In mathematics, the term quadratic describes something that pertains to squares, to the operation of squaring, to terms of the second degree, or equations or formulas that involve such terms. Quadratus is Latin for square.
In mathematics, the term quadratic describes something that pertains to squares, to the operation of squaring, to terms of the second degree, or equations or formulas that involve such terms. Quadratus is Latin for square.
In mathematics, an equation is a mathematical formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign =. The word equation and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an équation is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation.
In mathematics, a polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of indeterminates and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and exponentiation to nonnegative integer powers, and has a finite number of terms. An example of a polynomial of a single indeterminate x is x2 − 4x + 7. An example with three indeterminates is x3 + 2xyz2 − yz + 1.
In mathematics, a quadratic equation is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as where the variable x represents an unknown number, and a, b, and c represent known numbers, where a ≠ 0. The numbers a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation and may be distinguished by respectively calling them, the quadratic coefficient, the linear coefficient and the constant coefficient or free term.
In mathematics, a square root of a number x is a number y such that ; in other words, a number y whose square is x. For example, 4 and −4 are square roots of 16 because .
In mathematics, the discriminant of a polynomial is a quantity that depends on the coefficients and allows deducing some properties of the roots without computing them. More precisely, it is a polynomial function of the coefficients of the original polynomial. The discriminant is widely used in polynomial factoring, number theory, and algebraic geometry.
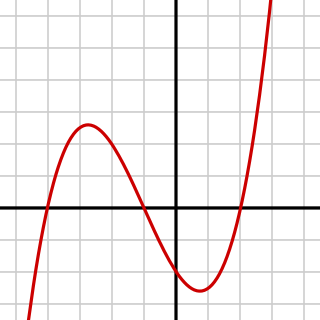
In algebra, a cubic equation in one variable is an equation of the form in which a is not zero.
In mathematics, a quadratic form is a polynomial with terms all of degree two. For example,

In algebra, a quartic function is a function of the form
In mathematics, an algebraic equation or polynomial equation is an equation of the form , where P is a polynomial with coefficients in some field, often the field of the rational numbers. For example, is an algebraic equation with integer coefficients and
In mathematics, an expression or equation is in closed form if it is formed with constants, variables and a finite set of basic functions connected by arithmetic operations and function composition. Commonly, the allowed functions are nth root, exponential function, logarithm, and trigonometric functions. However, the set of basic functions depends on the context.
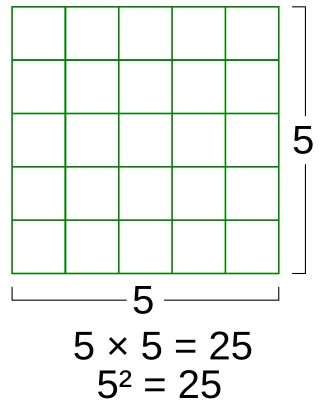
In mathematics, a square is the result of multiplying a number by itself. The verb "to square" is used to denote this operation. Squaring is the same as raising to the power 2, and is denoted by a superscript 2; for instance, the square of 3 may be written as 32, which is the number 9. In some cases when superscripts are not available, as for instance in programming languages or plain text files, the notations x^2 (caret) or x**2 may be used in place of x2. The adjective which corresponds to squaring is quadratic.
In mathematics, an algebraic expression is an expression built up from constants variables, and the basic algebraic operations: addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (×), division (÷), whole number powers, and roots .. For example, is an algebraic expression. Since taking the square root is the same as raising to the power 1/2, the following is also an algebraic expression:
Algebra is one of the main branches of mathematics, covering the study of structure, relation and quantity. Algebra studies the effects of adding and multiplying numbers, variables, and polynomials, along with their factorization and determining their roots. In addition to working directly with numbers, algebra also covers symbols, variables, and set elements. Addition and multiplication are general operations, but their precise definitions lead to structures such as groups, rings, and fields.
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.