
YaST is a Linux operating system setup and configuration tool.

Advanced package tool, or APT, is a free-software user interface that works with core libraries to handle the installation and removal of software on Debian and Debian-based Linux distributions. APT simplifies the process of managing software on Unix-like computer systems by automating the retrieval, configuration and installation of software packages, either from precompiled files or by compiling source code.

Gambas is the name of an object-oriented dialect of the BASIC programming language, as well as the integrated development environment that accompanies it. Designed to run on Linux and other Unix-like computer operating systems, its name is a recursive acronym for Gambas Almost Means Basic. Gambas is also the word for prawns in the Spanish, French, and Portuguese languages, from which the project's logos are derived.

Synaptic is a GTK-based graphical user interface designed for the APT package manager used by the Debian Linux distribution and its derivatives. Synaptic is usually used on systems based on deb packages but can also be used on systems based on RPM packages. It can be used to install, remove and upgrade software packages and to add repositories.

GNOME Terminal is a terminal emulator for the GNOME desktop environment written by Havoc Pennington and others. Terminal emulators allow users to access a UNIX shell while remaining on their graphical desktop.

Audacious is a free and open-source audio player software with a focus on low resource use, high audio quality, and support for a wide range of audio formats. It is designed primarily for use on POSIX-compatible Unix-like operating systems, with limited support for Microsoft Windows. Audacious was the default audio player in Ubuntu Studio in 2011–12, and was the default music player in Lubuntu until October 2018, when it was replaced with VLC.

ClamTk is a free and open-source graphical interface for the ClamAV command-line antivirus software program for Linux desktop users. It provides both on-demand and scheduled scanning. The project was started by Dave Mauroni in February 2004. As of April 2024, the program is no longer maintained.

Conky is a free software desktop system monitor for the X Window System. It is available for Linux, FreeBSD, and OpenBSD. Conky is highly configurable and is able to monitor many system variables including the status of the CPU, memory, swap space, disk storage, temperatures, processes, network interfaces, battery power, system messages, e-mail inboxes, Arch Linux updates, many popular music players, weather updates, breaking news, and much more. Unlike system monitors that use high-level widget toolkits to render their information, Conky is drawn directly in an X window. This allows it to be configured such that it consumes relatively few system resources.

Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu, bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications. It can provide full out-of-the-box multimedia support for those who choose to include proprietary software such as multimedia codecs. Linux Mint can come with three different desktop environments by default; Cinnamon, Xfce, and MATE.
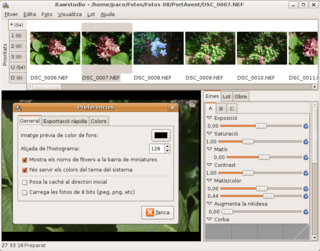
Rawstudio is a free and open source stand-alone application software to read and manipulate images in raw image formats from digital cameras. It is designed for working rapidly with a large volume of images, whereas similar tools are designed to work with one image at a time.

Xarchiver is a front-end to various command line archiving tools for Linux and BSD operating systems, designed to be independent of the desktop environment. It is the default archiving application of Xfce and LXDE. Deepin's archive manager is based on Xarchiver.

LightDM is a free and open-source X display manager that aims to be lightweight, fast, extensible and multi-desktop. It can use various front-ends to draw the user interface, also called Greeters. It also supports Wayland.

f.lux is a cross-platform computer program that adjusts a display's color temperature according to location and time of day, offering functional respite for the eyes. The program is designed to reduce eye strain during night-time use, helping to reduce disruption of sleep patterns.

Leafpad is a free and open-source graphical text editor for Linux, Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), and Maemo that is similar to the Microsoft Windows program Notepad. Created with the focus of being a lightweight text editor with minimal dependencies, it is designed to be simple-to-use and easy-to-compile.

mpv is free and open-source media player software based on MPlayer, mplayer2 and FFmpeg. It runs on several operating systems, including Unix-like operating systems and Microsoft Windows, along with having an Android port called mpv-android. It is cross-platform, running on ARM, PowerPC, x86/IA-32, x86-64, and MIPS architecture.

Snap is a software packaging and deployment system developed by Canonical for operating systems that use the Linux kernel and the systemd init system. The packages, called snaps, and the tool for using them, snapd, work across a range of Linux distributions and allow upstream software developers to distribute their applications directly to users. Snaps are self-contained applications running in a sandbox with mediated access to the host system. Snap was originally released for cloud applications but was later ported to also work for Internet of Things devices and desktop applications.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL is not available to all Windows 10 users by default. It can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.
Zstandard is a lossless data compression algorithm developed by Yann Collet at Facebook. Zstd is the corresponding reference implementation in C, released as open-source software on 31 August 2016.

Foliate is a free and open-source program for reading e-books in Linux. In English, foliate is an adjective meaning to be shaped like a leaf, from the Latin foliatus, meaning leafy.

Qalculate! is an arbitrary precision cross-platform software calculator. It supports complex mathematical operations and concepts such as derivation, integration, data plotting, and unit conversion. It is a free and open-source software released under GPL v2.

















