The black-browed albatross, also known as the black-browed mollymawk, is a large seabird of the albatross family Diomedeidae; it is the most widespread and common member of its family.

Anyphaenidae is a family of araneomorph spiders, sometimes called anyphaenid sac spiders. They are distinguished from the sac spiders of the family Clubionidae and other spiders by having the abdominal spiracle placed one third to one half of the way anterior to the spinnerets toward the epigastric furrow on the underside of the abdomen. In most spiders the spiracle is just anterior to the spinnerets. Like clubionids, anyphaenids have eight eyes arranged in two rows, conical anterior spinnerets and are wandering predators that build silken retreats, or sacs, usually on plant terminals, between leaves, under bark or under rocks. There are more than 600 species in over 50 genera worldwide.
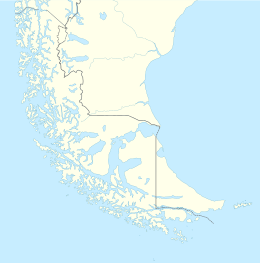
The extreme points of South America are the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. The continent's southernmost point is often said to be Cape Horn, but Águila Islet of the Diego Ramírez Islands lies further south.

The Diego Ramírez Islands are a small group of subantarctic islands located in the southernmost extreme of Chile.

Antártica Chilena Province is the southernmost and one of four provinces in Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region (XII). The capital is Puerto Williams. The province comprises the extreme southern part of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, the islands south and west of Isla Grande, and Chile's claims in Antarctica. The province is administratively divided into two communes (comunas): Cabo de Hornos, located at the southern tip of South America, and Antártica, a wedge-shaped claim of Antarctica, which is not internationally recognized. Its total area of 1,265,853.7 km2 (488,749 sq mi) makes it almost twice as large as all other provinces of Chile combined.
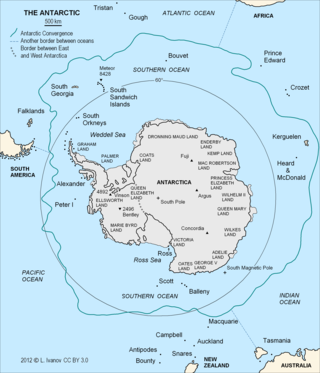
The Antarctic Convergence or Antarctic Polar Front is a marine belt encircling Antarctica, varying in latitude seasonally, where cold, northward-flowing Antarctic waters meet the relatively warmer waters of the sub-Antarctic. Antarctic waters predominantly sink beneath the warmer subantarctic waters, while associated zones of mixing and upwelling create a zone very high in marine productivity, especially for Antarctic krill.

Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America, Cape Horn marks the northern boundary of the Drake Passage and marks where the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans meet.

The Hermite Islands are the islands Hermite, Herschel, Deceit and Hornos as well as the islets Maxwell, Jerdán, Arrecife, Chanticleer, Hall, Deceit (islet), and Hasse at almost the southernmost end of South America. The smallest and southernmost of the major islands is Hornos Island, the location of Cape Horn. The islands are located south of the Wollaston Islands and separated from them by the Franklin Channel. The islets Terhalten, Sesambre, Evout and Barnevelt are located easterly and are not considered part of the Hermite islands.

The García de Nodal expedition was chartered in 1619 by King Philip III of Spain to reconnoiter the passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, rounding Cape Horn, south of Tierra del Fuego, just discovered by the Dutch merchants Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten. It was a successful expedition, as all goals were reached. In addition, neither lives nor ships were lost and the whole was done in a small amount of time.

Hornos Island is a Chilean island at the southern tip of South America. The island is mostly known for being the location of Cape Horn. It is generally considered South America's southernmost island, but the Diego Ramírez Islands are farther south. The island is one of the Hermite Islands, part of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago.

The Wollaston Islands are a group of islands in Chile south of Navarino Island and north of Cape Horn and east of the Hoste Island. The islands are Grevy, Bayly, Wollaston and Freycinet, as well as the islets Dédalo, Surgidero, Diana, Otarie, Middle and Adriana. The islands are part of Cabo de Hornos National Park.
Diego de Almagro Island, formerly known as Cambridge Island, is an island in the Magallanes Region, Chile. It is located South-West of Hanover Island. It is named after Diego de Almagro.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Chile:

Tricontinental Chile is a geopolitical concept denoting Chile's unique position with its mainland in South America, Easter Island in Oceania (Polynesia) and the Chilean Antarctic Territory in Antarctica.

Isla Bartolomé is an uninhabited subantarctic island. Administratively it belongs to Chile.

Isla Gonzalo is a subantarctic island, uninhabited except for a weather and research station operated by the Chilean Navy. With an area of 38 hectares, it is the second largest of the Chilean Diego Ramírez Archipelago after Isla Bartolomé. The archipelago lies in the Drake Passage between the continents of South America and Antarctica. It is an important breeding site for black-browed and grey-headed albatrosses, as well as for southern giant petrels.

The landmass known as Patagonia hosts a series of archipelagoes, all of them located on its western and southern coast. These archipelagoes, with the exception of Tierra del Fuego, lie in Chile and in the Pacific Ocean, covering about one third of Chile's coast.

Nelson Strait is a channel in the Chilean Archipelago. It is located in Magallanes y Antártica Chilena Region of Chilean Patagonia.

Diego Alfonso Valdés Contreras is a Chilean professional footballer who plays as an attacking midfielder for Liga MX club América and the Chile national team.