
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates, and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion ; as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously.

A mosquito is any member of a group of about 3,500 species of small insects belonging to the order Diptera (flies). Within Diptera, mosquitoes constitute the family Culicidae. The word "mosquito" is Spanish and Portuguese for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts.

Anopheles is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which cause malaria in humans in endemic areas. Anopheles gambiae is one of the best known, because of its predominant role in the transmission of the most dangerous malaria parasite species – Plasmodium falciparum.
Gnathostomiasis is the human infection caused by the nematode (roundworm) Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or Gnathostoma hispidum, which infects vertebrates.

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.

Osmia lignaria, commonly known as the orchard mason bee or blue orchard bee, is a megachilid bee that makes nests in reeds and natural holes, creating individual cells for its brood that are separated by mud dividers. Unlike carpenter bees, it cannot drill holes in wood. O. lignaria is a common species used for early spring fruit bloom in Canada and the United States, though a number of other Osmia species are cultured for use in pollination.
Gnathostoma spinigerum is a parasitic nematode that causes gnathostomiasis in humans, also known as its clinical manifestations are creeping eruption, larva migrans, Yangtze edema, Choko-Fuschu Tua chid and wandering swelling. Gnathostomiasis in animals can be serious, and even fatal. The first described case of gnathostomiasis was in a young tiger that died in the London Zoo in 1835. The larval nematode is acquired by eating raw or undercooked fish and meat.

Culex is a genus of mosquitoes, several species of which serve as vectors of one or more important diseases of birds, humans, and other animals. The diseases they vector include arbovirus infections such as West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis, or St. Louis encephalitis, but also filariasis and avian malaria. They occur worldwide except for the extreme northern parts of the temperate zone, and are the most common form of mosquito encountered in some major U.S. cities, such as Los Angeles.
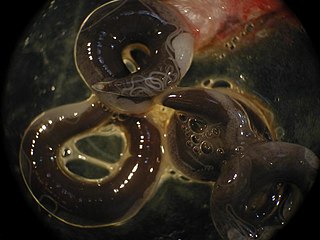
Anguillicoloides crassus is a parasitic nematode worm that lives in the swimbladders of eels and appears to spread easily among eel populations after introduction to a body of water. It is considered to be one of the threats to the sustainability of populations of European eel. It was introduced to the European continent in the 1980s, where it was reported independently from Germany and Italy in 1982, having probably been introduced from Taiwan. It is thought to have reached England in 1987 from continental Europe. It is a natural parasite of the Japanese eel in its native range.

The Culicinae are the most extensive subfamily of mosquitoes (Culicidae) and have species in every continent except Antarctica, but are highly concentrated in tropical areas. Mosquitoes are best known as parasites to many vertebrate animals and vectors for disease. They are holometabolous insects, and most species lay their eggs in stagnant water, to benefit their aquatic larval stage.

The Strongylida suborder includes many of the important nematodes found in the gastrointestinal tracts of ruminants, horses, and swine, as well as the lungworms of ruminants and the hookworms of dogs and cats.

Mermithidae is a family of nematode worms that are endoparasites in arthropods. As early as 1877, Mermithidae was listed as one of nine subdivisions of the Nematoidea. Mermithidae are confused with the horsehair worms of the phylum Nematomorpha that have a similar life history and appearance.
Dactylogyrus vastator is a species of hermaphroditic flatworms of class Monogenea. It is an ectoparasite of fish which infests the gills. It is problematic on fish farms. It is otherwise non-hazardous to humans.

The sirex woodwasp is a species of horntail, native to Europe, Asia, and northern Africa. Adults vary in length from 9 to 36 mm.
Eustrongylidosis is a parasitic disease that mainly affects wading birds worldwide; however, the parasite's complex, indirect lifecycle involves other species, such as aquatic worms and fish. Moreover, this disease is zoonotic, which means the parasite can transmit disease from animals to humans. Eustrongylidosis is named after the causative agent Eustrongylides, and typically occurs in eutrophicated waters where concentrations of nutrients and minerals are high enough to provide ideal conditions for the parasite to thrive and persist. Because eutrophication has become a common issue due to agricultural runoff and urban development, cases of eustrongylidosis are becoming prevalent and hard to control. Eustrongylidosis can be diagnosed before or after death by observing behavior and clinical signs, and performing fecal flotations and necropsies. Methods to control it include preventing eutrophication and providing hosts with uninfected food sources in aquaculture farms. Parasites are known to be indicators of environmental health and stability, so should be studied further to better understand the parasite's lifecycle and how it affects predator-prey interactions and improve conservation efforts.
Dirofilaria tenuis is a species of nematode, a parasitic roundworm that infects the subcutaneous tissue of vertebrates. D. tenuis most commonly infects raccoons, but some human cases have been reported. They are vectored by mosquitoes and follow similar development and transmission patterns as other Dirofilaria.
Paragordius varius, also known as the nematomorphs or horsehair worm, are known to control their definitive host to jump into a pool of water, thus allowing the adult worm to escape and reproduce. They are similar to nematodes but are much longer and very thin. P. varius is usually found in water or wet areas. These worms definitive hosts consist of grasshoppers, crickets, cockroaches, and some beetles.

Cuterebra fontinella, the mouse bot fly, is a species of New World skin bot fly in the family Oestridae. C. fontinella is typically around 1 mm long with a black and yellow color pattern. C. fontinella develops by parasitizing nutrients from its host, typically the white-footed mouse. C. fontinella has even been known to parasitize humans in rare cases. Individuals parasitized by C. fontinella will develop a large bump on the skin that is indicative of parasitization.
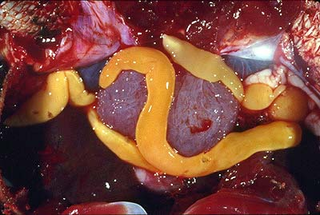
Australamphilina elongata is a species of parasitic worm in the order Amphilinidea. Amphilinids are commonly considered to be tapeworms, yet differ from true tapeworms, subclass Eucestoda, because their bodies are unsegmented and are not divided into proglottids. It is an internal parasite of freshwater turtles including the eastern long-necked turtle. It is found in eastern Australia.

Contracaecum is genus of parasitic nematodes from the family Anisakidae. These nematodes are parasites of warm-blooded, fish eating animals, i.e. mammals and birds, as sexually mature adults. The eggs and the successive stages of their larvae use invertebrates and increasing size classes of fishes as intermediate hosts. It is the only genus in the family Anisakidae which can infect terrestrial, marine and freshwater animals.













