
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniotic, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all tetrapods excluding the amniotes. All extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass Lissamphibia, with three living orders: Anura, Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems. Their life cycle typically starts out as aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this.

A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura. The oldest fossil "proto-frog" Triadobatrachus is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history.

The common frog or grass frog, also known as the European common frog, European common brown frog, European grass frog, European Holarctic true frog, European pond frog or European brown frog, is a semi-aquatic amphibian of the family Ranidae, found throughout much of Europe as far north as Scandinavia and as far east as the Urals, except for most of the Iberian Peninsula, southern Italy, and the southern Balkans. The farthest west it can be found is Ireland. It is also found in Asia, and eastward to Japan. The nominative, and most common, subspecies Rana temporaria temporaria is a largely terrestrial frog native to Europe. It is distributed throughout northern Europe and can be found in Ireland, the Isle of Lewis and as far east as Japan.

Confuciusornis is a genus of basal crow-sized avialan from the Early Cretaceous Period of the Yixian and Jiufotang Formations of China, dating from 125 to 120 million years ago. Like modern birds, Confuciusornis had a toothless beak, but closer and later relatives of modern birds such as Hesperornis and Ichthyornis were toothed, indicating that the loss of teeth occurred convergently in Confuciusornis and living birds. It was thought to be the oldest known bird to have a beak, though this title now belongs to an earlier relative Eoconfuciusornis. It was named after the Chinese moral philosopher Confucius. Confuciusornis is one of the most abundant vertebrates found in the Yixian Formation, and several hundred complete specimens have been found.

Rana is a genus of frogs commonly known as the Holarctic true frogs, pond frogs or brown frogs. Members of this genus are found through much of Eurasia and western North America. Many other genera were formerly included here. These true frogs are usually largish species characterized by their slim waists and wrinkled skin; many have thin ridges running along their backs, but they generally lack "warts" as in typical toads. They are excellent jumpers due to their long, slender legs. The typical webbing found on their hind feet allows for easy movement through water. Coloration is mostly greens and browns above, with darker and yellowish spots.

Papurana daemeli is a species of "true frog", family Ranidae. It is found in New Guinea, northern Australia, and some smaller islands. It is the only ranid frog found in Australia. In Australia, the species is restricted to the rainforest of northern Queensland and the eastern border of Arnhem Land, in the Northern Territory. In Australia, it is usually known as wood frog or sometimes as water frog. Other vernacular names are Australian wood frog, Australian bullfrog, and Arnhem rana.

Agalychnis callidryas, commonly known as the red-eyed tree frog or red-eyed leaf frog, is a species of frog in the subfamily Phyllomedusinae. It is one of the most recognizable frogs. It is native to forests from Central America to north-western South America. This species is known for its bright coloration, namely its vibrant green body with blue and yellow stripes on the side. It has a white underside, brightly red and orange colored feet, and is named after its distinctive bright red eyes. One particular and special feature of the frogs coloration is its exceptional high reflectance in the near-

The agile frog is a European frog in the genus Rana of the true frog family, Ranidae.

The moor frog is a slim, reddish-brown, semiaquatic amphibian native to Europe and Asia. Moor frogs are known for their ability to freeze solid and survive thawing. The frog makes use of various cryoprotectants i.e. antifreeze that decrease its internal freezing temperature. The species is distributed over a large range, covering a significant portion of Eurasia. Male moor frogs are known to turn blue temporarily during the height of mating season. This coloration is assumed to signal a mate's fitness. Moor frogs typically mate through multimale amplexus a form of polyandry.

The Italian agile frog, also known as Lataste's frog, is a species of frog in the family Ranidae. The species is native to southern Europe, primarily found in the Po River Basin of Italy. It is one of the most endangered amphibian species in Europe, with its populations declining sharply in recent years, and has been the focus of multiple conservation plans.

The pig frog is a species of aquatic frog found in the Southeastern United States, from South Carolina to Texas. Some sources also refer to it as the lagoon frog or the southern bullfrog.

The Oregon spotted frog is a member of the frog family Ranidae of order Anura. It is a medium-sized aquatic frog endemic to the Pacific Northwest and historically well distributed in the Puget Trough/Willamette Valley province and the Cascade Mountains of south-central Washington and Oregon. It is relatively rare within its range and is listed globally as vulnerable.
Limnonectes shompenorum is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is found in Great Nicobar Island (India), its type locality, and in western Sumatra (Indonesia). It is similar to Limnonectes macrodon. The name refers to Shompen people, the indigenous people of the interior of Great Nicobar Island.

The Cascades frog is a species of frog in the family Ranidae found in the Pacific Northwest, mainly in the Cascade Range and Olympic Mountains.
Minervarya charlesdarwini is a species of frogs in the family Dicroglossidae. It is endemic to the Andaman Islands, India, and is known from the South Andaman Island, Long Island, and North Andaman Island.

The river frog is a species of aquatic frog in the family Ranidae. It is endemic to the southeastern United States. Its natural habitats are temperate rivers, swamps, freshwater lakes and freshwater marshes. It is threatened by habitat loss.
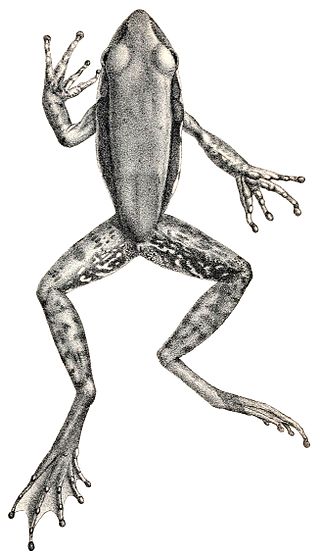
Papurana kreffti is a species of true frog, family Ranidae. It is native to New Ireland and Buka Island and the Solomon Islands. The specific name kreffti honours Gerard Krefft, a German adventurer who settled in Australia and became there to be regarded as the father of Australian herpetology. Common names San Cristoval frog and San Cristobal treefrog have been coined for it.

Mercurana is a genus of arboreal frogs belonging to the family Rhacophoridae. The genus was named from the only known species Mercurana myristicapalustris, which was described in 2013 from the Western Ghats of Kerala, India. The generic name was derived from and given as a tribute to Freddie Mercury, the late vocalist of the British rock band Queen, in combination with the Latin name for "frog". The frog is different from other related frogs in that it has extensively webbed toes, lives only in swampy lowlands, and lays its eggs on mud with which it carefully mixes leaf litter.

Avimaia is a genus of fossil birds of the Enantiornithes clade that lived about 115 million years ago in Northwest China. The only known species is A. schweitzerae. The holotype fossil of the bird was found in the Xiagou Formation, and is noted as the first discovered fossil bird with an unlaid egg. Abnormalities, including egg binding in which the egg becomes stuck within the body of the bird causing death, were found in the egg suggesting that the preserved egg may have caused this bird's demise. Egg binding is a serious and lethal condition that is fairly common in small birds undergoing stress.
Yuanjiawaornis is an extinct genus of large enantiornithean bird known from the early Cretaceous of present-day China. It is monotypic, with only type species Y. virisosus known.
















