The Holocene is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 9,700 years before the Common Era (BCE). It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.

The Quaternary is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene and the Holocene although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not officially recognised by the ICS.
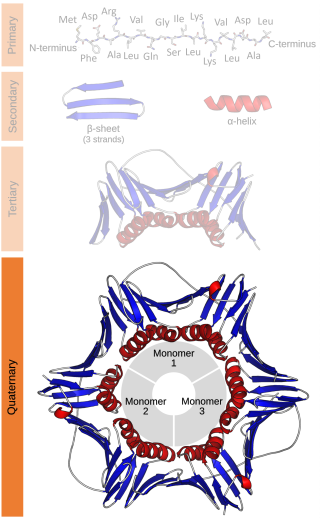
Protein quaternary structure is the fourth classification level of protein structure. Protein quaternary structure refers to the structure of proteins which are themselves composed of two or more smaller protein chains. Protein quaternary structure describes the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi-subunit complex. It includes organizations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits. In contrast to the first three levels of protein structure, not all proteins will have a quaternary structure since some proteins function as single units. Protein quaternary structure can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors.
The Younger Dryas, which occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years BP, was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum, which lasted from circa 27,000 to 20,000 years BP. The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch that spanned from 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and longest lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial, an interval of relative warmth that lasted from 14,670 to 12,900 BP.

The Toba eruption was a supervolcano eruption that occurred around 74,000 years ago during the Late Pleistocene at the site of present-day Lake Toba in Sumatra, Indonesia. It is one of the largest known explosive eruptions in the Earth's history. The Toba catastrophe theory holds that this event caused a severe global volcanic winter of six to ten years and contributed to a 1,000-year-long cooling episode, leading to a genetic bottleneck in humans.

A loess is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loesses or similar deposits.

A raised beach, coastal terrace, or perched coastline is a relatively flat, horizontal or gently inclined surface of marine origin, mostly an old abrasion platform which has been lifted out of the sphere of wave activity. Thus, it lies above or under the current sea level, depending on the time of its formation. It is bounded by a steeper ascending slope on the landward side and a steeper descending slope on the seaward side. Due to its generally flat shape, it is often used for anthropogenic structures such as settlements and infrastructure.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the Last Ice Age or simply Ice Age, occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago.
Before Present (BP) years, also known as "time before present" or "years before present (YBP)", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1 January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale. The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must now account for.
A glacial period is an interval of time within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state.

The Anglian Stage is the name used in the British Isles for a middle Pleistocene glaciation. It precedes the Hoxnian Stage and follows the Cromerian Stage in the British Isles. The Anglian Stage is correlated to Marine Isotope Stage 12, which started about 478,000 years ago and ended about 424,000 years ago.
The Hoxnian Stage was a middle Pleistocene stage of the geological history of the British Isles. It was an interglacial which preceded the Wolstonian Stage and followed the Anglian Stage. It is equivalent to Marine Isotope Stage 11. Marine Isotope Stage 11 started 424,000 years ago and ended 374,000 years ago. The Hoxnian is divided into sub-stages Ho I to Ho IV.

In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively-charged polyatomic ions of the structure [NR4]+, where R is an alkyl group, an aryl group or organyl group. Unlike the ammonium ion and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule.

The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently defined as the time between c. 129,000 and c. 11,700 years ago. The Late Pleistocene equates to the proposed Tarantian Age of the geologic time scale, preceded by the officially ratified Chibanian and succeeded by the officially ratified Greenlandian. The estimated beginning of the Tarantian is the start of the Eemian interglacial period. It is held to end with the termination of the Younger Dryas, some 11,700 years ago when the Holocene Epoch began.

Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which paleoenvironmental or archaeological records can be placed. Such an established event provides a "tephra horizon". The premise of the technique is that each volcanic event produces ash with a unique chemical "fingerprint" that allows the deposit to be identified across the area affected by fallout. Thus, once the volcanic event has been independently dated, the tephra horizon will act as time marker. It is a variant of the basic geological technique of stratigraphy.
Quaternary science is the subfield of geology which studies the Quaternary Period commonly known as the ice age. The Quaternary Period is a time period that started around 2.58 million years ago and continues today. This period is divided into two epochs – the Pleistocene Epoch and the Holocene Epoch. The aim of Quaternary science is to understand everything that happened during the Pleistocene Epoch and the Holocene Epoch to be able to acquire fundamental knowledge about Earth's environment, ecosystem, climate changes, etc. Quaternary science was first studied during the nineteenth century by Georges Cuvier, a French scientist. Most Quaternary scientists have studied the history of the Quaternary to predict future changes in climate.
Geografiska Annaler is a scientific journal published by the Swedish Society for Anthropology and Geography in Stockholm, Sweden. The journal is founded in 1919. Since 1965 the journal is published in two series A and B. Series A deals with arctic research, physical geography, glaciology and quaternary science in general. Series B covers the topics of human geography and economic geography, with a special, but not exclusive, focus on the Nordic and Baltic countries.
Estella Bergere Leopold is an American paleobotanist and a conservationist. As a researcher in the United States Geological Survey, she aided in uncovering records of plant life from the Miocene around the Eniwetok and Bikini Atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean and from the Cenozoic era in the Rocky Mountains. As a professor of botany and forest sciences at the University of Washington, she directed the Quaternary Research Center, researched the forest history of the Pacific Northwest, and collaborated with Chinese paleobotanists. Leopold's work as a conservationist includes taking legal action to help save the Florissant Fossil Beds in Colorado, and fighting pollution. She is the daughter and only surviving child of Aldo Leopold.
Quaternary International is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on quaternary science published by Elsevier on behalf of the International Union for Quaternary Research. The journal was established in 1989 and covers full spectrum of the physical and natural sciences that are commonly employed in solving problems related to the quaternary period. The editor-in-chief is Min-Te Chen.
Quaternary Science Reviews is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering quaternary science. It was established in 1982 by Pergamon Press and is currently published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is C.V. Murray Wallace. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2013 impact factor of 4.571.










