
The Islamabad Capital Territory is the only federal territory of Pakistan that is centred around Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan, located on the northern edge of the Pothohar Plateau, at the foot of the Margalla Hills, in the northwestern area of the Punjab region. The territory shares borders with the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in the west and with the province of Punjab in the remaining directions. It covers an area of 906.5 square kilometres (350.0 sq mi) and, according to 2023 census, has a population of over 2.3 million.

The Politics of Pakistan takes place within the framework established by the constitution. The country is a federal parliamentary republic in which provincial governments enjoy a high degree of autonomy and residuary powers. Executive power is vested with the national cabinet which is headed by Prime Minister of Pakistan, who works with the bicameral parliament and the judiciary. Stipulations set by the constitution provide a delicate check and balance of sharing powers between executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the government.

West Pakistan was the western province of Pakistan between 1955 and 1970, covering the territory of present-day Pakistan. Its land borders were with Afghanistan, India and Iran, with a maritime border with Oman in the Gulf of Oman in the Arabian Sea.

Islamabad is the capital city of Pakistan. It is the country's tenth-most populous city with a population of 1,108,872 people and is federally administered by the Pakistani government as part of the Islamabad Capital Territory. Built as a planned city in the 1960s and established in 1967, it replaced Karachi as Pakistan's national capital.

The president of Pakistan is the head of state of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. The president is the nominal head of the executive and the supreme commander of the Pakistan Armed Forces. The presidency is a ceremonial position in Pakistan. The president is bound to act on advice of the prime minister and cabinet. Asif Ali Zardari is the current president since 10 March 2024.

The administrative units of Pakistan comprise four provinces, one federal territory, and two disputed territories: the provinces of Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan; the Islamabad Capital Territory; and the administrative territories of Azad Jammu and Kashmir and Gilgit–Baltistan. As part of the Kashmir conflict with neighbouring India, Pakistan has also claimed sovereignty over the Indian-controlled territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh since the First Kashmir War of 1947–1948. It also has a territorial dispute with India over Junagadh, but has never exercised administrative authority over either regions. All of Pakistan's provinces and territories are subdivided into divisions, which are further subdivided into districts, and then tehsils, which are again further subdivided into union councils.

The prime minister of Pakistan is the head of government of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and his chosen cabinet, despite the president of Pakistan serving as the nominal head of executive. The prime minister is often the leader of the party or the coalition with a majority in the lower house of the Parliament of Pakistan, the National Assembly where he serves as Leader of the House. Prime minister holds office by virtue of their ability to command the confidence of the National Assembly. The prime minister is designated as the "chief executive of the Islamic Republic".

The National Assembly of Pakistan is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Pakistan, with the upper house being the Senate. As of 2023, the National Assembly has a maximum membership of 336, of which 266 are directly elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, while 60 are elected on reserved seats for women and religious minorities from all over the country. Members hold their seats for five years or until the house is dissolved by the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. The house convenes at the Parliament House, Red Zone, Islamabad.

The Parliament of Pakistan is the supreme legislative body of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. It is a bicameral federal legislature, composed of the President of Pakistan and two houses: the Senate and the National Assembly. The president, as head of the legislature, has the power to summon or prorogue either house of the Parliament. The president can dissolve the National Assembly, only on the Prime Minister's advice.

The National Security Council is a federal institutional and consultative body chaired by the prime minister of Pakistan as its chairman. The NSC is a principal forum that is mandated for considering national security and foreign policy matters with the senior national security advisers and Cabinet ministers. The idea and inception of National Security Council was first conceived in 1969 under the President Yahya Khan, its functions were to advise and assist the president and prime minister on national security and foreign policies.

The Government of Pakistan, constitutionally known as the Federal Government, commonly known as the Centre, is the national authority of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, a federal republic located in South Asia, consisting of four provinces and one federal territory. The territories of Gilgit-Baltistan and Azad Kashmir are also part of the country but have separate systems and are not part of the federation.

The Aiwan-e-Sadr, or Presidential Palace, is the official residence and workplace of the president of Pakistan. It is located in northeastern Islamabad on Constitution Avenue, between the Parliament Building and the Cabinet block of the Pakistan Secretariat. Residences for the presidential staff, known as the President's Colony, are also located behind the presidency, adjacent to 4th Avenue.

Pakistan is a federal republic with three tiers of government: national, provincial and local. Local government is protected by the constitution in Articles 32 and 140-A, and each province also has its own local-government-enabling legislation and ministries responsible for implementation. District councils and metropolitan corporations are respectively the highest rural and urban tiers of local government in the provinces. Both urban and rural local government have two or three tiers in all provinces except Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where councils are not identified as either urban or rural. There are 129 district councils across the four provinces, 619 urban councils made up of one city district, four metropolitan corporations, 13 municipal corporations, 96 municipal committees, 148 town councils, 360 urban union committees, and 1,925 rural councils. Additionally there are 3339 neighbourhood, ‘tehsil’ and village councils in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.

The Cabinet of Pakistan is a formal body composed of senior government officials chosen and led by the Prime Minister. All cabinet members sworn in are designated Minister and are seated at their respective ministries located in the Pakistan Secretariat.

Islamabad is located in the Pothohar Plateau in the northern part of Pakistan, within the Islamabad Capital Territory. It is a well-organized city divided into different sectors and zones. It was ranked as a Gamma + world city in 2020. The city is home to Pakistan Monument, which is built on top of a hill in Shakarparian, and the Faisal Mosque, one of the largest mosques in South Asia and the sixth -largest mosque as per area in the world. The Capital Development Authority is tasked with developing the city and its facilities.

Constitution Avenue, also known as Shahrah-e-Dastoor, is a major north-south avenue in Islamabad, Pakistan that passess through the Red Zone. Its north end meets with the Khayban-e-Iqbal intersection and south end with an intersection of Srinagar Highway.
The 2014 Tsunami March, also called the Azadi movement, was a protest march in Pakistan from 14 August to 17 December 2014. The march was organized by the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) and Pakistan Awami Tehreek (PAT) against the Pakistani government of Nawaz Sharif. PTI claimed systematic election-rigging in the 2013 general election, and PAT demanded justice for the culprits in the 2014 Lahore clash. Then PTI chairman Imran Khan had announced plans for an August march from Lahore to Islamabad with a group of protesters in a PTI jalsa (demonstration) in Bahawalpur on 27 June 2014. On 17 December, a day after the 2014 Peshawar school massacre, Khan called off the protest.
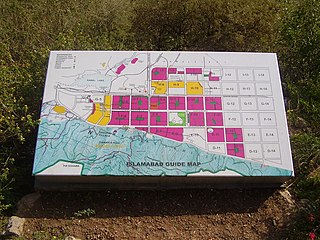
Sectors of Islamabad are administrative divisions of Zone I and Zone II of the Islamabad Capital Territory region. The capital territory is divided into 5 zones, of which Zone I and Zone II have been designated urban development zones.
The first 100 days of Imran Khan's premiership began with his oath of office ceremony on 18 August 2018 as the 22nd Prime Minister of Pakistan – shortly after the oath-taking of the 15th National Assembly of Pakistan on 13 August, and the elected parliament's vote of confidence for Khan's premiership on 17 August. The 100th day of his premiership was 25 November 2018.













