Related Research Articles
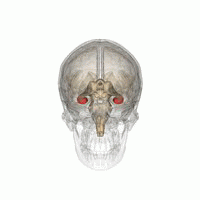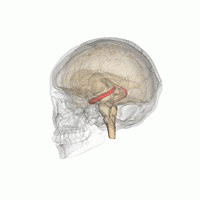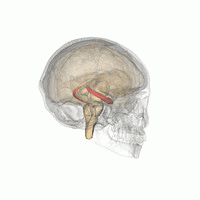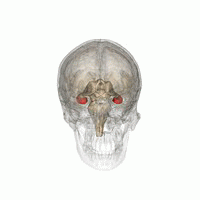
The hippocampus is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper, and the dentate gyrus.

The Cavendish Laboratory is the Department of Physics at the University of Cambridge, and is part of the School of Physical Sciences. The laboratory was opened in 1874 on the New Museums Site as a laboratory for experimental physics and is named after the British chemist and physicist Henry Cavendish. The laboratory has had a huge influence on research in the disciplines of physics and biology.

In neuroscience, long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent strengthening of synapses based on recent patterns of activity. These are patterns of synaptic activity that produce a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between two neurons. The opposite of LTP is long-term depression, which produces a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength.

The School of Informatics is an academic unit of the University of Edinburgh, in Scotland, responsible for research, teaching, outreach and commercialisation in informatics. It was created in 1998 from the former Department of Artificial Intelligence, the Centre for Cognitive Science and the Department of Computer Science, along with the Artificial Intelligence Applications Institute (AIAI) and the Human Communication Research Centre.

Archibald "Archie" Howie is a British physicist and Emeritus Professor at the University of Cambridge, known for his pioneering work on the interpretation of transmission electron microscope images of crystals. Born in 1934, he attended Kirkcaldy High School and the University of Edinburgh. He received his PhD from the University of Cambridge, where he subsequently took up a permanent post. He has been a fellow of Churchill College since its foundation, and was President of its Senior Combination Room (SCR) until 2010.

The hippocampal formation is a compound structure in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. It forms a c-shaped bulge on the floor of the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle. There is no consensus concerning which brain regions are encompassed by the term, with some authors defining it as the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus proper and the subiculum; and others including also the presubiculum, parasubiculum, and entorhinal cortex. The hippocampal formation is thought to play a role in memory, spatial navigation and control of attention. The neural layout and pathways within the hippocampal formation are very similar in all mammals.

Alan Richard Bundy is a professor at the School of Informatics at the University of Edinburgh, known for his contributions to automated reasoning, especially to proof planning, the use of meta-level reasoning to guide proof search.

Christopher Michael Bishop is the Laboratory Director at Microsoft Research Cambridge, Honorary Professor of Computer Science at the University of Edinburgh and a Fellow of Darwin College, Cambridge. Bishop is a member of the UK AI Council. He was also recently appointed to the Prime Minister's Council for Science and Technology.
Jean Duthie Beggs CBE FRS FRSE DSc is a Scottish geneticist. She is the Royal Society Darwin Trust Professor in the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology at the University of Edinburgh.
Wilson Sibbett is a British physicist noted for his work on ultrashort pulse lasers and Streak cameras. He is the Wardlaw Professor of Physics at St Andrews University.

Edvard Ingjald Moser is a Norwegian psychologist and neuroscientist, who is a professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) in Trondheim. In 2005, he and his then-wife May-Britt Moser discovered grid cells in the brain's medial entorhinal cortex. Grid cells are specialized neurons that provide the brain with a coordinate system and a metric for space. In 2018, he discovered a neural network that expresses your sense of time in experiences and memories] located in the brain's lateral entorhinal cortex.

May-Britt Moser is a Norwegian psychologist and neuroscientist, who is a Professor of Psychology and Neuroscience at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). She and her then-husband, Edvard Moser, shared half of the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, awarded for work concerning the grid cells in the entorhinal cortex, as well as several additional space-representing cell types in the same circuit that make up the positioning system in the brain. Together with Edvard Moser she established the Moser research environment at NTNU, which they lead. Since 2012 she has headed the Centre for Neural Computation.
James Norman Davidson CBE PRSE FRS was a British biochemist, pioneer molecular biologist and textbook author. The Davidson Building at the University of Glasgow is named for him.
Timothy Vivian Pelham Bliss FRS is a British neuroscientist. He is an adjunct professor at the University of Toronto, and a group leader emeritus at the Francis Crick Institute, London.
Graham Leon Collingridge is a British neuroscientist and professor at the University of Toronto and at the University of Bristol. He is also a senior investigator at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto.

Eleanor Anne Maguire is an Irish neuroscientist. Since 2007, she has been Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London where she is also a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow.

John O'Keefe, is an American-British neuroscientist, psychologist and a professor at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour and the Research Department of Cell and Developmental Biology at University College London. He discovered place cells in the hippocampus, and that they show a specific kind of temporal coding in the form of theta phase precession. He shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2014, together with May-Britt Moser and Edvard Moser; he has received several other awards. He has worked at University College London for his entire career, but also held a part-time chair at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology at the behest of his Norwegian collaborators, the Mosers.
The Royal Society of Chemistry awards the designation of Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry for distinguished service in the field of chemistry.

Neil Burgess is a Professor of Cognitive neuroscience at University College London and a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow. He has made important contributions to understanding memory and spatial cognition by developing computational models relating behaviour to activity in biological neural networks.
Andrew Dawson Taylor is director of the Science and Technology Facilities Council National Laboratories – Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Daresbury Laboratory, and the UK Astronomy Technology Centre in Edinburgh.
References
- 1 2 "Prof Richard Morris, CBE, FRS". Debrett's. Archived from the original on 12 November 2012. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ Morris, R. G. M. (May 1981). "Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues". Learning and Motivation . 12 (2): 239–260. doi:10.1016/0023-9690(81)90020-5.
- ↑ Andersen, P; Morris, R; Amaral, D; Bliss, T; O'Keefe, J, eds. (2007). The Hippocampus Book. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. pp. xx+832. ISBN 978-0-19-510027-3. OCLC 64444087.
- ↑ Nadel, Lynn (November 2007). "Book review: The hippocampus book, edited by P. Andersen, R. Morris, D. Amaral, T. Bliss, & J. O'Keefe". Hippocampus. 17 (11): 1013–1016. doi:10.1002/hipo.20355.
- ↑ "People/Administration". Centre for Cognitive and Neural Systems. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ "People/Academic Staff – Prof. Richard Morris, CBE, FRS". Centre for Cognitive and Neural Systems. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ "Professor Richard Graham Michael Morris CBE FRS FRSE, FMedSci". The Royal Society of Edinburgh. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- ↑ "Fellows of the Royal Society". Royal Society. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ↑ "Professor Richard Morris, profile: Scientist and Brain Prize winner". The Independent. Retrieved 19 August 2018.
- ↑ "2020 NAS Election". National Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 28 April 2020.