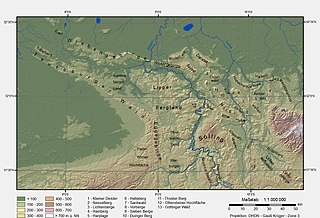
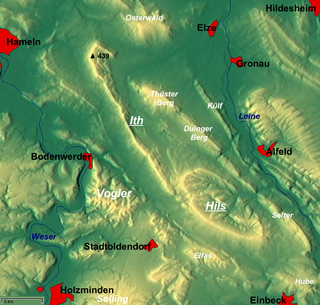
The Holzberg is a small range of hills up to 444.5 m above sea level (NN) in south Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Vorholz is a ridge up to 243 m high in the districts of Hildesheim and Wolfenbüttel in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Ahlsburg is a range of bunter sandstone hills, relatively small in area and up to 411.4 m above sea level (NN), in the southern part of Lower Saxony, Germany. It lies within the Solling foreland and is part of the Weser-Leine Uplands.

The Elfas is a range of hills up to 409.6 m above sea level (NN) in the districts of Holzminden and Northeim in Lower Saxony (Germany). Its name is derived from the Lower Saxon word Fast, which means an area of upland that descends on two sides.

The Hildesheim Forest is a range of hills up to 359 m above sea level (NN) in the district of Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Sieben Berge are a ridge of hills up to 395 m above sea level (NN) in the Lower Saxon Hills in the district of Hildesheim, Lower Saxony (Germany). Together with the Vorberge and the Sackwald the Sieben Berge belong to the geological formation of the Sackmulde.

The Thüster Berg is a ridge, up to 441 m above NN, in the Lower Saxon Hills in central Germany. It is situated in the districts of Hameln-Pyrmont and Hildesheim in the federal state of Lower Saxony.
The Sauberge is a hill range up to 317 m above sea level (NN) in the Innerste Uplands in the district of Hildesheim in eastern Lower Saxony in Germany.

The Sackwald is a ridge, up to 374 m above sea level (NN) high, in the Lower Saxon Hills in the district of Hildesheim in the North German state of Lower Saxony. It is named after the village of Sack in the borough of Alfeld, the name meaning "Sack Forest".

The Osterwald is a ridge in the Calenberg Uplands and together with the Nesselberg and the Kleiner Deister forms a unified group of three adjacent ranges in the Leine Uplands. It lies between Coppenbrügge, Eldagsen and Elze in the North German state of Lower Saxony.

The Selter is a ridge, up to 395 m above NN, in the Lower Saxon Hills in the districts of Hildesheim, Holzminden and Northeim in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Amtsberge are a relatively small ridge, up to 392.2 m above sea level (NN), near Dassel in southern Lower Saxony in Germany.

The Vorberge are a ridge, up to 353 m above sea level (NN) high, in the Lower Saxon Hills and within the district of Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony. Together with the Sieben Berge and the Sackwald, the Vorberge belong to the geological formation of the Sackmulde.
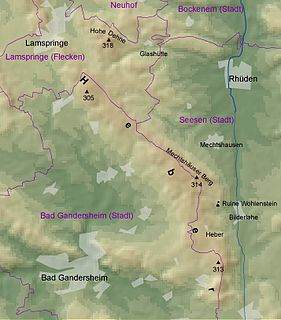
The Heber is a hogback ridge, relatively small in area and up to 313.5 metres high, in the Lower Saxon Hills within the districts of Goslar, Northeim and Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Rotenberg is a hill range, up to 317.3 m high, in the Lower Saxon Hills in southeastern Lower Saxony, Germany.
The Giesen Hills are a ridge, up to 162.6 metres high, in the district of Hildesheim in the German state of Lower Saxony.