
The mullets or grey mullets are a family (Mugilidae) of ray-finned fish found worldwide in coastal temperate and tropical waters, and some species in fresh water. Mullets have served as an important source of food in Mediterranean Europe since Roman times. The family includes about 78 species in 20 genera.

The goatfishes are perciform fish of the family Mullidae. The family is also sometimes referred to as the red mullets, which also refers more narrowly to the genus Mullus.

Upeneichthys lineatus, also known as the blue-striped mullet, blue-lined goatfish. blue-striped goatfish, blue-spotted goatfish and blue striped red mullet, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a goatfish from the family Mullidae. It is native to the Pacific coast of Australia. It occurs in sheltered areas over rocky and sandy substrates and can be found 5 to 100 metres, though rarer below 40 metres (130 ft). This species can reach a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) FL. This species is commercially important.

The Lessepsian migration is the migration of marine species across the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction.

Mullus barbatus is a species of goatfish found in the Mediterranean Sea, Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea and the eastern North Atlantic Ocean, where its range extends from Scandinavia to Senegal. They are fished, mostly by trawling, with the flesh being well regarded. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed their conservation status as being of "least concern".

The striped red mullet or surmullet is a species of goatfish found in the Mediterranean Sea, eastern North Atlantic Ocean, and the Black Sea. They can be found in water as shallow as 5 metres (16 ft) or as deep as 409 metres (1,342 ft) depending upon the portion of their range that they are in. This species can reach a length of 40 centimetres (16 in) SL though most are only around 25 centimetres (9.8 in). The greatest recorded weight for this species is 1 kilogram (2.2 lb). This is a commercially important species and is also sought after as a game fish.
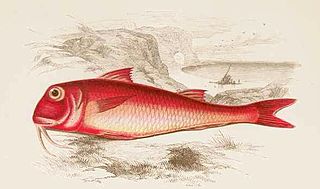
Mullus is a subtropical marine genus of perciform fish of the family Mullidae (goatfish) and includes the red mullets, occurring mainly in the southwest Atlantic near the South American coast and in the Eastern Atlantic including the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. These fish are benthic and can be found resting and feeding over soft substrates.

Parupeneus cyclostomus, the gold-saddle goatfish, blue goatfish or yellowsaddle goatfish, is a species of goatfish native to the Indo-Pacific. It is a commercially important species, as well as being sought out as a game fish, though it has been reported as carrying the ciguatera toxin. It can also be found in the aquarium trade.

The Missolonghi-Aitoliko lagoons complex is located in the north part of the Gulf of Patras in the central west coast of Greece. It is one of the most important Mediterranean lagoons. It is a shallow area of 150 km2, extended between the Acheloos and Evinos rivers. It is protected by the Ramsar Convention and it is also included in the Natura 2000 network.

Mulloidichthys is a genus of fish in the family Mullidae native to coral and rocky reefs of the tropical Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Coastal fish, also called inshore fish or neritic fish, inhabit the sea between the shoreline and the edge of the continental shelf. Since the continental shelf is usually less than 200 metres (660 ft) deep, it follows that pelagic coastal fish are generally epipelagic fish, inhabiting the sunlit epipelagic zone. Coastal fish can be contrasted with oceanic fish or offshore fish, which inhabit the deep seas beyond the continental shelves.

Upeneichthys vlamingii, the blue-spotted goatfish, southern goatfish, black-striped goatfish, blue-striped red mullet, southern red mullet or western red mullet, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a goatfish from the family Mullidae native to the coast of southern Australia.

Fishing in Israel is a branch of the Israeli economy with historical significance. The three main natural fishing zones are the Mediterranean Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Kinneret. A fourth area that was once historically significant, Lake Hula, no longer exists, as it was drained in the 1950s. In addition, aquaculture the growth of fish in ponds or in cages, is rising in prominence.

The harvesting and consuming of seafoods are ancient practices that may date back to at least the Upper Paleolithic period which dates to between 50,000 and 10,000 years ago. Isotopic analysis of the skeletal remains of Tianyuan man, a 40,000-year-old modern human from eastern Asia, has shown that he regularly consumed freshwater fish. Archaeology features such as shell middens, discarded fish bones and cave paintings show that sea foods were important for survival and consumed in significant quantities. During this period, most people lived a hunter-gatherer lifestyle and were, of necessity, constantly on the move. However, where there are early examples of permanent settlements such as those at Lepenski Vir, they are almost always associated with fishing as a major source of food.

The yellowfin goatfish is a species of goatfish native to the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.

Upeneus moluccensis, the goldband goatfish, golden-banded goatfish or Moluccan goatfish, is a species of Indo-Pacific goatfish from the red mullet and goatfish family, the Mullidae. It is widespread in the warmer waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans as far east as New Caledonia and has colonised the eastern Mediterranean Sea from the Red Sea via the Suez Canal, making it a Lessepsian migrant.

Parupeneus forsskali, common name Red Sea goatfish, is a species of goatfish belonging to the family Mullidae.
Mullus auratus, the red goatfish or northern goatfish, is a species of ray-finned fish, a goatfish from the family Mullidae which is native to the western Atlantic Ocean.
Upeneus pori, Por's goatfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a goatfish from the family Mullidae which is found in western Indian Ocean and the eastern Mediterranean Sea.

















