
Neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) also known as frequenin homolog (Drosophila) (freq) is a protein that is encoded by the FREQ gene in humans. NCS-1 is a member of the neuronal calcium sensor family, a class of EF hand containing calcium-myristoyl-switch proteins.

Peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASK gene. This gene is also known by several other names: CMG 2, calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase 3 and membrane-associated guanylate kinase 2. CASK gene mutations are the cause of XL-ID with or without nystagmus and MICPCH, an X-linked neurological disorder.
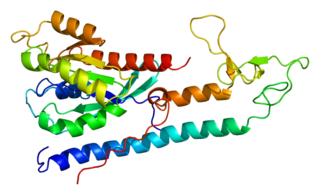
Ras-related protein Rab-3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB3A gene. It is involved in calcium-triggered exocytosis in neurons.

Synaptotagmin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYT1 gene.

43 kDa receptor-associated protein of the synapse (rapsyn) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAPSN gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF1B gene.

SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK2 gene. Two alternative splice variants, encoding distinct isoforms, are reported. Additional splice variants exist but their full-length nature has not been determined.

Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIMS1 gene.

Rabphilin-3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPH3A gene. It contains two C2 domains and binds calcium ions at low micromolar concentration. Rabphilin was shown to regulate neurotransmitter release in hippocampal neurons after neurons had an increased synaptic activity and their release rate was depressed.

V-type proton ATPase subunit G 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP6V1G2 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 5, also known as cysteine string protein or CSP is a protein, that in humans encoded by the DNAJC5 gene. It was first described in 1990.

Sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporter 2, also known as glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A5 gene.

Protein piccolo is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PCLO gene.

Syntaxin-binding protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STXBP5 gene. It is also known as tomosyn, after 友, "friend" in Japanese, for its role as a binding protein.

Double C2-like domain-containing protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DOC2B gene.
The ribbon synapse is a type of neuronal synapse characterized by the presence of an electron-dense structure, the synaptic ribbon, that holds vesicles close to the active zone. It is characterized by a tight vesicle-calcium channel coupling that promotes rapid neurotransmitter release and sustained signal transmission. Ribbon synapses undergo a cycle of exocytosis and endocytosis in response to graded changes of membrane potential. It has been proposed that most ribbon synapses undergo a special type of exocytosis based on coordinated multivesicular release. This interpretation has recently been questioned at the inner hair cell ribbon synapse, where it has been instead proposed that exocytosis is described by uniquantal release shaped by a flickering vesicle fusion pore.

Synapsin I, is the collective name for Synapsin Ia and Synapsin Ib, two nearly identical phosphoproteins that in humans are encoded by the SYN1 gene. In its phosphorylated form, Synapsin I may also be referred to as phosphosynaspin I. Synapsin I is the first of the proteins in the synapsin family of phosphoproteins in the synaptic vesicles present in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Synapsin Ia and Ib are close in length and almost the same in make up, however, Synapsin Ib stops short of the last segment of the C-terminal in the amino acid sequence found in Synapsin Ia.
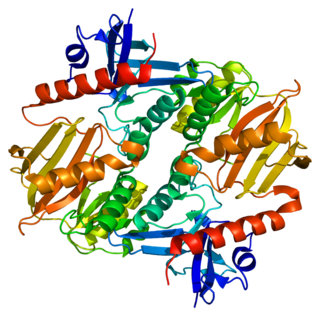
Synapsin II is the collective name for synapsin IIa and synapsin IIb, two nearly identical phosphoproteins in the synapsin family that in humans are encoded by the SYN2 gene. Synapsins associate as endogenous substrates to the surface of synaptic vesicles and act as key modulators in neurotransmitter release across the presynaptic membrane of axonal neurons in the nervous system.

Unc-13 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UNC13A gene.



















