
Assam is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of 78,438 km2 (30,285 sq mi). It is the second largest state in northeastern India by area and the largest in terms of population, with more than 31 million inhabitants. The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a 22-kilometre-wide (14 mi) strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Boro are the official languages of Assam. Meitei (Manipuri) is the official language of Hojai district and the entirety of the Barak Valley region, while Bengali is an official language in the three districts of Barak Valley.
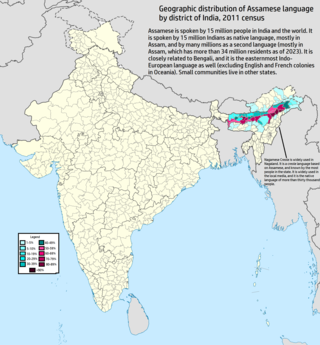
Assamese or Asamiya is an Indo-Aryan language spoken mainly in the north-eastern Indian state of Assam, where it is an official language. It serves as a lingua franca of the wider region and has over 15 million native speakers according to Ethnologue.

Indira Goswami, known by her pen name Mamoni Raisom Goswami and popularly as Mamoni Baideo, was an Indian writer, poet, professor, scholar and editor.

Zubeen Garg is an Indian singer–songwriter, composer, lyricist, music director, music producer, actor, film director, film producer, screenwriter, poet and philanthropist. He primarily works for and sings in the Assamese, Bengali and Hindi-language film and music industries, but has sung in 40 other languages and dialects, including Bishnupriya Manipuri, Boro, English, Goalpariya, Kannada, Karbi, Khasi, Malayalam, Marathi, Mising, Nepali, Odia, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Tiwa. He is also a multi-instrumentalist and plays 12 instruments including anandalahari, dhol, dotara, drums, guitar, harmonica, harmonium, mandolin, keyboard, tabla and various percussion instruments. He is Assam's highest-paid singer.

Assamese cinema is the Indian film industry of Assamese language. It is based in Assam, India. The industry was born in 1935 when Jyoti Prasad Agarwala released his movie Joymoti. Since then the Assamese cinema has developed a slow-paced, sensitive style. In the beginning the industry were called Jollywood, for Agarwala's Jyoti Chitraban Film Studio.

Prof Bhabananda Deka was a pioneer Assam economist and author who conducted novel research on the economy of the far eastern part of India. He was also a leading Indian-Assamese litterateur of the famed 'Awahon-Ramdhenu Era' of Assamese literature during the mid-20th century. He was the author of a total of 115 English and Assamese books including textbooks on a range of fifteen subjects including economics, ancient Assamese literature, philosophy, education, religion, mythology, archaeology, tribal study, poetry, drama, memoirs, civics, political science, biographies; he also edited books and journals. He also authored a variety of research papers and articles about the state of Assam, a state in the north-eastern part of India. He pioneered the writing of books on Economics in Assamese. His Assamese book Axomor Arthaneeti was the first ever research-based comprehensive book on Assam Economics, which was published for the first time in 1963. He was conferred with the honorary title of 'Asom Ratna' -- 'Jewel of Assam' by the intellectuals of Assam on 19 August 2007 at a public meet held under the presidency of Prof. (Dr) Satyendra Narayan Goswami.
Mithinga Daimary was the Central Publicity Secretary of the banned outfit ULFA since the previous publicity secretary Siddhartha Phukan's surrender in 1992. He was born in the Barama village in Nalbari district of Assam on 17 May 1967 with the birth name Deepak Kachari.

Jeevan Baator Logori is a 2009 Indian Assamese language drama film directed by Timothy Das Hanche under the banner Hills Motion Pictures Association of Diphu. The film is set in the rural and urban areas of Assam and shot at Cinemascope on the 35mm format.

Assam separatist movements refers to a series of multiple insurgent and separatist movements that had been operated in the Northeast Indian state of Assam. The conflict started in the 1970s following tension between the native indigenous Assamese people and the Indian government over alleged neglect, political, social, cultural, economic issues and increased levels of illegal immigration from Bangladesh. The conflict has resulted in the deaths of 12,000 United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA) militants and 18,000 others.
The Dark Age of the Assamese language is a 37 year long time-frame, from 1836 to 1873, during which Bengali eclipsed the Assamese language. During British India, the Bengali language was imposed over Assamese as the British took over Assam. The clerical and technical workers that they brought were Bengali, in order to impose Bengali as the medium of instruction in schools and colleges, and for all official purposes.

Dwaar is a 2013 Indian Assamese drama film directed by Bidyut Chakravarty, with his own screenplay, and produced by Sanjive Narain and Bidyut Chakravarty himself. It was adapted from the Assamese short story Bahiroloi Jowa Baat by Apurba Sarma. Dwaar stars Kapil Bora, Zerifa Wahid and Mahika Sharma in the lead roles. The literal translation of the title means Door.
Kamrupi dialects are a group of regional dialects of Assamese, spoken in the Kamrup region. It formerly enjoyed prestige status. It is one of two western dialect groups of the Assamese language, the other being Goalpariya. Kamrupi is heterogeneous with three subdialects— Barpetia dialect, Nalbariya dialect and Palasbaria dialect.

Ekhon Nedekha Nodir Xhipare is a 2012 Assamese language socio-political thriller film, with some dialogue in Hindi, starring Sanjay Suri and Bidita Bag in the lead roles. It was directed by Bidyut Kotoky and produced by National Film Development Corporation of India. The film was simultaneously made in Hindi as As the river flows.
Dipali Barthakur was an Indian singer from Assam. Her songs were sung mainly in the Assamese language. She received the fourth-highest civilian award of India, the Padma Shri, in the year 1998.

Cotton University is a public state university located in Guwahati, Assam, India. It was established in 2017 by the provisions of an Act from the Assam Legislative Assembly which merged Cotton College State University and Cotton College. The university has progressed to become one of the top 200 institutions of the country. However, as of 2024, Cotton University is ranked 373rd in the NIRF, whereas Gauhati University holds a commendable 40th position in the same ranking.

Nalini Prava Deka was an author, poet, storyteller, actress and playwright from Assam, a state in India encompassing the Brahmaputra Valley. She was honoured at a 2012 gathering in Ledo by the Assam Sahitya Sabha. Deka promoted Assamese heritage, traditional customs, weaving and fabric art, cooking and folk music with her husband, Bhabananda Deka. They researched traditional Assamese lifestyle, art, literature and culture. Deka was the first female editor and publisher of a children's magazine, Phul (Flower), and wrote 30 critically praised books. All India Radio broadcast Deka's radio plays on issues related to women and children.

Karabi Deka Hazarika is an Indian writer from the state of Assam in Northeastern India.
The Assamese Language Movement refers to a series of political activities demanding the recognition of the Assamese language as the only sole official language and medium of instruction in the educational institutions of Assam, India.

Utpal Borpujari is a double National Film Award winner; one, as a film critic, and the other, as a filmmaker. In 2003, he won the Swarna Kamal for Best Film Critic at the 50th National Film Awards of India. In 2018, he won the National Film Award, and 5 Assam State Film Awards for his debut feature film Ishu
Purab ki Awaz is an Indian Historical drama film directed by Chandra Mudoi and produced by Loknath Deka. the film features Urmila Mahanta, Nipon Goswami, Debashis Borthakur, Rina Bora and others. this film release in All India on 10 March and will be releasing soon in Assam in August 2017.














