Ring finger and CCCH-type domains 1, also known as Roquin-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RC3H1 gene. [5]
Ring finger and CCCH-type domains 1, also known as Roquin-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RC3H1 gene. [5]

This gene encodes a protein containing RING-type and C3H1-type zinc finger motifs. The encoded protein recognizes and binds to a constitutive decay element (CDE) in the 3' UTR of mRNAs, leading to mRNA deadenylation and degradation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014].

Inducible T-cell costimulator is an immune checkpoint protein that in humans is encoded by the ICOS gene.

The autoimmune regulator (AIRE) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIRE gene. It is a 13kb gene on chromosome 21q22.3 that has 545 amino acids. AIRE is a transcription factor expressed in the medulla of the thymus. It is part of the mechanism which eliminates self-reactive T cells that would cause autoimmune disease. It exposes T cells to normal, healthy proteins from all parts of the body, and T cells that react to those proteins are destroyed.

X-box binding protein 1, also known as XBP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the XBP1 gene. The XBP1 gene is located on chromosome 22 while a closely related pseudogene has been identified and localized to chromosome 5. The XBP1 protein is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes important to the proper functioning of the immune system and in the cellular stress response.

CBL-B is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that in humans is encoded by the CBLB gene. CBLB is a member of the CBL gene family.

Chemokine receptor 6 also known as CCR6 is a CC chemokine receptor protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR6 gene. CCR6 has also recently been designated CD196. The gene is located on the long arm of Chromosome 6 (6q27) on the Watson (plus) strand. It is 139,737 bases long and encodes a protein of 374 amino acids.

G-protein coupled receptor 183 also known as Epstein-Barr virus-induced G-protein coupled receptor 2 (EBI2) is a protein (GPCR) expressed on the surface of some immune cells, namely B cells and T cells; in humans it is encoded by the GPR183 gene. Expression of EBI2 is one critical mediator of immune cell localization within lymph nodes, responsible in part for the coordination of B cell, T cell, and dendritic cell movement and interaction following antigen exposure. EBI2 is a receptor for oxysterols. The most potent activator is 7α,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7α,25-OHC), with other oxysterols exhibiting varying affinities for the receptor. Oxysterol gradients drive chemotaxis, attracting the EBI2-expressing cells to locations of high ligand concentration. The GPR183 gene was identified due to its upregulation during Epstein-Barr virus infection of the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line BL41, hence its name: EBI2.

ELAV-like protein 1 or HuR is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELAVL1 gene.

Tristetraprolin (TTP), also known as zinc finger protein 36 homolog (ZFP36), is a protein that in humans, mice and rats is encoded by the ZFP36 gene. It is a member of the TIS11 family, along with butyrate response factors 1 and 2.

5′-nucleotidase (5′-NT), also known as ecto-5′-nucleotidase or CD73, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5E gene. CD73 commonly serves to convert AMP to adenosine.

Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 13B (TNFRSF13B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFRSF13B gene.
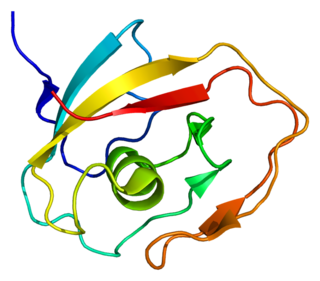
Cochlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COCH gene. It is an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein highly abundant in the cochlea and vestibule of the inner ear, constituting the major non-collagen component of the ECM of the inner ear. The protein is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively.

Programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD1LG2 gene. PDCD1LG2 has also been designated as CD273. PDCD1LG2 is an immune checkpoint receptor ligand which plays a role in negative regulation of the adaptive immune response. PD-L2 is one of two known ligands for Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1).

Zinc finger CCCH-type antiviral protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZC3HAV1 gene.

Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZC3H11A gene. ZC3H11A is a part of the transcription export (TREX) complex and plays a role in exporting of mRNAs from nucleus to cytoplasm. It is considered as stress-induced nuclear protein and maintains mRNAs exporting when the cells are under stress. Loss of functioning of ZC3H11A gene in HeLa cells results in abortion of the replication of nuclear replicating viruses but not cytoplasmic replicating viruses. It is discovered that ZC3H11A is significant for viability and metabolic regulation of mouse embryo

RNA-binding motif protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM7 gene.

Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain is a protein involved in assembly of high-affinity Interleukin-2 receptor, consisting of alpha (IL2RA), beta (IL2RB) and the common gamma chain (IL2RG). As the name indicates, this receptor interacts with pleiotropic cytokine called Interleukin-2, which effect is mainly important for immune homeostasis.

Follicular helper T cells (also known as follicular B helper T cells and abbreviated as TFH), are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the periphery within B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5. Upon cellular interaction and cross-signaling with their cognate follicular (Fo B) B cells, TFH cells trigger the formation and maintenance of germinal centers through the expression of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and the secretion of IL-21 and IL-4. TFH cells also migrate from T cell zones into these seeded germinal centers, predominantly composed of rapidly dividing B cells mutating their Ig genes. Within germinal centers, TFH cells play a critical role in mediating the selection and survival of B cells that go on to differentiate either into long-lived plasma cells capable of producing high affinity antibodies against foreign antigen, or germinal center-dependent memory B cells capable of quick immune re-activation in the future if ever the same antigen is re-encountered. TFH cells are also thought to facilitate negative selection of potentially autoimmune-causing mutated B cells in the germinal center. However, the biomechanisms by which TFH cells mediate germinal center tolerance are yet to be fully understood.

MiR-155 is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR155 host gene or MIR155HG. MiR-155 plays a role in various physiological and pathological processes. Exogenous molecular control in vivo of miR-155 expression may inhibit malignant growth, viral infections, and enhance the progression of cardiovascular diseases.
In molecular biology mir-346 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

Regulator of microtubule dynamics protein 3 (RMDN3), more commonly known as Protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51 (PTPIP51), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RMDN3 gene on chromosome 15. This protein contributes to multiple biological functions, including cellular differentiation, proliferation, motility, cytoskeleton formation, and apoptosis, and has been associated with numerous cancers.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.