
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).

The electric power industry covers the generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electric power to the general public and industry. The commercial distribution of electric power started in 1882 when electricity was produced for electric lighting. In the 1880s and 1890s, growing economic and safety concerns lead to the regulation of the industry. What was once an expensive novelty limited to the most densely populated areas, reliable and economical electric power has become an essential aspect for normal operation of all elements of developed economies.

The Dinorwig Power Station, known locally as Electric Mountain, or Mynydd Gwefru, is a pumped-storage hydroelectric scheme, near Dinorwig, Llanberis in Snowdonia national park in Gwynedd, north Wales. The scheme can supply a maximum power of 1,728 MW (2,317,000 hp) and has a storage capacity of around 9.1 GWh (33 TJ).

Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the power supplied commands a much higher price per kilowatt hour than base load power. Peak load power plants are dispatched in combination with base load power plants, which supply a dependable and consistent amount of electricity, to meet the minimum demand.

A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel GenSet) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of an engine generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel, but some types are adapted for other liquid fuels or natural gas (CNG).

The Lakeview Generating Station was an Ontario Power Generation coal-burning power station located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, in the Lakeview neighbourhood on Lakeshore Road just east of Cawthra Road. The former station, constructed in 1958–1962, had four smokestacks known as the Four Sisters; the eight boilers of the generating plant all 'twinned' their emissions into common stacks. The station was a landmark for years and was shut down in April, 2005, after 43 years of service. The four stacks, which could be seen from as far away as Burlington to the west and downtown Toronto to the east, were demolished on June 12, 2006. The rest of the building was demolished on June 28, 2007.

National Grid, Malaysia is the high-voltage electric power transmission network in Peninsular Malaysia. It is operated and owned by Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB) by its Transmission Division. There are two other electrical grids in Sabah and Sarawak operated by Sabah Electricity Sdn Bhd (SESB) and Sarawak Energy Berhad (SEB).
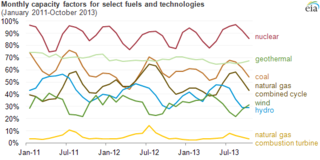
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind, the sun or hydro-electric installations. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

The Huntly Power Station is the largest thermal power station in New Zealand and is located in the town of Huntly in the Waikato. It is operated by Genesis Energy Limited, a publicly listed company. The station has five operational generating units – three 250 MW coal-and-gas-fired steam turbine units, a 50 MW gas peaking plant, and a 403 MW combined cycle gas turbine plant. The station also plays an important role in voltage support for the Northland, Auckland and Waikato regions.
A load-following power plant, regarded as producing mid-merit or mid-priced electricity, is a power plant that adjusts its power output as demand for electricity fluctuates throughout the day. Load-following plants are typically in between base load and peaking power plants in efficiency, speed of start-up and shut-down, construction cost, cost of electricity and capacity factor.

Sultan Salahuddin Abdul Aziz Power Station is a power station, which fires natural gas, bunker oil and coal, located in Kapar, Klang District, Selangor, Malaysia. It was opened in March 1987 by then Sultan of Selangor, Sultan Salahuddin Abdul Aziz Shah, and the station was named after him. In terms of power producing capacity, it remains the largest power station in Malaysia, despite the commissioning of several new power stations with 700MW steam turbines. It is also the first coal-fired power plant in the country.

The Littlebrook Power Station were a series of four oil and coal-fired power stations situated on the south bank of the River Thames, next to the Queen Elizabeth 2 Bridge and the Dartford Tunnel in Dartford, Kent. The final power station, Littlebrook D, ceased operating in March 2015, and has now been demolished.
A Simple-Cycle Combustion Turbine (SCCT) is a type of gas turbine typically used in the power generation, aviation, and oil and gas industries. The simple-cycle combustion turbine follows the Brayton Cycle and differs from a combined cycle operation in that it has only one power cycle.
Availability Based Tariff (ABT) is a frequency based pricing mechanism applicable in India for unscheduled electric power transactions. The ABT falls under electricity market mechanisms to charge and regulate power to achieve short term and long term network stability as well as incentives and dis-incentives to grid participants against deviations in committed supplies as the case may be.
Tamar Valley Power Station is a $230 million natural gas-fired power station located in Bell Bay in the Tamar Valley, Tasmania. It is owned by Hydro Tasmania, and is immediately adjacent to the decommissioned Bell Bay Power Station, which is also owned by Hydro Tasmania.

Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable energy sources, such as dammed hydroelectricity or bioenergy, or relatively constant sources, such as geothermal power.
Basin Bridge Gas Turbine Power Station is a state-owned gas fuel-based power plant located in Basin Bridge, Chennai. It has a capacity of 120 MW and is operated by the Tamil Nadu State Electricity Board.
Watford Power Station was a coal-fired power station situated in Watford's Riverside area. The station was built by the Watford Corporation Electricity Department starting with the installation of cables in 1899 with completion around 1900, near the banks of the River Colne. A gas turbine power station was commissioned in 1980.














