
Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, 450 kilometres (240 nmi) from continental Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway and, along with Bouvet Island and Queen Maud Land, composes one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and Subantarctic. The island measures approximately 11 by 19 kilometres, with an area of 156 km2 (60 sq mi); its highest point is the ultra-prominent, 1,640-metre-tall (5,380 ft) Lars Christensen Peak. Nearly all the island is covered by a glacier, and it is surrounded most of the year by pack ice, making it inaccessible during these times. There is little vertebrate animal life on the island, apart from some seabirds and seals.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

Joinville Island is the largest island of the Joinville Island group, about 40 nautical miles long in an east–west direction and 12 nautical miles wide, lying off the northeastern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by the Antarctic Sound.
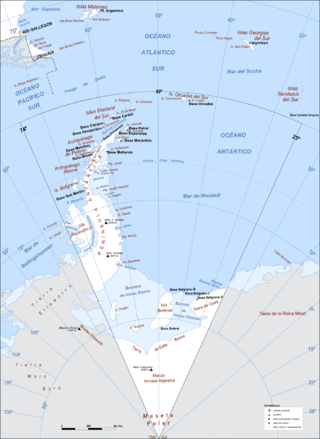
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.
Mikkelsen Bay is a bay, 15 nautical miles wide at its mouth and indenting 10 nautical miles, entered between Bertrand Ice Piedmont and Cape Berteaux along the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.
Northeast Glacier is a steep, heavily crevassed glacier, 13 nautical miles long and 5 nautical miles wide at its mouth, which flows from McLeod Hill westward and then south-westwards into Marguerite Bay between the Debenham Islands and Roman Four Promontory, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

Jenny Island or Isla Juanita is a rocky island 3.7 km (2 nmi) long which rises to 500 m (1,600 ft), lying 5.6 km (3 nmi) east of Cape Alexandra, the southeastern extremity of Adelaide Island, in northern Marguerite Bay. Jenny Island is located at 67°44′S68°24′W.

The French Antarctic Expedition is any of several French expeditions in Antarctica.

The Arctowski Peninsula is a peninsula, 15 nautical miles long in a north-south direction, lying between Andvord Bay and Wilhelmina Bay on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

Robertson Bay is a large, roughly triangular bay that indents the north coast of Victoria Land between Cape Barrow and Cape Adare. Discovered in 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, who named it for Dr. John Robertson, surgeon on HMS Terror.
The Bugge Islands are a small group of ice-covered islands lying close off the front of Wordie Ice Shelf and between 7 and 20 km northwest of Mount Guernsey, off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. They were first seen from the air and photographed by the British Graham Land Expedition in 1936, and later roughly mapped from the photographs. They were observed in 1947 from the Port of Beaumont, Texas by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Finn Ronne, who named these islands for his niece, Ruth Bugge, who supplied woolen clothing from Norway for the RARE. The group was also visited by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition, 1947, which named the islands Isla Aldea, Isla Eleuterio Ramírez, Isla Latorre, after heroes of the naval battle of Iquique.
Cecil Cave is a sea cave which indents the southern part of Cape Ingrid on the west coast of Peter I Island in Antarctica. It was discovered and named by a Norwegian expedition under Eyvind Tofte in the Odd I in January 1927. Tofte and the second mate rowed into the cave in an unsuccessful attempt to land on the island.

Olstad Glacier is a heavily crevassed glacier descending to the west coast of Peter I Island about 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Tofte Glacier. Peter I Island was circumnavigated by the Norwegian whale catcher Odd I in January 1927 and was explored from the Norvegia in February 1929.
Neptune Glacier is a glacier on the east coast of Alexander Island, Antarctica, 12 nautical miles (22 km) long and 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide, flowing east into George VI Sound and the George VI Ice Shelf to the south of Triton Point. Although Neptune Glacier is not located within the mountain range Planet Heights, the glaciers name derives from the mountain range along with many other nearby glaciers named after planets of the Solar System. There are also other nearby landforms named in association with these glaciers. The glacier was first sighted from the air by Lincoln Ellsworth on November 23, 1935, and roughly mapped from photos obtained on that flight by W.L.G. Joerg. The mouth of the glacier was positioned in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE). Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for the planet Neptune following a Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) survey in 1949. The head of the glacier was mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, by Searle of the FIDS in 1960.
Evans Piedmont Glacier is a broad ice sheet occupying the low-lying coastal platform between Tripp Island and Cape Archer in Victoria Land, Antarctica.
Tvistein Pillars are two flat-topped pillar rocks standing 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) southwest of Cape Eva, the north extremity of Peter I Island, off the coast of Antarctica. The rocks were sighted from the Odd I by a Norwegian expedition under Eyvind Tofte in 1927. The name Tvistein was applied by a Norwegian expedition under Nils Larsen which charted the island from the Norvegia in 1929.
Sandefjord Cove is a cove between Cape Ingrid and the terminus of Tofte Glacier on the west side of Peter I Island. A Norwegian expedition under Eyvind Tofte circumnavigated Peter I Island in the Odd I in 1927. In February 1929, the Norvegia under Nils Larsen carried out a series of investigations all around the island, landing on February 2 to hoist the Norwegian flag. The cove was named for Sandefjord, Norway, center of the Norwegian whaling industry.
The Lazarev Coast is a coastal area in Antarctic. It is located on the southern side of the Bellingshausen Sea, on the Peter I Island.

The Ryder Bay Islands Important Bird Area is a 520 ha designated site on the south-east coast of Adelaide Island, Antarctica. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports significant numbers of breeding seabirds, notably south polar skuas. The site encompasses the Léonie Islands lying at the mouth of Ryder Bay, as well as Rothera Point, the eastern headland of the bay.









