
The Rajendra Vilas is a palace-hotel atop Chamundi Hills in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It is now closed and in a state of neglect and can only be visited with prior permission. [1] [2]

The Rajendra Vilas is a palace-hotel atop Chamundi Hills in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It is now closed and in a state of neglect and can only be visited with prior permission. [1] [2]
The Rajendra Vilas palace is located on top of Chamundi Hills, at an elevation of nearly 300 metres. An older building existed at the location dating back to 1822, which was used as a summer palace by the Wodeyars of Mysore. Maharaja Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV was taught philosophy and English in this building. The conception of a much larger building was initiated in the 1920s. The palace was commissioned by Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV, and was completed in 1938–39. However, its plans were scaled down due to financial issues, and the building was not constructed as elaborately as planned.
After Indian independence, the state government of Karnataka considered the building as a heritage structure. However, it remained as a possession of Srikantha Datta Narasimharaja Wodeyar, the descendant of the Wodeyars, who converted it into a palace hotel. In the 1980s, it was closed due to labour problems, during which time the palace was not open to the public. In the early 2000s, renovation work began on the palace. In May 2004, it was announced that 'ITC welcome group' would take over management of the hotel. In the same year, Srikantadatta Narasimharaja Wodeyar contested elections in India for a Lok Sabha seat (Member of Parliament). Rajendra Vilas palace was included in the mandatory declaration of his immovable property assets, and declared to be worth Rs 60 million. In Sep 2006, during Dasara, a powerful beam of light that is visible up to 30 km was installed on the premises of Rajendra Vilas Palace atop the hills, to add to the festivities of the city. The renovation work was expected to be completed by December 2006, but it was not completed. Currently it remains as a partial ruin.
It has four chhatris and a central dome. The chhatris are in Rajasthani style, with the other stylistic elements being distinctly Indo-Sarcenic. The central dome rests on a high neck in the style of Mysore Palace. The central tower is ribbed and showcases a lantern. A semi-circular verandah to the north provides a panoramic view of the city. The first floor opens to spacious terraces adjoining the chhatris. The palace-hotel has about 25 suites.

Mysore, officially Mysuru, is the second-most populous city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the Kingdom of Mysore for almost six centuries. Known for its heritage structures, palaces, and its culture, Mysore has been called the "City of Palaces", the "Heritage City", and the "Cultural Capital of Karnataka". It is one of the cleanest cities in India according to the Swachh Survekshan.

The Wadiyar dynasty, also referred to as the Wadiyars of Mysore, is a late-medieval Indian royal family of former maharajas of Mysore from the Urs clan originally based in Mysore city.
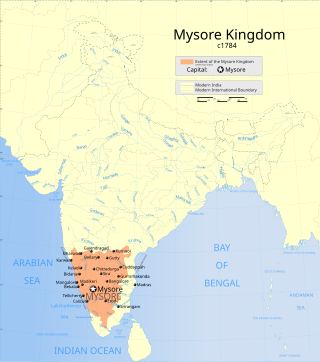
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted substantially throughout the kingdom's lifetime. While originally a feudal vassal under the Vijayanagara Empire, it became a princely state in British India from 1799 to 1947, marked in-between by major political changes.
Vilas may refer to:

The Chamundi Hills are located 13 km east of Mysore, Karnataka, India. The name comes from the Chamundeshwari Temple at the peak. The average elevation is 1,060 metres (3,480 ft).

Chamarajendra Wadiyar X was the twenty-third Maharaja of Mysore between 1868 and 1894.

Mysore Palace, also known as Amba Vilas Palace, is a historical palace and a royal residence. It is located in Mysore, Karnataka, India. It used to be the official residence of the Wadiyar dynasty and the seat of the Kingdom of Mysore. The palace is in the centre of Mysore, and faces the Chamundi Hills eastward. Mysore is commonly described as the 'City of the Palaces', and there are seven palaces including this one. However, the Mysore Palace refers specifically to the one within the new fort.

Mysore district, officially Mysuru district, is an administrative district located in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Mysore division. Chamarajanagar District was carved out of the original larger Mysore District in the year 1998. The district is bounded by Chamrajanagar district to the southeast, Mandya district to the east and northeast, Kerala state to the south, Kodagu district to the west, and Hassan district to the north.

Kanteerava Narasimharaja Wadiyar was the heir apparent of the Kingdom of Mysore from 1895 until his death in 1940, during the reign of his brother, Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV. Krishnaraja Wadiyar died less than six months after Narasimharaja Wadiyar did.

The Lalitha Mahal, now renamed Lalitha Mahal Palace Hotel, is a luxury hotel located in a former royal residence, and the second largest palace in the southern Indian city of Mysore, Karnataka, after the Mysore Palace. It is located near the Chamundi Hills, east of the city. The palace was built in 1921 by Maharaja Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV for the exclusive stay of the Governor-General of India.

The Daly Memorial Hall, is a heritage building located in Bangalore, Karnataka that houses the Mythic Society. The Mythic society, founded in 1909, is a pioneering institution of Catholic-Indic studies in South India. Daly Memorial Hall, built at a cost of INR 24,783, was inaugurated on 25 July 1917 by the Kanteerava Narasimharaja Wadiyar (the Yuvaraja of Mysore. The Hall is named after Sir Hugh Daly, who served as the Resident of Mysore State and Chief Commissioner of Coorg.

Jayalakshmi Vilas Mansion is a heritage building in Mysore.
Chamarajendra Academy of Visual Arts (CAVA) is a visual art school in Mysore, in the state of Karnataka in India. The academy is affiliated to the University of Mysore and offers courses in drawing, painting, sculpture, graphics, applied arts, photography and photo-journalism and art history. CAVA awards degrees in Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) and Master of Fine Arts (MFA).

Mysore is a city in the state of Karnataka, India. It is known as the cultural capital of Karnataka. Mysore was the capital of the Wodeyar kings who ruled over the Mysore Kingdom for many centuries. Wodeyars were great patrons of art and music and have contributed significantly to make Mysore a cultural centre. Mysore is well known for its palaces, museums and art galleries and the festivities that take place here during the period of Dasara attract a worldwide audience. Mysore has also lent its name to popular dishes like Mysore Masala Dosa and Mysore Pak. Mysore is also the origin of the popular silk sari known as Mysore silk sari and has also given rise to a popular form of painting known as Mysore painting.

The Kingdom of Mysore (1399–1950) was founded by Yaduraya in 1399 as a feudatory of the Vijayanagara Empire and became an independent kingdom in the early 17th century, after the decline of the Vijayanagara Empire. Many musicians and composers have presumably adorned the courts of the Mysore kings from Yaduraya's time, furthering the Dakshinadi school of music that had developed in earlier centuries. However, records are only available from the time of King Ranadheera Kanteerava Narasaraja Wodeyar (1638). Musical treatises surviving from this time, though, provide ample information on the music, musical instruments, the types of compositions, the raga (melodies) and the tala (rhythms) used. Though all the Mysore kings patronised music, the golden age of Carnatic music was considered to be during the reigns of Kings Krishnaraja Wodeyar III (1794–1868), Chamaraja Wodeyar IX (1862–1894), Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV (1884–1940) and Jaya Chamaraja Wodeyar (1919–1974). The reign of Krishnaraja Wodeyar IV is regarded as particularly important in musical terms.
The antiquity of architecture of Karnataka can be traced to its southern Neolithic and early Iron Age, Having witnessed the architectural ideological and utilitarian transformation from shelter- ritual- religion. Here the nomenclature 'Architecture' is as old as c.2000 B.C.E. The upper or late Neolithic people in order to make their shelters by their own they constructed huts made of wattle and doab, that were buttressed by stone boulders, presumably having conical roof resting on the bamboo or wooden posts into red murram or paved granite chips as revealed in archaeological excavations in sites like Brhamagiri, Sanganakallu, Tekkalakota, Piklihal. Megaliths are the dominant archaeological evidence of the early Iron Age. There are more than 2000 early Iron Age burial sites on record, who laid the foundation for a high non-perishable architecture in the form of various distinct architectural styles of stone-built burials, which are ritualistic in its character. The active religious architecture is evident 345 with that of the Kadamba Dynasty. Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India originally known as the State of Mysore. Over the centuries, architectural monuments within the region displayed a diversity of influences, often relaying much about the artistic trends of the rulers of twelve different dynasties. Its architecture ranges dramatically from majestic monolith, such as the Gomateshwara, to Hindu and Jain places of worship, ruins of ancient cities, mausoleums and palaces of different architectural hue. Mysore Kingdom (Wodeyar) rule has also given an architectural master structure in the St. Philomena's Church at Mysore which was completed in 1956, in addition to many Dravidian style architectural temples. Two of the monuments are listed under the UNESCO World Heritage List of 22 cultural monuments in India. Styles of Indo-Saracenic, Renaissance, Corinthian, Hindu, Indo-Greek and Indo-British style palaces were built in Mysore, the city of palaces. Sikh architecture at Bidar (1512) and also in Bangalore in 1956 can also be cited as having an impact on the architectural composition of the state.

The Mysore Dasara 2013 is the 403rd edition of the annual royal festive gala event, a show of pomp and tradition that is held in the Mysore city in Karnataka, India for 10 days. The festival is called the Navaratri (meaning nine nights or Dussehra or Vijayadashami which conforms to the bright half of the month of Ashvin, from pratipadathithi to navamithithi in the Hindu calendar corresponding to 5 to 13 October during 2013. The festival is also called Nada Habba in Kannada language. The first day of the nine-day festivity started on 5 October with the traditional and religious special puja performed to Goddess Chamundeshwari in the Chamundi Temple on top of the Chamundi Hill, which forms the backdrop to the city; the temple was beautifully decorated with flowers and tourist from Gujarat, Rajasthan and other states enthralled the audience with their bhajan singing. On this occasion, floral tribute wa offered to the goddess by Jnanpith Award winner Chandrashekhara Kambara and festivities will continue for ten days. The ninth day of the festival is a special event called the Mahanavami when the royal sword is worshipped and taken in a procession of elephants, camels and horses. The festival concludes on 14 October on the dashami day with the grand finale of Jambusavari with the idol of Chamundeshawri set in a golden howdah mounted on a richly caparisoned elephant. The procession is taken through the streets of the city and ends in the Banni Mantap where, in the evening, a torch light parade is held. Symbolically, the festival represents the victory of good over evil.

The group of temples at the Amba Vilas Palace in Mysore were constructed during various periods by the kings of the Wodeyar dynasty who ruled the Kingdom of Mysore from about 1399 to 1947 A.D. These temples are protected monuments under the Karnataka state division of the Archaeological Survey of India.

Chamarajapuram is one of the earliest settlements and localities in Mysore, Karnataka, India, located in the centre of Mysore city. Initially an agraharam inhabited by the Mysore nobility, parts of it were later allotted other local dwellers as well.