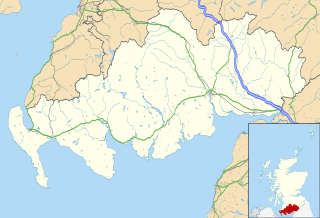
Dumfries and Galloway is one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland, located in the western part of the Southern Uplands. It is bordered by East Ayrshire, South Ayrshire, and South Lanarkshire to the north; Scottish Borders to the north-east; the English county of Cumbria, the Solway Firth, and the Irish Sea to the south, and the North Channel to the west. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, located 76 miles (122 km) to the west of Dumfries on the North Channel coast.

The River Dee, in south-west Scotland, flows from its source in Loch Dee amongst the Galloway Hills, firstly to Clatteringshaws Loch, then into Loch Ken, where it joins the Water of Ken. From there, the Dee flows 15 miles (24 km) southwards to Kirkcudbright, and into Kirkcudbright Bay to reach the Solway Firth. The distance is just over 38 miles (61 km) in total. Together with its tributaries, the Dee's total catchment area is over 400 square miles (1,000 km2).

Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.

The River Eden is a river that flows through Cumbria, England. It rises on Black Fell Moss, near the village of Outhgill, and runs in a generally north-westerly direction through the Vale of Eden and Solway Plain before reaching the sea at the Solway Firth.

The River Spey is a river in the northeast of Scotland. At 98 mi (158 km) it is the eighth longest river in the United Kingdom and the second longest and fastest-flowing river in Scotland. (The Tay is the longest with the Clyde third in Scotland. It is an important location for the traditions of salmon fishing and whisky production in Scotland.

The River Esk, also called the Lothian Esk, is a river that flows through Midlothian and East Lothian, Scotland.

Liddesdale, the valley of the Liddel Water, in the County of Roxburgh, southern Scotland, extends in a south-westerly direction from the vicinity of Peel Fell to the River Esk, a distance of 21 miles (34 km). The Waverley route of the North British Railway ran down the dale, and the Catrail, or Picts' Dyke, crosses its head.

Eskdalemuir is a civil parish and small village in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, with a population of 265. It is around 10 miles (16 km) north-west of Langholm and 10 miles (16 km) north-east of Lockerbie.

Gilnockie Tower is a 17th-century tower house, located at the hamlet of Hollows, 2.2 km north of Canonbie, in Dumfriesshire, south-west Scotland. The tower is situated on the west bank of the River Esk. It was originally known as Hollows Tower.

Liddel Water is a river running through southern Scotland and northern England, for much of its course forming the border between the two countries, and was formerly one of the boundaries of the Debatable Lands.
Canonbie is a small village in Dumfriesshire within the local authority area of Dumfries and Galloway in Scotland, 6 miles south of Langholm and 2 miles north of the Anglo-Scottish border. It is on the A7 road from Carlisle to Edinburgh, and the River Esk flows through it. There are frequent references in older documents to it as Canobie.

The Anglo-Scottish border is an internal border of the United Kingdom separating Scotland and England which runs for 96 miles (154 km) between Marshall Meadows Bay on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west.

The North Esk is a river in Angus and Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is formed by the meeting of the Water of Mark and the Water of Lee, and enters the North Sea four miles north of Montrose. It forms the boundary between Angus and Aberdeenshire at certain stages in its course. It was also noted in the 19th century as a good point for fishing.
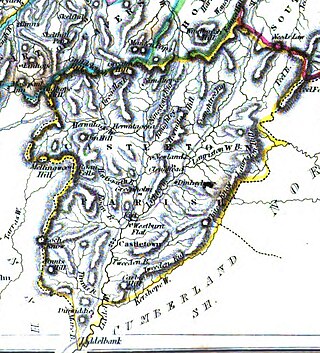
Castleton is a civil parish in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland, in the former Roxburghshire, in the extreme south of the Borders area. It is bounded by Northumberland (England), Dumfries and Galloway, and the parishes of Hobkirk, Southdean and Teviothead. The village of Castleton was commenced in 1793. It was built as a result of the land clearances in the 1790s when people were forced to move from Old Castleton village. While the parish retained the name Castleton, the village later became identified as New Castleton or Newcastleton. The parish is also known by its older name Liddesdale

The Kirtle Water is a river in Dumfries and Galloway in southern Scotland. It rises on the southern slopes of Haggy Hill where its headwaters are impounded to form Winterhope Reservoir. Below the dam it flows in a generally southerly direction passing Waterbeck and Eaglesfield to the village of Kirtlebridge along which stretch it is closely followed both by the A74(M) motorway and the mainline railway between Carlisle and Glasgow. From Kirtlebridge it turns southeastwards to flow by Kirkpatrick-Fleming and on, to the west of Gretna, to empty into the estuary of the Border Esk at the eastern limit of the Solway Firth.

The River Nairn is a 35 mile long river in the Scottish Highlands.
Castle O'er Forest is a forest south of Eskdalemuir, Dumfries and Galloway, in southern Scotland.
















