Related Research Articles

Arctica, or Arctida is a hypothetical ancient continent which formed approximately 2.565 billion years ago in the Neoarchean era. It was made of Archaean cratons, including the Siberian Craton, with its Anabar/Aldan shields in Siberia, and the Slave, Wyoming, Superior, and North Atlantic cratons in North America. Arctica was named by Rogers 1996 because the Arctic Ocean formed by the separation of the North American and Siberian cratons. Russian geologists writing in English call the continent "Arctida" since it was given that name in 1987, alternatively the Hyperborean craton, in reference to the hyperboreans in Greek mythology.

The Moine Thrust Belt or Moine Thrust Zone is a linear tectonic feature in the Scottish Highlands which runs from Loch Eriboll on the north coast 190 kilometres (120 mi) southwest to the Sleat peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The thrust belt consists of a series of thrust faults that branch off the Moine Thrust itself. Topographically, the belt marks a change from rugged, terraced mountains with steep sides sculptured from weathered igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in the west to an extensive landscape of rolling hills over a metamorphic rock base to the east. Mountains within the belt display complexly folded and faulted layers and the width of the main part of the zone varies up to ten kilometres, although it is significantly wider on Skye.

The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago (Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the Laurentia and Baltica continents and the Avalonia microcontinent collided.

The Dalradian Supergroup is a stratigraphic unit in the lithostratigraphy of the Grampian Highlands of Scotland and in the north and west of Ireland. The diverse assemblage of rocks which constitute the supergroup extend across Scotland from Islay in the west to Fraserburgh in the east and are confined by the Great Glen Fault to the northwest and the Highland Boundary Fault to the southeast. Much of Shetland east of the Walls Boundary Fault is also formed from Dalradian rocks. Dalradian rocks extend across the north of Ireland from County Antrim in the north east to Clifden on the Atlantic coast, although obscured by younger Palaeogene lavas and tuffs or Carboniferous rocks in large sections.

The Gascoyne Complex is a terrane of Proterozoic granite and metamorphic rock in the central-western part of Western Australia. The complex outcrops at the exposed western end of the Capricorn Orogen, a 1,000 km-long arcuate belt of folded, faulted and metamorphosed rocks between two Archean cratons; the Pilbara craton to the north and the Yilgarn craton to the south. The Gascoyne Complex is thought to record the collision of these two different Archean continental fragments during the Capricorn Orogeny at 1830–1780 Ma.
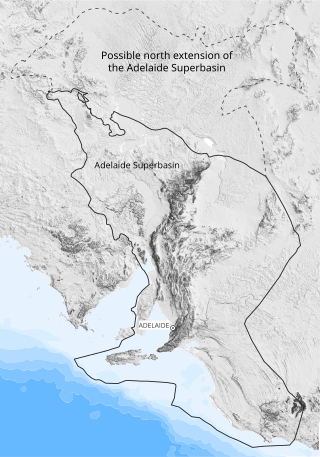
The Adelaide Superbasin is a major Neoproterozoic to middle Cambrian geological province in central and south-east South Australia, western New South Wales, and western Victoria.

Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although originally it also included the cratonic areas of Greenland and the Hebridean Terrane in northwest Scotland. During other times in its past, Laurentia has been part of larger continents and supercontinents and consists of many smaller terranes assembled on a network of early Proterozoic orogenic belts. Small microcontinents and oceanic islands collided with and sutured onto the ever-growing Laurentia, and together formed the stable Precambrian craton seen today.
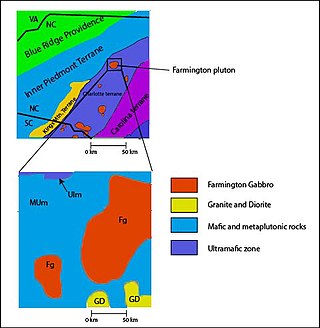
The Carolina Terrane, also called the Carolina Superterrane or Carolinia, is an exotic terrane running ~370 miles (600 km) approximately North-South from central Georgia to central Virginia in the United States. It constitutes a major part of the eastern Piedmont Province.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.

The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions. The Aravalli Mountains consist of the Aravalli and Delhi fold belts, and are collectively known as the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt. The whole mountain range is about 700 km long. Unlike the much younger Himalayan section nearby, the Aravalli Mountains are believed much older and can be traced back to the Proterozoic Eon. They are arguably the oldest geological feature on Earth. The collision between the Bundelkhand craton and the Marwar craton is believed to be the primary mechanism for the development of the mountain range.
The Badenoch Group is a sequence of metamorphosed Tonian age sedimentary rocks that outcrop across the Central Highlands of Scotland, east of the Great Glen. This rock sequence has formerly been referred to as the Central Highland Migmatite Complex and the Central Highland Division.

The Torridonian is the informal name given to a sequence of Mesoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic sedimentary rocks that outcrop in a strip along the northwestern coast of Scotland and some parts of the Inner Hebrides from the Isle of Mull in the southwest to Cape Wrath in the northeast. They lie unconformably on the Archaean to Paleoproterozoic basement rocks of the Lewisian complex and unconformably beneath the Cambrian to Lower Ordovician rocks of the Ardvreck Group.

The Mazatzal orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1650 to 1600 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1700-1600 Mya age Mazatzal island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The Yavapai orogeny was an orogenic (mountain-building) event in what is now the Southwestern United States that occurred between 1710 and 1680 million years ago (Mya), in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Recorded in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1800-1700 Mya age Yavapai island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the first in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The Loch Ness Supergroup is one of the subdivisions of the Neoproterozoic sequence of sedimentary rocks in the Scottish Highlands. It is found everywhere in tectonic contact above the older Wester Ross Supergroup. It is thought to be unconformably overlain by the Cryogenian to Cambrian Dalradian Supergroup.

The Wester Ross Supergroup is one of the subdivisions of the Neoproterozoic sequence of sedimentary rocks in the Scottish Highlands. It lies unconformably on medium to high-grade metamorphic rocks and associated igneous rocks of the Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age Lewisian complex or locally over the Mesoproterozoic sedimentary rocks of the Stoer Group. The contact between the Wester Ross Supergroup and the next youngest of the Neoproterozoic sequences in the Scottish Highlands, the Loch Ness Supergroup, is everywhere a tectonic one.
The Knoydartian Orogeny is a Tonian tectonic and metamorphic event, or group of events, that is recognised in the rocks of the Wester Ross and Loch Ness supergroups of the Scottish Highlands. It is dated to about 820–725 Ma, predating the deposition of the Cryogenian to Cambrian Dalradian Supergroup. It is named after Knoydart, one of the localities where the event was first recognised.
The Sgurr Beag Thrust is an important tectonic structure within the Neoproterozoic metasedimentary rock sequences of the Scottish Highlands. The thrust, or similar structures correlated with it, form the boundary between rocks of the Glennfinnan Group and the underlying Morar Group. It divides the Wester Ross Supergroup from the Loch Ness Supergroup. The history of this structure remains poorly understood although it is thought to be at least partly of Caledonian age.

The Morar Group is a sequence of Tonian sedimentary rocks that have been subjected to a series of tectonic and metamorphic events since their deposition. Originally interpreted to be lowest (oldest) part of a "Moine Supergroup", this sequence now forms part of the Wester Ross Supergroup. They lie unconformably on Archean to Paleoproterozoic basement of the Lewisian complex. The contact with the overlying Glenfinnan Group of the Loch Ness Supergroup is everywhere a tectonic one, formed by the Sgurr Beag Thrust or related structures.

The Moinian or just the Moine, formerly the Moine Supergroup, is a sequence of Neoproterozoic metasediments that outcrop in the Northwest Highlands between the Moine Thrust Belt to the northwest and the Great Glen Fault to the southeast and one part of the Grampian Highlands to the southeast of the fault. It takes its name from A' Mhòine, a peat bog in northern Sutherland.
References
- 1 2 3 Bird, A.; Cutts, K.; Strachan, R.; Thirlwall, M.F.; Hand, M. (2018). "First evidence of Renlandian (c. 950–940 Ma) orogeny in mainland Scotland: Implications for the status of the Moine Supergroup and circum-North Atlantic correlations". Precambrian Research. 305: 283–294. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.12.019.
- ↑ Cawood, P.A.; Strachan, R.; Cutts, K.; Kinny, P.D.; Hand, M.; Pisarevsky, S. (2010). "Neoproterozoic orogeny along the margin of Rodinia: Valhalla orogen, North Atlantic". Geology. 38 (2): 99–102. doi:10.1130/G30450.1.
- ↑ Gee, D.G. (2014). "Correlation of stratigraphy, structure, metamorphism and intrusion in the Caledonian allochthons of East Greenland and Svalbard" . Retrieved 6 June 2024.
- ↑ Krabbendam, M.; Strachan, R.; Prave, T. (2022). "A new stratigraphic framework for the early Neoproterozoic successions of Scotland". Journal of the Geological Society. 179. doi:10.1144/jgs2021-054. hdl: 10023/24155 .