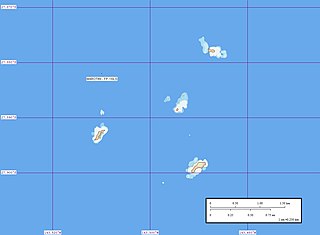
Marotiri is a group of four uninhabited volcanic rocks protruding from the sea, forming the southeastern end of the Austral Islands of French Polynesia. Marotiri is also known as Bass Rocks, maybe according to the name of the European explorer George Bass. Marotiri is very isolated, located about 1,167 km (725 mi) west-south-westward of Pitcairn Island. The closest island is Rapa Iti, 75 km farther northwest, but separated from it by an ocean depth of more than 1,500 meters. The rocks are part of the municipality of Rapa.

The Bass Islands consist primarily of Rapa Iti and Marotiri. They are usually considered to be the southernmost of the Austral Islands, although this classification is more one of geographic and political expediency than because of similarities between them and the rest of the Austral Islands. The Bass Islands, lying several degrees outside the tropics, are the southernmost islands in French Polynesia. Culturally, the Bass Islands appear to have been colonized about the same time as Tahiti and the Marquesas, and the culture and language (Rapan) appear to have diverged about the same time as well, indicating that they developed in relative isolation almost from the time of first settlement.

The United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO) is the UK's agency for providing hydrographic and marine geospatial data to mariners and maritime organisations across the world. The UKHO is a trading fund of the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and is located in Taunton, Somerset, with a workforce of approximately 900 staff.
Mong Chau was an island off South Kwai Chung, in the Rambler Channel, Hong Kong. The island was incorporated in the reclamation for the Chung Container Port. It was located between what is now Container Terminals 3 and 4.

Qelelevu or Nggelelevu is a coral islet in Fiji, a member of the Ringgold Isles archipelago, which forms an outlier to the northern island of Vanua Levu.

Selsey Bill is a headland into the English Channel on the south coast of England in the county of West Sussex.
Cobia Island is an island in Fiji, and is a member of the Ringgold Isles archipelago, which forms an outlier group to the northern island of Vanua Levu. It has a land area of 69.29 hectares. The island is shaped like a crescent moon.
The Australian Hydrographic Service is the Australian Commonwealth Government agency responsible for providing hydrographic services that meet Australia's obligations under the SOLAS convention and the national interest; enabling safe navigation, maritime trade and supporting protection of the marine environment. The agency, headquartered at the Australian Hydrographic Office in Wollongong, New South Wales, is an element of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), and serves both military and civilian functions. The names Australian Hydrographic Service and the Australian Hydrographic Office are commonly abbreviated as AHS or AHO respectively.
Funafala is an islet of Funafuti, Tuvalu that is inhabited by five families, with a church also located on the islet. Funafala means 'the pandanus of Funa', the name of a chief, after whom also the group has been named Funafuti.
Funamanu is a small narrow island that is part of Funafuti atoll in Tuvalu. It is a motu (islet) or very small island and is located 2.6 miles southwestward of the southwest tip of Funafuti. The islet is known to be covered in coconut trees which grow 70 feet high. Te Ava Pua Pua is the passage through the reef, with a least depth of 12.7 metres, between the islets of Funamanu to the north and Fale Fatu to the south, in the southeast of Funafuti atoll.

Cape Spencer is a headland in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south west tip of Yorke Peninsula in the gazetted locality of Inneston. It was named after George Spencer, 2nd Earl Spencer by Matthew Flinders during March 1802. It has been the site of an operating navigation aid since 1950 and has been located within the Innes National Park since 1970.
The Hozier Islands are a Baffin Island offshore island group located in the Arctic Archipelago in the territory of Nunavut's Qikiqtaaluk Region. The uninhabited island group lies in the Labrador Sea, east of Hall Peninsula. The Leybourne Islands are 5 km (3.1 mi) to the north. The largest of the Hozier Islands is about 5 miles (8.0 km) long.

Broughton Island is an island 14 km north-east of Port Stephens on the Mid North Coast of New South Wales, Australia. It is part of the Myall Lakes National Park.(map)

The Meade Islands are a group of two large islands, Zverino Island and Cave Island, the minor Pisanitsa Island, and several rocks lying in the north entrance to McFarlane Strait, off Archar Peninsula, Greenwich Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The surface areas of the first two islands are 48 hectares and 18 hectares. respectively. The area was visited by early 19th-century sealers.

HMS Dart was a schooner of the Royal Navy, built by the Barrow Shipbuilding Company, Barrow and launched in 1877 as Cruiser for Lord Eglinton. She was subsequently purchased by the Colonial Office for the use of Sir Arthur Hamilton Gordon as governor of the Fiji Islands. On his appointment to New Zealand, Cruiser was purchased by the Royal Navy as a tender for the training ship Britannia and the name changed to Dart in March 1882.

Bamburgh Lighthouse was built by Trinity House in 1910 to guide shipping both passing along the Northumberland coast and in the waters around the Farne Islands. It was extensively modernised in 1975 and is now monitored from the Trinity House Operations and Planning Centre in Harwich. Routine maintenance is carried out by a local attendant. It is the most northerly land-based lighthouse in England.

Klimash Passage is the 1.9 km wide passage in the South Shetland Islands between Table Island and Bowler Rocks on the northwest and Morris Rock and Chaos Reef, Aitcho Islands to the SE. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Goritsa Rocks are the two contiguous rocks in Zed Islands off Varna Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands extending 330 m in northwest-southeast direction and 70 m wide. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers.

Nukutula is an island in the Haʻapai Archipelago, belonging to the Kingdom of Tonga. Among neighboring islands are Telekitonga, Kelefesia, Nomuka, Tonumea, Fonoifua.