Related Research Articles

An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which live in the root nodules of legumes, single-cell algae inside reef-building corals and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to insects.

Companion planting in gardening and agriculture is the planting of different crops in proximity for any of a number of different reasons, including weed suppression, pest control, pollination, providing habitat for beneficial insects, maximizing use of space, and to otherwise increase crop productivity. Companion planting is a form of polyculture.

Rickettsia is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci, bacilli, or threads. The genus was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever.

Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving live birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs.

In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist guest (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms, cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner.

In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation.
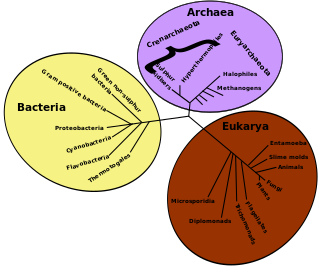
Evolutionary ecology lies at the intersection of ecology and evolutionary biology. It approaches the study of ecology in a way that explicitly considers the evolutionary histories of species and the interactions between them. Conversely, it can be seen as an approach to the study of evolution that incorporates an understanding of the interactions between the species under consideration. The main subfields of evolutionary ecology are life history evolution, sociobiology, the evolution of interspecific interactions and the evolution of biodiversity and of ecological communities.

Buchnera aphidicola, a member of the Pseudomonadota and the only species in the genus Buchnera, is the primary endosymbiont of aphids, and has been studied in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Buchnera is believed to have had a free-living, Gram-negative ancestor similar to a modern Enterobacterales, such as Escherichia coli. Buchnera is 3 μm in diameter and has some of the key characteristics of its Enterobacterales relatives, such as a Gram-negative cell wall. However, unlike most other Gram-negative bacteria, Buchnera lacks the genes to produce lipopolysaccharides for its outer membrane. The long association with aphids and the limitation of crossover events due to strictly vertical transmission has seen the deletion of genes required for anaerobic respiration, the synthesis of amino sugars, fatty acids, phospholipids, and complex carbohydrates. This has resulted not only in one of the smallest known genomes of any living organism, but also one of the most genetically stable.
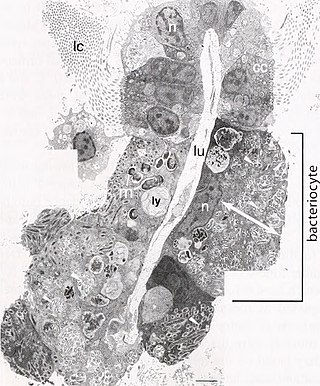
A bacteriocyte, also known as a mycetocyte, is a specialized adipocyte found primarily in certain insect groups such as aphids, tsetse flies, German cockroaches, weevils. These cells contain endosymbiotic organisms such as bacteria and fungi, which provide essential amino acids and other chemicals to their host. Bacteriocytes may aggregate into a specialized organ called the bacteriome.

Parasitoid wasps are a large group of hymenopteran superfamilies, with all but the wood wasps (Orussoidea) being in the wasp-waisted Apocrita. As parasitoids, they lay their eggs on or in the bodies of other arthropods, sooner or later causing the death of these hosts. Different species specialise in hosts from different insect orders, most often Lepidoptera, though some select beetles, flies, or bugs; the spider wasps (Pompilidae) exclusively attack spiders.
Nancy A. Moran is an American evolutionary biologist and entomologist, University of Texas Leslie Surginer Endowed Professor, and co-founder of the Yale Microbial Diversity Institute. Since 2005, she has been a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences. Her seminal research has focused on the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum and its bacterial symbionts including Buchnera (bacterium). In 2013, she returned to the University of Texas at Austin, where she continues to conduct research on bacterial symbionts in aphids, bees, and other insect species. She has also expanded the scale of her research to bacterial evolution as a whole. She believes that a good understanding of genetic drift and random chance could prevent misunderstandings surrounding evolution. Her current research goal focuses on complexity in life-histories and symbiosis between hosts and microbes, including the microbiota of insects.

Acyrthosiphon pisum, commonly known as the pea aphid, is a sap-sucking insect in the family Aphididae. It feeds on several species of legumes worldwide, including forage crops, such as pea, clover, alfalfa, and broad bean, and ranks among the aphid species of major agronomical importance. The pea aphid is a model organism for biological study whose genome has been sequenced and annotated.

Chemical defense is a strategy employed by many organisms to avoid consumption by producing toxic or repellent metabolites or chemical warnings which incite defensive behavioral changes. The production of defensive chemicals occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria, as well as invertebrate and vertebrate animals. The class of chemicals produced by organisms that are considered defensive may be considered in a strict sense to only apply to those aiding an organism in escaping herbivory or predation. However, the distinction between types of chemical interaction is subjective and defensive chemicals may also be considered to protect against reduced fitness by pests, parasites, and competitors. Repellent rather than toxic metabolites are allomones, a sub category signaling metabolites known as semiochemicals. Many chemicals used for defensive purposes are secondary metabolites derived from primary metabolites which serve a physiological purpose in the organism. Secondary metabolites produced by plants are consumed and sequestered by a variety of arthropods and, in turn, toxins found in some amphibians, snakes, and even birds can be traced back to arthropod prey. There are a variety of special cases for considering mammalian antipredatory adaptations as chemical defenses as well.
The hologenome theory of evolution recasts the individual animal or plant as a community or a "holobiont" – the host plus all of its symbiotic microbes. Consequently, the collective genomes of the holobiont form a "hologenome". Holobionts and hologenomes are structural entities that replace misnomers in the context of host-microbiota symbioses such as superorganism, organ, and metagenome. Variation in the hologenome may encode phenotypic plasticity of the holobiont and can be subject to evolutionary changes caused by selection and drift, if portions of the hologenome are transmitted between generations with reasonable fidelity. One of the important outcomes of recasting the individual as a holobiont subject to evolutionary forces is that genetic variation in the hologenome can be brought about by changes in the host genome and also by changes in the microbiome, including new acquisitions of microbes, horizontal gene transfers, and changes in microbial abundance within hosts. Although there is a rich literature on binary host–microbe symbioses, the hologenome concept distinguishes itself by including the vast symbiotic complexity inherent in many multicellular hosts. For recent literature on holobionts and hologenomes published in an open access platform, see the following reference.

Cinara, the conifer aphids or giant conifer aphids, is a genus of aphids in the family Aphididae. They are widespread in the Northern Hemisphere.
Serratia symbiotica is a species of bacteria that lives as a symbiont of aphids. In the aphid Cinara cedri, it coexists with Buchnera aphidicola, given the latter cannot produce tryptophan. It is also known to habitate in Aphis fabae. Together with other endosymbionts, it provides aphids protection against parasitoids.
Hamiltonella defensa is a species of bacteria. It is maternally or sexually transmitted and lives as an endosymbiont of whiteflies and aphids, meaning that it lives within a host, protecting its host from attack. It does this through bypassing the host's immune responses by protecting its host against parasitoid wasps. However, H. defensa is only defensive if infected by a virus. H. defensa shows a relationship with Photorhabdus species, together with Regiella insecticola. Together with other endosymbionts, it provides aphids protection against parasitoids. It is known to habitate Bemisia tabaci.
Arsenophonus nasoniae is a species of bacterium which was previously isolated from Nasonia vitripennis, a species of parasitoid wasp. These wasps are generalists which afflict the larvae of parasitic carrion flies such as blowflies, houseflies and flesh flies. A. nasoniae belongs to the phylum Pseudomonadota and family Morganellaceae. The genus Arsenophonus, has a close relationship to the Proteus (bacterium) rather than to that of Salmonella and Escherichia. The genus is composed of gammaproteobacterial, secondary-endosymbionts which are gram-negative. Cells are non-flagellated, non-motile, non-spore forming and form long to highly filamentous rods. Cellular division is exhibited through septation. The name 'Arsenophonus nasoniae gen. nov., sp. nov.' was therefore proposed for the discovered bacterium due to its characteristics and its microbial interaction with N. vitripennis. The type strain of A. nasoniae is Strain SKI4.
Vertical transmission of symbionts is the transfer of a microbial symbiont from the parent directly to the offspring. Many metazoan species carry symbiotic bacteria which play a mutualistic, commensal, or parasitic role. A symbiont is acquired by a host via horizontal, vertical, or mixed transmission.

Lysiphlebus is a genus of parasitoid wasps belonging to the family Braconidae.
References
- ↑ Moran, N. A.; Russell, J. A.; Koga, R.; Fukatsu, T. (2005). "Evolutionary Relationships of Three New Species of Enterobacteriaceae Living as Symbionts of Aphids and Other Insects". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 71 (6): 3302–3310. Bibcode:2005ApEnM..71.3302M. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.6.3302-3310.2005. ISSN 0099-2240. PMC 1151865 . PMID 15933033.
- ↑ Vorburger, C.; Gehrer, L.; Rodriguez, P. (2009). "A strain of the bacterial symbiont Regiella insecticola protects aphids against parasitoids" (PDF). Biology Letters. 6 (1): 109–111. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0642. ISSN 1744-9561. PMC 2817266 . PMID 19776066.