
Brunswick Town is an area in Hove, in the city of Brighton and Hove, England. It is best known for the Regency architecture of the Brunswick estate.
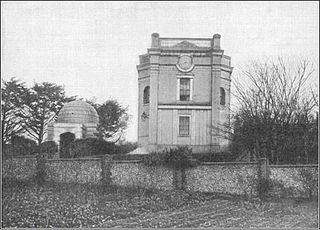
The Montefiore Synagogue is the former private synagogue of Sir Moses Montefiore. It is an 1833, Grade II* listed building in Ramsgate, Kent, England. The synagogue and mausoleum are cared for and maintained by the Montefiore Endowment. The endowment also maintains the nearby Ramsgate Jewish Cemetery.
David Alfred Mocatta (1806–1882) was a British architect and a member of the Anglo-Jewish Mocatta family.

The Brighton Unitarian Church, previously known as Christ Church, is a Unitarian chapel in Brighton, England. Built in 1820 by prolific local architect Amon Henry Wilds on land sold to the fledgling Unitarian community by the Prince Regent, the stuccoed Greek Revival building occupies a prominent position near the corner of Church Road and New Road in the centre of Brighton, near the Royal Pavilion and the city's main theatres. It has had Grade II listed status since 1952. It is a member of the General Assembly of Unitarian and Free Christian Churches, the umbrella organisation for British Unitarians.

The Middle Street Synagogue is a synagogue in the centre of Brighton, part of the English city of Brighton and Hove. It was the centre for Jewish worship in Brighton and Hove for more than a century. Although it is not in full-time use, the building is still open at certain times, and services are still held at certain times of the year. It has been listed at Grade II*, reflecting its architectural and historic importance.

There are 24 Grade I listed buildings in the city of Brighton and Hove, England. The city, on the English Channel coast approximately 52 miles (84 km) south of London, was formed as a unitary authority in 1997 by the merger of the neighbouring towns of Brighton and Hove. Queen Elizabeth II granted city status in 2000.

The Union Chapel, also known as the Union Street Chapel, Elim Free Church, Four Square Gospel Tabernacle or Elim Tabernacle of the Four Square Gospel, is a former chapel in the centre of Brighton, a constituent part of the city of Brighton and Hove, England. After three centuries of religious use by various congregations, the chapel—which had been Brighton's first Nonconformist place of worship—passed into secular use in 1988 when it was converted into a pub. It was redesigned in 1825, at the height of Brighton's Georgian building boom, by at least one of the members of the Wilds–Busby architectural partnership, Brighton's pre-eminent designers and builders of the era, but may retain some 17th-century parts. It has been listed at Grade II in view of its architectural importance.

Bristol Road Methodist Church is a former Methodist place of worship in the Kemptown area of Brighton, part of the English city of Brighton and Hove. Built in 1873 to an Italian Romanesque Revival design, it served this part of eastern Brighton for more than a century until its closure in 1989, after which it became a recording studio. It is owned by Brighton College, an independent school based nearby. The building has been listed at Grade II in view of its architectural importance.

The Sassoon Mausoleum is the former grave of Sir Albert Sassoon and other members of his family, including Sir Edward Sassoon, 2nd Baronet, of Kensington Gore. It stands at 83 St. George's Road in Brighton, England. The single-storey building, which is Grade II listed, has since served as a furniture depository and an air-raid shelter, and since being purchased by a brewery in 1949 has remained a pub or bar.

The Cheltenham Synagogue is a synagogue in Cheltenham noted for its Regency architecture. It is an independent congregation located in the town centre on Synagogue Lane, off St James's Square.

The Plymouth Synagogue is a synagogue in the city of Plymouth, England and the home of the Plymouth Hebrew Congregation. Built in 1762, it is a listed Grade II* building and the oldest extant synagogue built by Ashkenazi Jews in the English speaking world.

Brighton Regency Synagogue is a Regency building in Devonshire Place, Brighton, that was built in 1824 as a synagogue and is now an apartment building. It is a Grade II listed building.

The former Merthyr Synagogue is located on Bryntirion Road in the Thomastown section of Merthyr Tydfil, Wales. It is a Grade II listed building and is the oldest purpose-built synagogue still standing in Wales.
Philip Salomons (1796–1867) was an English financier, Jewish leader and High Sheriff of Sussex.

The building at 11 Dyke Road in Brighton, part of the English city of Brighton and Hove, is now the Rialto Theatre, but it originally housed the Swan Downer School for poor girls, for whom it was designed and built in 1867 by prolific architect George Somers Leigh Clarke. The highly ornate brick structure, in a "freely inventive" European Gothic style, has also served as a chapel and an office since it was vacated by the school, whose pupils were recognisable around Brighton in their blue and white uniform. English Heritage has listed the building at Grade II for its architectural and historical importance.
Thomas Lainson (1825–1898) was a British architect. He is best known for his work in the East Sussex coastal towns of Brighton and Hove, where several of his eclectic range of residential, commercial and religious buildings have been awarded listed status by English Heritage. Working alone or in partnership with two sons as Lainson & Sons, he designed buildings in a wide range of styles, from Neo-Byzantine to High Victorian Gothic; his work is described as having a "solid style, typical of the time".

Round Hill is an inner suburban area of Brighton, part of the coastal city of Brighton and Hove in England. The area contains a mix of privately owned and privately rented terraced housing, much of which has been converted for multiple occupancies, and small-scale commercial development. It was developed mostly in the late 19th century on an area of high land overlooking central Brighton and with good views in all directions, the area became a desirable middle-class suburb—particularly the large terraced houses of Roundhill Crescent and Richmond Road, and the exclusive Park Crescent—and within a few decades the whole of the hill had been built up with smaller terraces and some large villas.

Tower House is a former private house in the Withdean area of the English coastal city of Brighton and Hove. Built in 1902 for a former jeweller to King Edward VII, it remained in private ownership until it was converted into flats and a daycare centre in 1988. It is one of the few large houses and villas to survive in the high-class Withdean area—many were demolished in favour of blocks of flats after World War II—and it has been described as "Brighton's finest example of a grand Edwardian house". English Heritage has listed the building at Grade II for its architectural and historical importance.

Princes House is an office and residential building in the centre of Brighton, part of the English coastal city of Brighton and Hove. The prominently sited building, an example of Harry Stuart Goodhart-Rendel's "inimitable response to Modernism", was purpose-built as the headquarters of the Brighton & Sussex Building Society, forerunner of the Alliance & Leicester. The office was later used by Norwich Union, another financial institution, and now houses a restaurant and flats. The steel-framed structure is clad in red bricks with inlaid mosaicwork, forming a carefully detailed façade, and the corner elevation has an arrangement of brickwork and windows which suggests "the pleated folds of a curtain". The building is listed at Grade II for its architectural and historical importance.



















