Transport in Bulgaria is dominated by road transport, despite nearly half of all paved roads belonging to the lowest category of roads. As of December 2015, the country had 829 kilometers of highways.
Bunavad was the first national airline of Bulgaria. The airline was conceived in late 1926, operated scheduled services between major Bulgarian cities from October 1927 and closed in 1930.

Dimitrovgrad alternatively Caribrod is a town and municipality located in the Pirot District of southeastern Serbia. According to 2011 census, the municipality of Dimitrovgrad has a population of 10,118 people and the town 6,278.

Yugoslav Railways, with standard acronym JŽ, was the state railway company of Yugoslavia, operational from the 1920s to the 1990s, with its final incarnation transferring to Serbia, the successor of JZ is the joint stock company of the Serbian Railways in 2006.

Makedonski Železnici is the public enterprise for railways in the Republic of North Macedonia. Railway operations are run by Železnici na Republika Severna Makedonija Transport and the infrastructure maintained by Makedonski Železnici Infrastruktura.
The Bulgarian State Railways are Bulgaria's state railway company and the largest railway carrier in the country, established as an entity in 1888. The company's headquarters are located in the capital Sofia. Since the 1990s the BDŽ has met serious competition from automotive transport. Up to 2002 the company also owned/managed the state railway infrastructure in the country, when according to EU regulations a new state company, the National Railway Infrastructure Company, was founded and became the owner of the infrastructure.

United Bulgarian Bank (UBB) is one of the leading Bulgarian commercial banks. It is the first and largest banking consolidation project in Bulgaria, accomplished through the merger of 22 state-owned commercial banks throughout the country. UBB was established on 30 September 1992. The Bank manages assets, worth approximately BGN 6.6 billion and renders services to its clients via nearly 200 branches and banking structures throughout the country. The core business of UBB is being supported through the activity of its subsidiaries, UBB Asset Management, UBB Factoring and UBB Insurance Broker.

Serbian Railways is a Serbian engineering and technical consulting company based in Belgrade, Serbia.

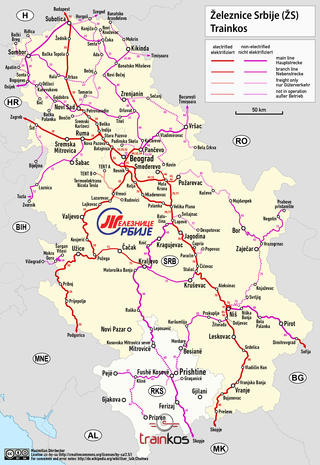
Trainkos, is the national railway company of Kosovo. It was originally formed as the Kosovo Railways J.S.C UNMIK Railways from the lines of the former Yugoslav Railways that lie on Kosovar territory. In 2011, the company was split into two public companies called Trainkos and Infrakos, the latter responsible for rail maintenance.

The Corridor X is one of the pan-European corridors. It runs between Salzburg in Austria and Thessaloniki in Greece. The corridor passes through Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia, North Macedonia, and Greece. It has four branches: Xa, Xb, Xc, and Xd.

The State Railways of the Republic of Turkey, abbreviated as TCDD, is a government-owned national railway company responsible with the ownership and maintenance of railway infrastructure in Turkey, as well as the planning and construction of new lines. TCDD was formed on 4 June 1929 as part of the nationalisation of railways in Turkey.

The Chemins de fer Orientaux was an Ottoman railway company operating in Rumelia and later European Turkey, from 1870 to 1937. The CO was one of the five pioneer railways in the Ottoman Empire and built the main trunk line in the Balkans. Between 1889 and 1937, the railway hosted the world-famous Orient Express.

The Bosphorus Express, also known as the Trans Balkan Express, is an international passenger train running between Istanbul, Turkey and Bucharest, Romania. It runs together with the Istanbul-Sofia Express as far as Dimitrovgrad upon entering Bulgaria, where the latter continues to Sofia. The train is jointly operated by three national railways: the TCDD Taşımacılık (TCDD), the Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ), and the Romanian State Railways (CFR). The train serves several important cities including Istanbul, Edirne, Stara Zagora, and Bucharest.

The Septemvri–Dobrinishte narrow-gauge line is the only operating 760 mm narrow-gauge line in Bulgaria. It is operated by Bulgarian State Railways (BDŽ). The line is actively used with four passenger trains running the length of the line in each direction per day. The journey takes five hours through the valleys and gorges between Rila, Pirin and Rhodopes.

The Corridor VIII is one of the Pan-European corridors. It comprises both road and rail routes. Both commence on the Italian Adriatic coast at Bari or Brindisi, with a ferry crossing to Durrës in Albania. From there the routes cross the southern Balkans into Bulgaria and thence to Varna, on the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. The road corridor follows the route: Tirana/Durrës/Vlorë – Elbasan – Skopje – Pernik – Sofia – Plovdiv – Burgas – Varna. Although as yet incomplete, it is broadly paralleled by the rail route: Durrës/Vlorë-Lin-Radožda-Kičevo-Skopje-Kumanovo-Beljakovtse-Kriva Palanka-Gyueševo-Sofija-Burgas-Varna.

The National Railway Infrastructure Company is Bulgaria's state railway infrastructure company, established as an entity on 1 January 2002. The company's headquarters are located in the capital city Sofia near Sofia Central Station. It is the owner and operator of most of the country's rail lines.

The Alexandroupoli–Svilengrad railway is a 178.5 kilometres (110.9 mi) long railway connecting the port of Alexandroupoli in Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, Greece with Svilengrad in Bulgaria, via the village of Ormenio. Despite its name, as of 2020 there is only passenger service on the section on Greek territory, between Alexandroupoli and Ormenio, as the international services to Sofia and Istanbul have been suspended as of 2011.

Bulgarian State Railways locomotives 142-150 provided motive power on Bulgaria's first railway, opened in 1866 to connect Ruse on the River Danube with Varna on the Black Sea. Ordered from England shortly after the opening of the railway, they were intended as mixed-traffic locomotives to supplement the line's original locomotive fleet. They were powerful 2-cylinder 0-6-0 locomotives with 6-wheeled tenders.