Dwarfing is a process in which a breed of animals or cultivar of plants is changed to become significantly smaller than standard members of their species. The effect can be induced through human intervention or non-human processes, and can include genetic, nutritional or hormonal means. Used most specifically, dwarfing includes pathogenic changes in the structure of an organism, in contrast to non-pathogenic proportional reduction in stature.
A satellite is a subviral agent that depends on the coinfection of a host cell with a helper virus for its replication. Satellites can be divided into two major classes: satellite viruses and satellite nucleic acids. Satellite viruses, which are most commonly associated with plants, but are also found in mammals, arthropods, and bacteria, encode structural proteins to enclose their genetic material, which are therefore distinct from the structural proteins of their helper viruses. Satellite nucleic acids, in contrast, do not encode their own structural proteins, but instead are encapsulated by proteins encoded by their helper viruses. The genomes of satellites range upward from 359 nucleotides in length for satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA (STobRV).

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are currently 485 species in this family, divided among 9 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.

Bromoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 36 species in this family, divided among 6 genera.
Luteoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 51 species in this family, divided among three genera, with seven unassigned species. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing symptoms.
Barley yellow dwarf (BYD) is a plant disease caused by the barley yellow dwarf virus (BYDV), and is the most widely distributed viral disease of cereals. It affects the economically important crop species barley, oats, wheat, maize, triticale and rice.

Maize streak virus (MSV) is a virus primarily known for causing maize streak disease (MSD) in its major host, and which also infects over 80 wild and domesticated grasses. It is an insect-transmitted maize pathogen in the genus Mastrevirus of the family Geminiviridae that is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa and neighbouring Indian Ocean island territories such as Madagascar, Mauritius and La Reunion. The A-strain of MSV (MSV-A) causes sporadic maize streak disease epidemics throughout the maize growing regions of Africa. MSV was first described by the South African entomologist Claude Fuller who referred to it in a 1901 report as "mealie variegation".
Fijivirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Spinareovirinae. Plants serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: galls (tumours) in infected plants and Fiji disease, with severe stunting, deformation and death. The group name derives from Fiji island the place where the first virus was isolated. There are currently nine species in this genus including the type species Fiji disease virus.
Maize Dwarf Mosaic Virus (MDMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae. Depending on the corn plant’s growth stage, the virus can have severe implications to the corn plant’s development which can also result in economic consequences to the producer of the crop.

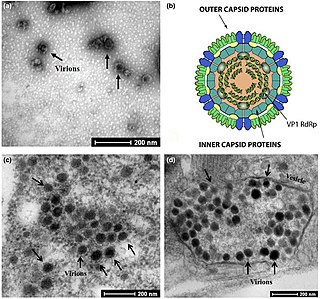
Rice dwarf virus (RDV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Reoviridae.
Rice stripe tenuivirus is an RNA plant pathogen of the genus Tenuivirus. It is prevalent in Japan, China, and Korea and can infect plants of the family Poaceae, which include wheat and corn. Damage from this disease causes major reductions in rice crop yield every year.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 22 species in this genus including the type species Tobacco streak virus.

Phytoreovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Reoviridae, in the subfamily Sedoreovirinae. They are non-turreted reoviruses that are major agricultural pathogens, particularly in Asia. Oryza sativa for RDV and RGDV, dicotyledonous for WTV, and leafhoppers serve as natural hosts. There are currently three species in this genus including the type species Wound tumor virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: WTV: galls (tumor). RDV: dwarf disease of rice. RGDV: dwarfing, stunting, and galls.
Sadwavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently five species in this genus, including the type species Satsuma dwarf virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: satsuma dwarf virus disease which causes spoon-shaped leaves on citrus tree. Symptoms are enations, multiple flushing, stunting or dwarfing, reduction in number and size of leaves and fruits. The name of this genus comes from its type species: Satsuma dwarf virus.
Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 86 species in this family, divided among 8 genera or not assigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Sedoreovirinae is a subfamily of the Reoviridae family of viruses. Viruses in this subfamily are distinguished by the absence of a turreted protein on the inner capsid to produce a smooth surface.
Cytorhabdovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Rhabdoviridae, order Mononegavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts.
Mastrevirus is a genus of ssDNA viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. Mostly monocotyledonous plants serve as natural hosts. They are vectored by planthoppers. There are currently 41 species in this genus including the type species Maize streak virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: maize streak virus: maize streak disease (MSD).
Waikavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants, poaceae, cyperaceae, and gramineae serve as natural hosts. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Rice tungro spherical virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: MCDV: plant stunting and chlorotic striping of tertiary leaf veins in maize.







