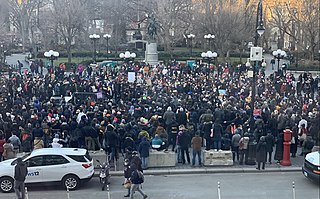Xenophobia is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression which is based on the perception that a conflict exists between an in-group and an out-group and it may manifest itself in suspicion of one group's activities by members of the other group, a desire to eliminate the presence of the group which is the target of suspicion, and fear of losing a national, ethnic, or racial identity.

A massage parlor, or massage parlour, is a place where massage services are provided. Some massage parlors are front organizations for prostitution and the term "massage parlor" has also become a euphemism for a brothel.

Prostitution in Thailand is not itself illegal, but public solicitation for prostitution is prohibited if it is carried out "openly and shamelessly" or "causes nuisance to the public". Due to police corruption and an economic reliance on prostitution dating back to the Vietnam War, it remains a significant presence in the country. It results from poverty, low levels of education and a lack of employment in rural areas. Prostitutes mostly come from the northeastern (Isan) region of Thailand, from ethnic minorities or from neighbouring countries, especially Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos. In 2019, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) estimated the total population of sex workers in Thailand to be 43,000.
Racism in Russia mainly appears in the form of negative attitudes towards non-ethnic Russian citizens, immigrants or tourists and negative actions against them by some Russians. Traditionally, Russian racism includes antisemitism and Tatarophobia, as well as hostility towards the various peoples of the Caucasus, Central Asia, East Asia and Africa.
Prostitution in South Korea is illegal, but according to The Korea Women's Development Institute, the sex trade in Korea was estimated to amount to 14 trillion South Korean won in 2007, roughly 1.6% of the nation's GDP. According to a survey conducted by the Department of Urology at the Korea University College of Medicine in 2015, 23.1% of males and 2.6% of females, aged 18–69, had sexual experience with a prostitute.
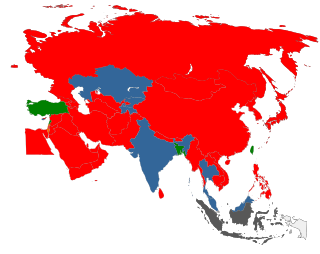
The legality of prostitution in Asia varies by country. There is often a significant difference in Asia between prostitution laws and the practice of prostitution. In 2011, the Asian Commission on AIDS estimated there were 10 million sex workers in Asia and 75 million male customers.

Prostitution is illegal in the vast majority of the United States as a result of state laws rather than federal laws. It is, however, legal in some rural counties within the state of Nevada. Additionally, it is decriminalized to sell sex in the state of Maine, but illegal to buy sex. Prostitution nevertheless occurs elsewhere in the country.
Prostitution in Rhode Island was outlawed in 2009. On November 3, 2009, Republican Governor Donald Carcieri signed into law a bill which makes the buying and selling of sexual services a crime.
Bay Area Sex Worker Advocacy Network (BAYSWAN) is a non-profit organization in the San Francisco Bay Area which works to improve working conditions, increase benefits, and eliminate discrimination on behalf of individuals working within both legal and criminalized adult entertainment industries. The organization provides advice and information to social service, policy reformers, media outlets, politicians, including the San Francisco Task Force on Prostitution and Commission on the Status of Women (COSW), and law enforcement agencies dealing with sex workers.
Prostitution in the Philippines is illegal, although somewhat tolerated, with law enforcement being rare with regards to sex workers. Penalties range up to life imprisonment for those involved in trafficking, which is covered by the Anti-Trafficking in Persons Act of 2003. Prostitution is available through bars, karaoke bars, massage parlors, brothels, street walkers, and escort services.

Sex workers' rights encompass a variety of aims being pursued globally by individuals and organizations that specifically involve the human, health, and labor rights of sex workers and their clients. The goals of these movements are diverse, but generally aim to legalize or decriminalize sex work, as well as to destigmatize it, regulate it and ensure fair treatment before legal and cultural forces on a local and international level for all persons in the sex industry.
Prostitution in Malaysia is restricted in all states despite it being widespread in the country. Related activities such as soliciting and brothels are illegal. In the two states of Terengganu and Kelantan, Muslims convicted of prostitution may be punishable with public caning.
According to the United States Department of State, "Thailand is a source, destination, and transit country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labour and sex trafficking." Thailand's relative prosperity attracts migrants from neighboring countries who flee conditions of poverty and, in the case of Burma, military repression. Significant illegal migration to Thailand presents traffickers with opportunities to coerce or defraud undocumented migrants into involuntary servitude or sexual exploitation. Police who investigated reaching high-profile authorities also received death threats in 2015.

The sex industry consists of businesses that either directly or indirectly provide sex-related products and services or adult entertainment. The industry includes activities involving direct provision of sex-related services, such as prostitution, strip clubs, host and hostess clubs, and sex-related pastimes, such as pornography, sex-oriented men's magazines, women's magazines, sex movies, sex toys, and fetish or BDSM paraphernalia. Sex channels for television and pre-paid sex movies for video on demand, are part of the sex industry, as are adult movie theaters, sex shops, peep shows, and strip clubs. The sex industry employs millions of people worldwide, mainly women. These range from the sex worker, also called adult service provider (ASP), who provides sexual services, to a multitude of support personnel.

Happy Endings? is a 2009 cinéma vérité documentary film directed and produced by Tara Hurley. Filmed over 27 months, it chronicles the lives of the women in massage parlors in Rhode Island during a battle in the state legislature to once again make prostitution illegal. During the period of filming, prostitution in Rhode Island was legal as long as it was conducted behind closed doors.

Human rights in the Dominican Republic constitute the civil and political rights and freedoms legally protected under the Constitution of the Dominican Republic and enforced by the government through common and statutory law. The majority of human rights disputes are presided over by the highest court of constitutional appeal, the Dominican Constitutional Tribunal. These rights and freedoms have developed over time in accordance with the Dominican Republic's expansion from the former Spanish colony of the Captaincy General of Santo Domingo to its modern state formation. The history of human rights in the state have also been marked by the oscillation between democratic administrations, such as the current presidency of Danilo Medina, and authoritarian administrations, most significantly the dictatorial regime of Rafael Trujillo between 16 August 1930 and 16 August 1938. As a member of the Organization of American States and the United Nations, the Dominican Republic is party to myriad legal treaties and covenants which propagate the human rights standards of the international community and have integrated the majority of these human rights directives into their domestic legislation.

The COVID-19 pandemic was first reported in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, in December 2019. The origins of the virus have subsequently led to an increase in acts and displays of sinophobia, as well as prejudice, xenophobia, discrimination, violence, and racism against people of East Asian and Southeast Asian descent and appearance around the world. With the spread of the pandemic and formation of hotspots, such as those in Asia, Europe, and the Americas, discrimination against people from these hotspots has been reported.

On March 16, 2021, a shooting spree occurred at two spas and a massage parlor in the metropolitan area of Atlanta, Georgia, United States. Eight people were killed and a ninth was wounded. A suspect, 21-year-old Robert Aaron Long, was taken into custody later that day. Long pleaded guilty to the charges and was sentenced to life in prison without the possibility of parole.
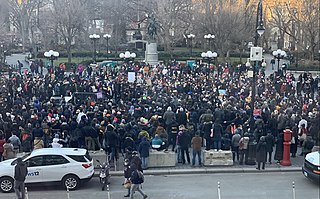
Stop Asian Hate was a slogan and name of a series of demonstrations, protests, and rallies against violence targeting Asians, Asian Americans, and others of Asian descent during the COVID-19 pandemic. It began in the United States in 2021 in response to racial discrimination against Asian Americans relating to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Emi Koyama is a Japanese-American activist, artist, and independent scholar. Koyama's work discusses issues of feminism, intersex human rights, domestic violence, and sex work among many others. Koyama is best known for her 2000 essay "The Transfeminist Manifesto", which has been republished in many anthologies and journals for transgender studies. She is a founder of the advocacy group Intersex Initiative.