Santiago de Compostela, simply Santiago, or Compostela, in the province of A Coruña, is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of St. James, a leading Catholic pilgrimage route since the 9th century. In 1985, the city's Old Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

Astorga is a municipality and city of Spain located in the central area of the province of León, in the autonomous community of Castilla y León, 43 kilometres (27 mi) southwest of the provincial capital. It is located in the transit between the Páramo Leonés and the mountains of León and acts as the backbone of the comarcas of Maragatería, La Cepeda and the Ribera del Órbigo. The city is the head of one of the most extensive and oldest dioceses of Spain, whose jurisdiction covers half of the province of León and part of Ourense and Zamora. It is also head of the judicial party number 5 of the province of León.

James the Great was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die, and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of Spain and, according to tradition, what are believed to be his remains are held in Santiago de Compostela in Galicia.

Conques is a former commune in the Aveyron department in Southern France, in the Occitania region. On 1 January 2016, it was merged into the new commune of Conques-en-Rouergue.
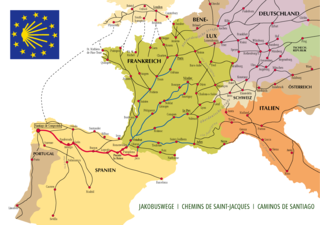
The Camino de Santiago, or in English the Way of St. James, is a network of pilgrims' ways or pilgrimages leading to the shrine of the apostle James in the cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwestern Spain, where tradition holds that the remains of the apostle are buried.

Ponferrada is a city of Spain, located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. Ponferrada, the second most populated municipality of the Province of León, is also the capital city of El Bierzo, the only comarca recognized as an administrative entity by law in the region.

Saint-Jean-Pied-de-Port is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in south-western France. It is close to Ostabat in the Pyrenean foothills. The town is also the old capital of the traditional Basque province of Lower Navarre. Saint-Jean-Pied-de-Port is also a starting point for the French Way Camino Francés, the most popular option for travelling the Camino de Santiago. It is a member of Les Plus Beaux Villages de France Association.

The Codex Calixtinus is a manuscript that is the main witness for the 12th-century Liber Sancti Jacobi, a pseudepigraph attributed to Pope Calixtus II. The principal author or compiler of the Liber is thus referred to as "Pseudo-Calixtus", but is often identified with the French scholar Aymeric Picaud. Its most likely period of compilation is 1138–1145.

Sarria is a municipality in the province of Lugo, in the autonomous community of Galicia, northwestern Spain. It belongs to the comarca of Sarria. Sarria is the most populous town on the French Way in Galicia, with 13,700 inhabitants and the major is Carmen José Lòpez. It is head of the region and the most popular starting point for the Camino de Santiago; many pilgrims choose Sarria because the distance from this point to Santiago allows them to cover the necessary kilometers to reach the Compostela. King Alfonso IX of León died in Sarria in 1230 while making a pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela.

The Monastery of Santo Toribio de Liébana is a Roman Catholic monastery located in the district of Liébana, near Potes in Cantabria, Spain. Located in the Cantabrian Mountains in northern Spain, the monastery is one of the five places in Roman Catholicism, together with Rome, Jerusalem, Santiago de Compostela and Caravaca de la Cruz, that has the privilege of issuing perpetual indulgences.

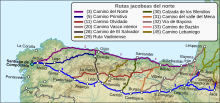
The Camino de Santiago, also known as the Way of St. James, extends from different countries of Europe, and even North Africa, on its way to Santiago de Compostela and Finisterre. The local authorities try to restore many of the ancient routes, even those used in a limited period, in the interest of tourism.

The Cathedral Basilica of Saint James is a Catholic cathedral in Bilbao, Spain. It is dedicated to the apostle James the Great, by virtue of being a point of transit for the pilgrims that followed the Northern Way of the Camino de Santiago. In 2015, it was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site together several other buildings along the route.

The French Way follows the GR 65 and is the most popular of the routes of the Way of St. James, the ancient pilgrimage route to Santiago de Compostela in Galicia, Spain. It runs from Saint-Jean-Pied-de-Port on the French side of the Pyrenees to Roncesvalles on the Spanish side and then another 780 km on to Santiago de Compostela through the major cities of Pamplona, Logroño, Burgos and León. A typical walk on the Camino francés takes at least four weeks, allowing for one or two rest days on the way. Some travel the Camino on bicycle or on horseback.

The Via Podiensis or the Le Puy Route is one of the four routes through France on the pilgrimage to the tomb of St. James the Great in Santiago de Compostela in Galicia in northwest Spain. It leaves from Le-Puy-en-Velay and crosses the countryside in stages to the stele of Gibraltar in the basque village of Uhart-Mixe. Near there it merges with two of the other routes, the via Turonensis and the via Lemovicensis which merge a little earlier.

Christianity has a strong tradition of pilgrimages, both to sites relevant to the New Testament narrative and to sites associated with later saints or miracles.

UNESCO designated the Routes of Santiago de Compostela in France as a World Heritage Site in December 1998. The routes pass through the following regions of France: Aquitaine, Auvergne, Basse-Normandie, Bourgogne, Centre, Champagne-Ardenne, Ile-de-France, Languedoc-Roussillon, Limousin, Midi-Pyrénées, Picardie, Poitou-Charentes, and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur. UNESCO cites the routes' role in "religious and cultural exchange", the development of "specialized edifices" along the routes, and their "exceptional witness to the power and influence of Christian faith among people of all classes and countries in Europe during the Middle Ages".
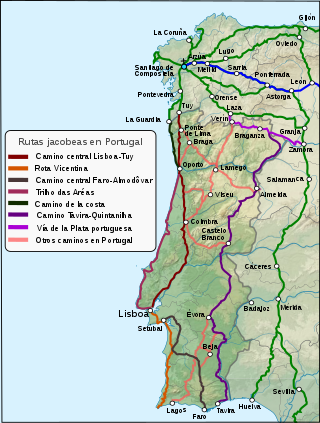
The Portuguese Way is the name of the Camino de Santiago pilgrimage routes starting in Portugal. It begins at Porto or Lisbon. From Porto, along the Douro River, pilgrims travel north crossing the five main rivers—the Ave, Cávado, Neiva, Lima and Minho—before entering Spain and passing through Pontevedra on the way to Santiago de Compostela.
The English Way or Camino Inglés is one of the paths of the Camino de Santiago. The Spanish section begins in the Galician port cities of Ferrol or A Coruña, with multiple additional sections in the UK and Ireland, and continues south to Santiago de Compostela.
The Primitive Way is one of the paths of the Camino de Santiago. It begins in the old Asturian capital of Oviedo and runs west to Lugo and then south to Santiago de Compostela joining the more popular French Way in Melide for the last two hiking days. According to the Confraternity of St James, the Camino Primitivo is approximately 320 km in length.

The Northern Way, also called the Coastal Way, is one of the routes of the Camino de Santiago. It is an 817 kilometres (508 mi), five-week coastal route from Irún (Gipuzkoa), near the border with France, following the northern coastline of Spain into Galicia where it heads inland towards Santiago de Compostela joining the French Way at Arzúa. This route follows the old Roman road, the Via Agrippa –which was used in the Middle Ages by Christian pilgrims when Muslim domination had extended northwards and was making travel along the French Way dangerous – for some of its way. The Northern Way coincides with the E9 European long distance path for most of its route.