gravity greater than 1 and sinks in water.

The Rapa Nui are the indigenous Polynesian peoples of Easter Island. The easternmost Polynesian culture, the descendants of the original people of Easter Island make up about 60% of the current Easter Island population and have a significant portion of their population residing in mainland Chile. They speak both the traditional Rapa Nui language and the primary language of Chile, Spanish. At the 2017 census there were 7,750 island inhabitants—almost all living in the village of Hanga Roa on the sheltered west coast.

Rano Raraku is a volcanic crater formed of consolidated volcanic ash, or tuff, and located on the lower slopes of Terevaka in the Rapa Nui National Park on Easter Island in Chile. It was a quarry for about 500 years until the early eighteenth century, and supplied the stone from which about 95% of the island's known monolithic sculptures (moai) were carved. Rano Raraku is a visual record of moai design vocabulary and technological innovation, where 887 moai remain. Rano Raraku is in the World Heritage Site of Rapa Nui National Park and gives its name to one of the seven sections of the park.

Katherine Maria Routledge was an English archaeologist and anthropologist who, in 1914, initiated and carried out much of the first true survey of Easter Island.

Aku-Aku: the Secret of Easter Island is a 1957 book by Thor Heyerdahl published in Norwegian, Swedish, Danish and Finnish, and in French and English the following year. The book describes the 1955–1956 Norwegian Archaeological Expedition's investigations of Polynesian history and culture at Easter Island, the Austral Islands of Rapa Iti and Raivavae, and the Marquesas Islands of Nuku Hiva and Hiva Oa. Visits to Pitcairn Island, Mangareva and Tahiti are described as well.

Rapa Nui National Park is a national park and UNESCO World Heritage Site located on Easter Island, Chile. Rapa Nui is the Polynesian name of Easter Island; its Spanish name is Isla de Pascua. The island is located in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeastern extremity of the Polynesian Triangle. The island was taken over by Chile in 1888. Its fame and World Heritage status arise from the 887 extant stone statues known by the name "moai", whose creation is attributed to the early Rapa Nui people who inhabited the island starting between 300 and 1200 AD. Much of the island has been declared as Rapa Nui National Park which, on 22 March 1996, UNESCO designated a World Heritage Site under cultural criteria (i), (iii), & (v). Rapa Nui National Park is now under the administrative control of the Ma´u Henua Polynesian Indigenous Community, which is the first autonomous institute on the island. The indigenous Rapa Nui people have regained authority over their ancestral lands and are in charge of the management, preservation and protection of their patrimony. On the first of December 2017, the ex-President Michelle Bachelet returned ancestral lands in the form of the Rapa Nui National Park to the indigenous people. For the first time in history, the revenue generated by the National Park is invested in the island and used to conserve the natural heritage.

Easter Island was traditionally ruled by a monarchy, with a king as its leader.

Hoa Hakananai'a is a moai, a statue from Easter Island. It was taken from Orongo, Easter Island in 1868 by the crew of a British ship and is now in the British Museum in London.

Ahu Tongariki is the largest ahu on Easter Island. Its moais were toppled during the island's civil wars, and in the twentieth century the ahu was swept inland by a tsunami. It has since been restored and has fifteen moai, including one that weighs eighty-six tonnes, the heaviest ever erected on the island. Ahu Tongariki is one kilometer from Rano Raraku and Poike in the Hotu-iti area of Rapa Nui National Park. All the moai here face sunset during the winter solstice.

Ahu Akivi is a particular sacred place on the Chilean island of Rapa Nui, looking out towards the Pacific Ocean. The site has seven moai, all of equal shape and size, and is also known as a celestial observatory that was set up around the 16th century. The site is located inland, rather than along the coast. Moai statues were considered by the early people of Rapa Nui as their ancestors or Tupuna that were believed to be the reincarnation of important kings or leaders of their clans. The Moais were erected to protect and bring prosperity to their clan and village.

Maunga Puna Pau is a small crater or cinder cone and prehistoric quarry on the outskirts of Hanga Roa in the south west of Easter Island. Puna Pau gives its name to one of the seven regions of the Rapa Nui National Park.
Since the removal from Easter Island in 1868 of the moai now displayed at the British Museum, a total of 12 moai are known to have been removed from Easter Island and to remain overseas. Some of the moai have been further transferred between museums and private collections, for reasons such as the moai's preservation, academic research and for public education. In 2006, one relocated moai was repatriated from the Centro Cultural Recoleta in Argentina after 80 years overseas. In 2022, one moai held in the Chilean National Museum of Natural History in Santiago was returned to the island after 150 years abroad.
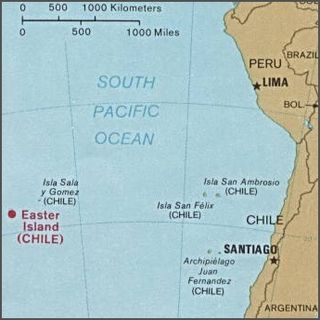
Geologically one of the youngest inhabited territories on Earth, Easter Island, located in the mid-Pacific Ocean, was, for most of its history, one of the most isolated. Its inhabitants, the Rapa Nui, have endured famines, epidemics of disease, civil war, environmental collapse, slave raids, various colonial contacts, and have seen their population crash on more than one occasion. The ensuing cultural legacy has brought the island notoriety out of proportion to the number of its inhabitants.

Easter Island is one of the world's most isolated inhabited islands. Its closest inhabited neighbours are the Chilean Juan Fernandez Islands, 1,850 km (1,150 mi) to the east, with approximately 850 inhabitants. The nearest continental point lies in central Chile near Concepción, at 3,512 kilometres (2,182 mi). Easter Island's latitude is similar to that of Caldera, Chile, and it lies 3,510 km (2,180 mi) west of continental Chile at its nearest point. Isla Salas y Gómez, 415 km (258 mi) to the east, is closer but is uninhabited. The Tristan da Cunha archipelago in the southern Atlantic competes for the title of the most remote island, lying 2,430 km (1,510 mi) from Saint Helena island and 2,816 km (1,750 mi) from the South African coast.
A mortuary cult is a ceremonial and religious form of a cult fostered over a certain duration of time, often lasting for generations or even dynasties. It concerns deceased peoples kept in the memories of their bereaved members, mostly family members or loyal servants.