In North American sports, realignment or releaguing refers to a major change in the competitive structure of one or more existing leagues. The mechanics differ somewhat between amateur and professional sports.
In North American sports, realignment or releaguing refers to a major change in the competitive structure of one or more existing leagues. The mechanics differ somewhat between amateur and professional sports.
In professional sports, this occurs when a league decides to change which teams are in which divisions, usually by creating new divisions. In all of the four major North American sports leagues, all of the teams are grouped into one of two conferences (or leagues in baseball) while each conference/league is further subdivided into divisions. Teams in the same division play each other more regularly than teams in the same conference, and much more often than teams in the other conference. Teams from the same division can form intense rivalries. The top team from a division is always guaranteed a playoff spot and guaranteed a higher seeding in the playoffs. Divisions are usually based on geography, both to minimise travel costs and to encourage regional rivalries.
Divisions are not always static. Sometimes a team may relocate to a new city, and as a result the division may become geographically skewed. For instance, when the Atlanta Thrashers of the NHL became the Winnipeg Jets in 2011, they would have been a team from a northwestern city playing in the Southeast Division, but the NHL chose not to realign at this time, leading to lengthy road trips for the Jets and the other teams in their division.
Also, divisions need to be roughly equal in size to ensure that each team has an equal chance of becoming division champion. When a league introduces new teams in new markets, placing them in the division best suited to their geography may result in more teams in that division, so realignment is necessary. The 1969 baseball realignment coincided with the addition of four teams, whereas its 1994 realignment creating extra divisions in both the American League and the National League came a year after the league added the Colorado Rockies and Florida Marlins. The National Football League realigned to its current eight-division format after a series of team relocations had created geographically skewed divisions.
Sometimes a sport will favor old division rivalries over geographical consistency. The rivalries the Dallas Cowboys of the NFL maintain with the teams of the eastern seaboard, especially the Washington Commanders, meant they were kept in an eastern division after realignment, even though they are geographically dissimilar to their division rivals.
In college sports, the term "realignment" is used to refer to a situation in which large numbers of schools switch their conference affiliation in a short period of time. Especially in the top level of college sports, NCAA Division I, several schools change their affiliations in one or more sports every year. However, the term is usually reserved for situations which affect large numbers of conferences—most notably in 1996, 2005, 2010–2014, and most recently the 2020s.
Each of the four realignment periods below was driven mainly by one or a few conferences:

The Big Ten Conference is the oldest NCAA Division I collegiate athletic conference in the United States. Founded as the Intercollegiate Conference of Faculty Representatives in 1896, it predates the founding of its regulating organization, the NCAA. It is based in the Chicago area in Rosemont, Illinois. For many decades the conference consisted of ten prominent universities, which accounts for its name. On August 2, 2024, the conference expanded to 18 member institutions and 2 affiliate institutions. The conference competes in the NCAA Division I and its football teams compete in the Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS), formerly known as Division I-A, the highest level of NCAA competition in that sport.

The Central Collegiate Hockey Association (CCHA) is a college athletic conference in the Midwestern United States that participates in the NCAA's Division I as a hockey-only conference. The current CCHA began play in the 2021–22 season; a previous incarnation, which the current CCHA recognizes as part of its history, existed from 1971 to 2013. Four of its nine members are located in the state of Michigan, with three in Minnesota and one each in Ohio and South Dakota. It has also had teams located in Alaska, Illinois, Indiana, Missouri and Nebraska over the course of its existence.
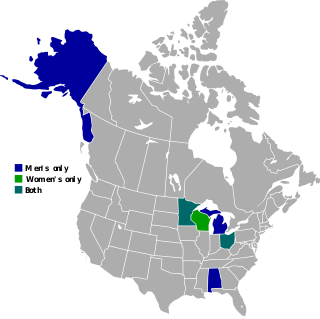
The Western Collegiate Hockey Association (WCHA) is a college ice hockey conference which operates in the Midwestern United States. It participates in the NCAA's Division I as a women's-only conference.

NCAA Division I (D-I) is the highest level of intercollegiate athletics sanctioned by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States, which accepts players globally. D-I schools include the major collegiate athletic powers, with large budgets, more elaborate facilities and more athletic scholarships than Division II and Division III as well as many smaller schools committed to the highest level of intercollegiate competition.

College ice hockey is played principally in the United States and Canada, though leagues exist outside North America.
Don Lucia is an American former ice hockey head coach, who was named as inaugural commissioner of the second Central Collegiate Hockey Association (CCHA) on June 17, 2020. The CCHA, which began play in the 2021–22 season, is a revival of an NCAA Division I men's hockey conference whose original version operated from 1971 to 2013 before folding in the wake of massive conference realignment in the sport.

The Alaska Nanooks men's ice hockey team is a National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I college ice hockey program that represents the University of Alaska Fairbanks. The Nanooks are an independent program. They play at the Carlson Center in Fairbanks, Alaska.

The Bemidji State Beavers are the athletic teams that represent Bemidji State University, located in Bemidji, Minnesota, in NCAA Division II intercollegiate sports. The Beavers compete as members of the Northern Sun Intercollegiate Conference for all 14 varsity sports with the exceptions of men's and women's ice hockey, which respectively compete as members of the Central Collegiate Hockey Association (CCHA) and Western Collegiate Hockey Association (WCHA).

The 2010–2014 NCAA conference realignment was a set of extensive changes in conference membership at all three levels of NCAA competition—Division I, Division II, and Division III—beginning in the 2010–11 academic year.
A superconference is an athletic conference noted for its large number of members, significant revenue generation, and substantial power that it wields in comparison to at least some of its counterpart conferences. The term is typically used in reference to college athletics in the United States. Because superconferences are emergent and not clearly defined, the term is often used in a hypothetical and speculative way, although one definition of American college superconferences posits that they must form from leagues that were Automatic Qualifying (AQ) conferences during the era of the now-defunct Bowl Championship Series, possess a significant multi-network television deal, and at least consider expanding to the "magic number" of 16 members. The term, though used infrequently before 2010, has historical roots in the proposed "Airplane Conference" of 1959, the Metro Conference's 1990 plan to expand to 16 members, the expansion of the Western Athletic Conference (WAC) to 16 members in 1996, and the creation of 12-team, two-division conferences with football championship games by the Southeastern Conference (SEC), Big 12 Conference, and Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC) in the 1990s and 2000s. Since major conference realignment began in 2010, the term has been used to describe the expanding ACC, Big 12, Big Ten, Pac-12, and SEC conferences.

The National Collegiate Hockey Conference (NCHC) is an NCAA men's Division I hockey conference for teams in the Midwestern United States. The league was formed on July 9, 2011 and began playing for the 2013–14 season, the same season that the Big Ten Conference began competition, as a combination of six previous members of the WCHA and two of the CCHA. The league is headquartered in Colorado Springs, Colorado.

The Michigan–Michigan State men's ice hockey rivalry is a college ice hockey rivalry between Michigan Wolverines men's ice hockey and Michigan State Spartans men's ice hockey that is part of the larger intrastate rivalry between the University of Michigan and Michigan State University. It constitutes the most-played rivalry in college hockey. The rivalry between the Spartans and Wolverines notably includes football and basketball rivalries, although it extends to almost all sports and many other forms of achievement.

The 2010–14 Big Ten Conference realignment refers to the Big Ten Conference dealing with several proposed and actual conference expansion and reduction plans among various NCAA conferences and institutions from 2010 to 2014. U.S. sports media credited expansion plans by the Big Ten as being the trigger for a massive wave of conference realignment during this period. While no Big Ten members announced plans to join other conferences, the league announced expansion from 11 members to an ultimate total of 14 full members and one single-sport associate member, with one full member joining in 2011 and the remaining schools joining in July 2014.

The 2013–14 NCAA Division I men's ice hockey season began in October 2013 and ended with the 2014 NCAA Division I Men's Ice Hockey Tournament's championship game in April 2014. This was the 67th season in which an NCAA ice hockey championship was held, and the 120th year overall in which an NCAA school fielded a team.
The 1987–88 NCAA Division I men's ice hockey season began in October 1987 and concluded with the 1988 NCAA Division I Men's Ice Hockey Tournament's championship game on April 2, 1988 at the Olympic Center in Lake Placid, New York. This was the 41st season in which an NCAA ice hockey championship was held and is the 94th year overall where an NCAA school fielded a team.
The 1980–81 NCAA Division I men's ice hockey season began in October 1980 and concluded with the 1981 NCAA Division I Men's Ice Hockey Tournament's championship game on March 28, 1981 at the Duluth Arena in Duluth, Minnesota. This was the 34th season in which an NCAA ice hockey championship was held and is the 87th year overall where an NCAA school fielded a team.

Beginning in the 2021–22 academic year, extensive changes occurred in NCAA conference membership, primarily at the Division I level.