
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than 150 to 200 °C and, often, elevated pressure of 100 megapascals (1,000 bar) or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock.
Tectonic uplift is the geologic uplift of Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of crustal thickening, changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere.
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift, the highest relief, among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentration of glaciers outside of the polar regions. This last feature earned the Himalaya its name, originating from the Sanskrit for "the abode of the snow".

The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. Each rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium conditions. For example, an igneous rock such as basalt may break down and dissolve when exposed to the atmosphere, or melt as it is subducted under a continent. Due to the driving forces of the rock cycle, plate tectonics and the water cycle, rocks do not remain in equilibrium and change as they encounter new environments. The rock cycle explains how the three rock types are related to each other, and how processes change from one type to another over time. This cyclical aspect makes rock change a geologic cycle and, on planets containing life, a biogeochemical cycle.

The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, from Labrador to Mexico, as well as to Scotland.

Namcha Barwa or Namchabarwa is a mountain peak lying in Tibet in the region of Pemako. The traditional definition of the Himalaya extending from the Indus River to the Brahmaputra would make it the eastern anchor of the entire mountain chain, and it is the highest peak of its own section as well as Earth's easternmost peak over 7,600 metres (24,900 ft). It lies in the Nyingchi Prefecture of Tibet. It is the highest peak in the 180 km long Namcha Barwa Himal range, which is considered the easternmost syntaxis/section of the Himalaya in southeastern Tibet and northeastern India where the Himalaya are said to end, although high ranges actually continue another 300 km to the east.
The Lewis Overthrust is a geologic thrust fault structure of the Rocky Mountains found within the bordering national parks of Glacier in Montana, United States and Waterton Lakes in Alberta, Canada. The structure was created due to the collision of tectonic plates about 59-75 million years ago that drove a several mile thick wedge of Precambrian rock 50 mi (80 km) eastwards, causing it to overlie softer Cretaceous age rock that is 1300 to 1400 million years younger.

The geology of Nepal is dominated by the Himalaya, the highest, youngest and a very highly active mountain range. Himalaya is a type locality for the study of on-going continent-continent collision tectonics. The Himalayan arc extends about 2,400 km (1,500 mi) from Nanga Parbat by the Indus River in northern Pakistan eastward to Namche Barwa by the gorge of the Tsangpo-Brahmaputra in eastern Tibet. About 800 km (500 mi) of this extent is in Nepal; the remainder includes Bhutan and parts of Pakistan, India, and China.

The interaction between erosion and tectonics has been a topic of debate since the early 1990s. While the tectonic effects on surface processes such as erosion have long been recognized, the opposite has only recently been addressed. The primary questions surrounding this topic are what types of interactions exist between erosion and tectonics and what are the implications of these interactions. While this is still a matter of debate, one thing is clear, Earth's landscape is a product of two factors: tectonics, which can create topography and maintain relief through surface and rock uplift, and climate, which mediates the erosional processes that wear away upland areas over time. The interaction of these processes can form, modify, or destroy geomorphic features on Earth's surface.
Ultra-high-pressure metamorphism refers to metamorphic processes at pressures high enough to stabilize coesite, the high-pressure polymorph of SiO2. It is important because the processes that form and exhume ultra-high-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks may strongly affect plate tectonics, the composition and evolution of Earth's crust. The discovery of UHP metamorphic rocks in 1984 revolutionized our understanding of plate tectonics. Prior to 1984 there was little suspicion that continental rocks could reach such high pressures.

The Indus Gorge is formed by the Indus River as it skirts the Nanga Parbat massif, the western anchor of the Greater Himalayas, and before it debouches into the plains of Punjab in Pakistan. The gorge is 4,500–5,200 m (14,800–17,100 ft) deep near the Nanga Parbat. The massive amounts of erosion due to the Indus River following the capture and rerouting through that area is thought to bring middle and lower crustal rocks to the surface. Gilgit is the westernmost tributary of the Indus River.

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the origin of sediments. The Earth is a dynamic planet, and all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks. Rocks exposed to the surface are sooner or later broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosional history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.
In geology, the term exhumation refers to the process by which a parcel of rock, approaches Earth's surface.

The Huangling Anticline or Complex represents a group of rock units that appear in the middle of the Yangtze Block in South China, distributed across Yixingshan, Zigui, Huangling, and Yichang counties. The group of rock involves nonconformity that sedimentary rocks overlie the metamorphic basement. It is a 73-km long, asymmetrical dome-shaped anticline with axial plane orientating in the north-south direction. It has a steeper west flank and a gentler east flank. Basically, there are three tectonic units from the anticline core to the rim, including Archean to Paleoproterozoic metamorphic basement, Neoproterozoic to Jurassic sedimentary rocks, and Cretaceous fluvial deposit sedimentary cover. The northern part of the core is mainly tonalite-trondhjemite-gneiss (TTG) and Cretaceous sedimentary rock called the Archean Kongling Complex. The middle of the core is mainly the Neoproterozoic granitoid. The southern part of the core is the Neoproterozoic potassium granite. Two basins are situated on the western and eastern flanks of the core, respectively, including the Zigui basin and Dangyang basin. Both basins are synforms while Zigui basin has a larger extent of folding. Yuanan Graben and Jingmen Graben are found within the Dangyang Basin area. The Huangling Anticline is an important area that helps unravel the tectonic history of the South China Craton because it has well-exposed layers of rock units from Archean basement rock to Cretaceous sedimentary rock cover due to the erosion of the anticline.
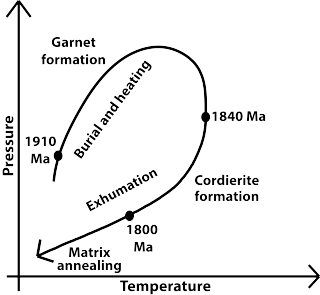
The Pressure-Temperature-time path is a record of the pressure and temperature (P-T) conditions that a rock experienced in a metamorphic cycle from burial and heating to uplift and exhumation to the surface. Metamorphism is a dynamic process which involves the changes in minerals and textures of the pre-existing rocks (protoliths) under different P-T conditions in solid state. The changes in pressures and temperatures with time experienced by the metamorphic rocks are often investigated by petrological methods, radiometric dating techniques and thermodynamic modeling.

Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) thermochronometry is a dating method used to determine the time since quartz and/or feldspar began to store charge as it cools through the effective closure temperature. The closure temperature for quartz and Na-rich K-feldspar is 30-35 °C and 25 °C respectively. When quartz and feldspar are beneath the earth, they are hot. They cool when any geological process e.g. focused erosion causes their exhumation to the earth surface. As they cool, they trap electron charges originating from within the crystal lattice. These charges are accommodated within crystallographic defects or vacancies in their crystal lattices as the mineral cools below the closure temperature.
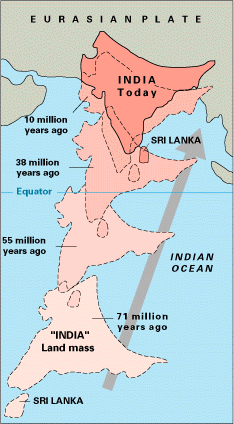
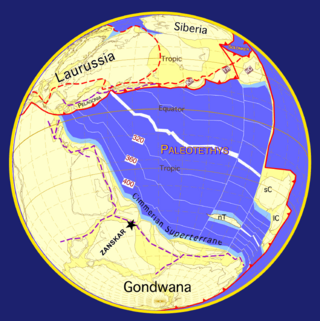
The paleogeography of the India–Asia collision system is the reconstructed geological and geomorphological evolution within the collision zone of the Himalayan orogenic belt. The continental collision between the Indian and Eurasian plate is one of the world's most renowned and most studied convergent systems. However, many mechanisms remain controversial. Some of the highly debated issues include the onset timing of continental collision, the time at which the Tibetan plateau reached its present elevation and how tectonic processes interacted with other geological mechanisms. These mechanisms are crucial for the understanding of Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution, paleoclimate and paleontology, such as the interaction between the Himalayas orogenic growth and the Asian monsoon system, as well as the dispersal and speciation of fauna. Various hypotheses have been put forward to explain how the paleogeography of the collision system could have developed. Important ideas include the synchronous collision hypothesis, the Lhasa-plano hypothesis and the southward draining of major river systems.

The geology of Himachal Pradesh is dominated by Precambrian rocks that were assembled and deformed during the India-Asia collision and the subsequent Himalayan orogeny. The Northern Indian State Himachal Pradesh is located in the Western Himalaya. It has a rugged terrain, with elevation ranging from 320m to 6975m. Rock materials in the region are largely from the Indian craton, and their ages range from the Paleoproterozoic to the present day. It is generally agreed that the Indian craton collided with Asia 50-60 million years ago (Ma). Rock sequences were thrust and folded immensely during the collision. The area has also been shaped by focused orographic precipitation, glaciation and rapid erosion.
A syntaxis is an abrupt major change in the dominant orientation of the main fold and thrust structures in an orogenic belt. For example, the Himalayan belt forms a continuous gentle curve in its main part, running almost perpendicular to the motion of the Indian Plate as it collides with the Eurasian Plate. This thrust-dominated plate boundary connects at both ends to the highly oblique, strike-slip dominated boundaries running through Pakistan and Myanmar, forming the Nanga Parbat syntaxis to the west and the Namche Barwa syntaxis in the east.
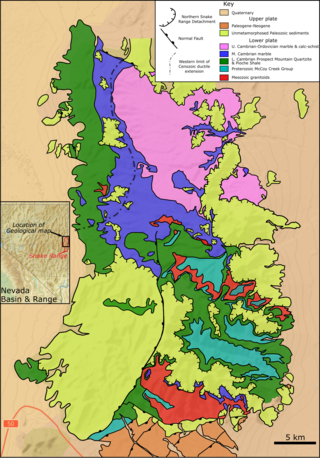
The Northern Snake Range metamorphic core complex is a gently domed structure that forms the northern part of the Snake Range in Nevada. The metamorphic core complex consists of an upper plate of brittlely-faulted Cambrian to Permian mainly carbonate sedimentary rocks, unconformably overlain by Cenozoic volcanic and clastic rocks and separated from a lower plate of ductilely-deformed and metamorphosed Neoproterozoic to Cambrian sedimentary rocks, cut by Mesozoic to Cenozoic intrusions, by the intensely-deformed fault zone of the Snake Range Detachment (SRD). It was selected as one of the first 100 geological heritage sites identified by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) to be of the highest scientific value.


















