
The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, and PowerPC 970MP are 64-bit PowerPC processors from IBM introduced in 2002. When used in PowerPC-based Macintosh computers, Apple referred to them as the PowerPC G5.
In computer engineering, out-of-order execution is a paradigm used in most high-performance central processing units to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted. In this paradigm, a processor executes instructions in an order governed by the availability of input data and execution units, rather than by their original order in a program. In doing so, the processor can avoid being idle while waiting for the preceding instruction to complete and can, in the meantime, process the next instructions that are able to run immediately and independently.
The POWER1 is a multi-chip CPU developed and fabricated by IBM that implemented the POWER instruction set architecture (ISA). It was originally known as the RISC System/6000 CPU or, when in an abbreviated form, the RS/6000 CPU, before introduction of successors required the original name to be replaced with one that used the same naming scheme (POWERn) as its successors in order to differentiate it from the newer designs.
SPARC64 is a microprocessor developed by HAL Computer Systems and fabricated by Fujitsu. It implements the SPARC V9 instruction set architecture (ISA), the first microprocessor to do so. SPARC64 was HAL's first microprocessor and was the first in the SPARC64 brand. It operates at 101 and 118 MHz. The SPARC64 was used exclusively by Fujitsu in their systems; the first systems, the Fujitsu HALstation Model 330 and Model 350 workstations, were formally announced in September 1995 and were introduced in October 1995, two years late. It was succeeded by the SPARC64 II in 1996.

The POWER4 is a microprocessor developed by International Business Machines (IBM) that implemented the 64-bit PowerPC and PowerPC AS instruction set architectures. Released in 2001, the POWER4 succeeded the POWER3 and RS64 microprocessors, enabling RS/6000 and eServer iSeries models of AS/400 computer servers to run on the same processor, as a step toward converging the two lines. The POWER4 was a multicore microprocessor, with two cores on a single die, the first non-embedded microprocessor to do so. POWER4 Chip was first commercially available multiprocessor chip. The original POWER4 had a clock speed of 1.1 and 1.3 GHz, while an enhanced version, the POWER4+, reached a clock speed of 1.9 GHz. The PowerPC 970 is a derivative of the POWER4.

The POWER3 is a microprocessor, designed and exclusively manufactured by IBM, that implemented the 64-bit version of the PowerPC instruction set architecture (ISA), including all of the optional instructions of the ISA such as instructions present in the POWER2 version of the POWER ISA but not in the PowerPC ISA. It was introduced on 5 October 1998, debuting in the RS/6000 43P Model 260, a high-end graphics workstation. The POWER3 was originally supposed to be called the PowerPC 630 but was renamed, probably to differentiate the server-oriented POWER processors it replaced from the more consumer-oriented 32-bit PowerPCs. The POWER3 was the successor of the P2SC derivative of the POWER2 and completed IBM's long-delayed transition from POWER to PowerPC, which was originally scheduled to conclude in 1995. The POWER3 was used in IBM RS/6000 servers and workstations at 200 MHz. It competed with the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) Alpha 21264 and the Hewlett-Packard (HP) PA-8500.

The CVAX is a microprocessor chipset developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) that implemented the VAX instruction set architecture (ISA). The chipset consisted of the CVAX 78034 CPU, CFPA floating-point accelerator, CVAX clock chip, and the associated support chips, the CVAX System Support Chip (CSSC), CVAX Memory Controller (CMCTL), and CVAX Q-Bus Interface Chip (CQBIC).

The R10000, code-named "T5", is a RISC microprocessor implementation of the MIPS IV instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by MIPS Technologies, Inc. (MTI), then a division of Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI). The chief designers are Chris Rowen and Kenneth C. Yeager. The R10000 microarchitecture is known as ANDES, an abbreviation for Architecture with Non-sequential Dynamic Execution Scheduling. The R10000 largely replaces the R8000 in the high-end and the R4400 elsewhere. MTI was a fabless semiconductor company; the R10000 was fabricated by NEC and Toshiba. Previous fabricators of MIPS microprocessors such as Integrated Device Technology (IDT) and three others did not fabricate the R10000 as it was more expensive to do so than the R4000 and R4400.

The R4000 is a microprocessor developed by MIPS Computer Systems that implements the MIPS III instruction set architecture (ISA). Officially announced on 1 October 1991, it was one of the first 64-bit microprocessors and the first MIPS III implementation. In the early 1990s, when RISC microprocessors were expected to replace CISC microprocessors such as the Intel i486, the R4000 was selected to be the microprocessor of the Advanced Computing Environment (ACE), an industry standard that intended to define a common RISC platform. ACE ultimately failed for a number of reasons, but the R4000 found success in the workstation and server markets.
The R8000 is a microprocessor chipset developed by MIPS Technologies, Inc. (MTI), Toshiba, and Weitek. It was the first implementation of the MIPS IV instruction set architecture. The R8000 is also known as the TFP, for Tremendous Floating-Point, its name during development.
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC processor and then keep designing general purpose PowerPC processors for personal computers. The first incarnation became the PowerPC 601 in 1993, and the second generation soon followed with the PowerPC 603, PowerPC 604 and the 64-bit PowerPC 620.

The Alpha 21064 is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation that implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). It was introduced as the DECchip 21064 before it was renamed in 1994. The 21064 is also known by its code name, EV4. It was announced in February 1992 with volume availability in September 1992. The 21064 was the first commercial implementation of the Alpha ISA, and the first microprocessor from Digital to be available commercially. It was succeeded by a derivative, the Alpha 21064A in October 1993. This last version was replaced by the Alpha 21164 in 1995.

The Alpha 21164, also known by its code name, EV5, is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation that implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA). It was introduced in January 1995, succeeding the Alpha 21064A as Digital's flagship microprocessor. It was succeeded by the Alpha 21264 in 1998.
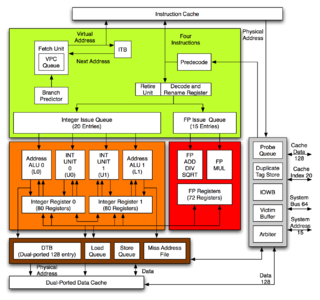
The Alpha 21264 is a Digital Equipment Corporation RISC microprocessor launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA).

The PA-8000 (PCX-U), code-named Onyx, is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Hewlett-Packard (HP) that implemented the PA-RISC 2.0 instruction set architecture (ISA). It was a completely new design with no circuitry derived from previous PA-RISC microprocessors. The PA-8000 was introduced on 2 November 1995 when shipments began to members of the Precision RISC Organization (PRO). It was used exclusively by PRO members and was not sold on the merchant market. All follow-on PA-8x00 processors are based on the basic PA-8000 processor core.
The IBM A2 is an open source massively multicore capable and multithreaded 64-bit Power ISA processor core designed by IBM using the Power ISA v.2.06 specification. Versions of processors based on the A2 core range from a 2.3 GHz version with 16 cores consuming 65 W to a less powerful, four core version, consuming 20 W at 1.4 GHz.

Fermi is the codename for a graphics processing unit (GPU) microarchitecture developed by Nvidia, first released to retail in April 2010, as the successor to the Tesla microarchitecture. It was the primary microarchitecture used in the GeForce 400 series and GeForce 500 series. It was followed by Kepler, and used alongside Kepler in the GeForce 600 series, GeForce 700 series, and GeForce 800 series, in the latter two only in mobile GPUs. In the workstation market, Fermi found use in the Quadro x000 series, Quadro NVS models, as well as in Nvidia Tesla computing modules. All desktop Fermi GPUs were manufactured in 40nm, mobile Fermi GPUs in 40nm and 28nm. Fermi is the oldest microarchitecture from NVIDIA that received support for the Microsoft's rendering API Direct3D 12 feature_level 11.
IBM POWER is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by IBM. The name is an acronym for Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC.
IBM Power microprocessors are designed and sold by IBM for servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Bull and Hitachi.
The Power Processing Element (PPE) comprises a Power Processing Unit (PPU) and a 512 KB L2 cache. In most instances the PPU is used in a PPE. The PPU is a 64-bit dual-threaded in-order PowerPC 2.02 microprocessor core designed by IBM for use primarily in the game consoles PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360, but has also found applications in high performance computing in supercomputers such as the record setting IBM Roadrunner.











