Related Research Articles

Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for in silico analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques.

Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers.

Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.
Rosalind or Rosalinde is a girls' name derived from the Germanic hros, which meant horse, and lind which meant soft or tender:

Learning classifier systems, or LCS, are a paradigm of rule-based machine learning methods that combine a discovery component with a learning component. Learning classifier systems seek to identify a set of context-dependent rules that collectively store and apply knowledge in a piecewise manner in order to make predictions. This approach allows complex solution spaces to be broken up into smaller, simpler parts.
Terrence Joseph Sejnowski is the Francis Crick Professor at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies where he directs the Computational Neurobiology Laboratory and is the director of the Crick-Jacobs center for theoretical and computational biology. He has performed pioneering research in neural networks and computational neuroscience.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing or scientific computation (SC), is a field in mathematics that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex problems. It is an area of science that spans many disciplines, but at its core, it involves the development of models and simulations to understand natural systems.

Orange is an open-source data visualization, machine learning and data mining toolkit. It features a visual programming front-end for explorative rapid qualitative data analysis and interactive data visualization.
Constructivist teaching is based on constructivist learning theory. Constructivist teaching is based on the belief that learning occurs as learners are actively involved in a process of meaning and knowledge construction as opposed to passively receiving information.

Crowdsourcing involves a large group of dispersed participants contributing or producing goods or services—including ideas, votes, micro-tasks, and finances—for payment or as volunteers. Contemporary crowdsourcing often involves digital platforms to attract and divide work between participants to achieve a cumulative result. Crowdsourcing is not limited to online activity, however, and there are various historical examples of crowdsourcing. The word crowdsourcing is a portmanteau of "crowd" and "outsourcing". In contrast to outsourcing, crowdsourcing usually involves less specific and more public groups of participants.
Math wars is the debate over modern mathematics education, textbooks and curricula in the United States that was triggered by the publication in 1989 of the Curriculum and Evaluation Standards for School Mathematics by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) and subsequent development and widespread adoption of a new generation of mathematics curricula inspired by these standards.
Computational thinking (CT) is the mental skill to apply concepts, methods, problem solving techniques, and logic reasoning, derived from computing and computer science, to solve problems in all areas, including our daily lives. In education, CT is a set of problem-solving methods that involve expressing problems and their solutions in ways that a computer could also execute. It involves automation of processes, but also using computing to explore, analyze, and understand processes.

Andrew Yan-Tak Ng is a British-born American computer scientist and technology entrepreneur focusing on machine learning and AI. Ng was a co-founder and head of Google Brain and was the former chief scientist at Baidu, building the company's Artificial Intelligence Group into a team of several thousand people.

Pavel Arkadevich Pevzner is the Ronald R. Taylor Professor of Computer Science and Director of the NIH Center for Computational Mass Spectrometry at University of California, San Diego. He serves on the Editorial Board of PLoS Computational Biology and he is a member of the Genome Institute of Singapore scientific advisory board.
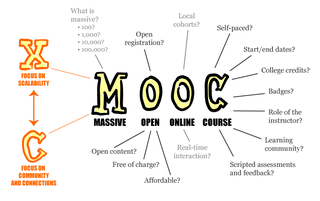
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012.

Competitive programming is a mind sport usually held over the Internet or a local network, involving participants trying to program according to provided specifications. Contestants are referred to as sport programmers. Competitive programming is recognized and supported by several multinational software and Internet companies, such as Google and Facebook.
Modern elementary mathematics is the theory and practice of teaching elementary mathematics according to contemporary research and thinking about learning. This can include pedagogical ideas, mathematics education research frameworks, and curricular material.

Coursera Inc. is a U.S.-based massive open online course provider founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Coursera works with universities and other organizations to offer online courses, certifications, and degrees in a variety of subjects. In 2021 it was estimated that about 150 universities offered more than 4,000 courses through Coursera.
Bing Liu is a Chinese-American professor of computer science who specializes in data mining, machine learning, and natural language processing. In 2002, he became a scholar at University of Illinois at Chicago. He holds a PhD from the University of Edinburgh (1988). His PhD advisors were Austin Tate and Kenneth Williamson Currie, and his PhD thesis was titled Reinforcement Planning for Resource Allocation and Constraint Satisfaction.

Topica Edtech Group is a multinational educational technology company. It provides online education including bachelor's degree programs, English speech tutoring courses and technology platform for massive online open courses in a variety of fields (Edumall).
References
- ↑ "Researchers Launch Innovative, Hands-on Online Tool for Science Education". Jacobsschool.ucsd.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-28.
- ↑ "Rosalind is a platform for learning bioinformatics through problem solving. | Hacker News". News.ycombinator.com. Retrieved 2015-02-28.
- ↑ "Q&A: UCSD's Philip Compeau Discusses Rosalind, a Problem-Oriented Bioinformatics Education Platform". Bioinform. 5 October 2012. Retrieved 2015-02-28.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Top Bioinformatics Contributions of 2012 « Homolog.us – Bioinformatics". Homolog.us. Archived from the original on 2013-03-15. Retrieved 2015-02-28.
- ↑ "ROSALIND Statistics Countries". ROSALIND. Retrieved 2022-07-20.
- ↑ "Free Online Courses From Top Universities". Coursera. Retrieved 2015-02-28.
- ↑ "Bioinformatics Algorithms - Stepic". Beta.stepic.org. Archived from the original on 2013-11-12. Retrieved 2015-02-28.