Related Research Articles
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term atom includes ions.

In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model was the first successful model of the atom. Developed from 1911 to 1918 by Niels Bohr and building on Ernest Rutherford's nuclear model, it supplanted the plum pudding model of J J Thomson only to be replaced by the quantum atomic model in the 1920s. It consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. It is analogous to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic force rather than gravity, and with the electron energies quantized.
Atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter–matter and light–matter interactions, at the scale of one or a few atoms and energy scales around several electron volts. The three areas are closely interrelated. AMO theory includes classical, semi-classical and quantum treatments. Typically, the theory and applications of emission, absorption, scattering of electromagnetic radiation (light) from excited atoms and molecules, analysis of spectroscopy, generation of lasers and masers, and the optical properties of matter in general, fall into these categories.

A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be quantized.

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules, electrons, positrons, protons, antiprotons and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.

In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, meaning that the 1s, 2s, and 2p subshells are occupied by two, two, and six electrons, respectively.
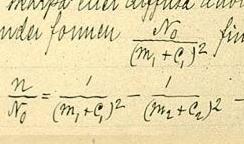
In atomic physics, the Rydberg formula calculates the wavelengths of a spectral line in many chemical elements. The formula was primarily presented as a generalization of the Balmer series for all atomic electron transitions of hydrogen. It was first empirically stated in 1888 by the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, then theoretically by Niels Bohr in 1913, who used a primitive form of quantum mechanics. The formula directly generalizes the equations used to calculate the wavelengths of the hydrogen spectral series.

The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to electrons making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photons is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances.

In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state. Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation.
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory (MO theory or MOT) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century. The MOT explains the paramagnetic nature of O2, which valence bond theory cannot explain.
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Research groups studying molecular physics are typically designated as one of these other fields. Molecular physics addresses phenomena due to both molecular structure and individual atomic processes within molecules. Like atomic physics, it relies on a combination of classical and quantum mechanics to describe interactions between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Experiments in the field often rely heavily on techniques borrowed from atomic physics, such as spectroscopy and scattering.
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds when a molecule is formed. In contrast, molecular orbital theory has orbitals that cover the whole molecule.
A Rydberg atom is an excited atom with one or more electrons that have a very high principal quantum number, n. The higher the value of n, the farther the electron is from the nucleus, on average. Rydberg atoms have a number of peculiar properties including an exaggerated response to electric and magnetic fields, long decay periods and electron wavefunctions that approximate, under some conditions, classical orbits of electrons about the nuclei. The core electrons shield the outer electron from the electric field of the nucleus such that, from a distance, the electric potential looks identical to that experienced by the electron in a hydrogen atom.

The emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen has been divided into a number of spectral series, with wavelengths given by the Rydberg formula. These observed spectral lines are due to the electron making transitions between two energy levels in an atom. The classification of the series by the Rydberg formula was important in the development of quantum mechanics. The spectral series are important in astronomical spectroscopy for detecting the presence of hydrogen and calculating red shifts.
Rydberg ionization spectroscopy is a spectroscopy technique in which multiple photons are absorbed by an atom causing the removal of an electron to form an ion.
A Rydberg molecule is an electronically excited chemical species. Electronically excited molecular states are generally quite different in character from electronically excited atomic states. However, particularly for highly electronically excited molecular systems, the ionic core interaction with an excited electron can take on the general aspects of the interaction between the proton and the electron in the hydrogen atom. The spectroscopic assignment of these states follows the Rydberg formula, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, and they are called Rydberg states of molecules. Rydberg series are associated with partially removing an electron from the ionic core.
A heavy Rydberg system consists of a weakly bound positive and negative ion orbiting their common centre of mass. Such systems share many properties with the conventional Rydberg atom and consequently are sometimes referred to as heavy Rydberg atoms. While such a system is a type of ionically bound molecule, it should not be confused with a molecular Rydberg state, which is simply a molecule with one or more highly excited electrons.
Photoelectrochemical processes are processes in photoelectrochemistry; they usually involve transforming light into other forms of energy. These processes apply to photochemistry, optically pumped lasers, sensitized solar cells, luminescence, and photochromism.
Triatomic hydrogen or H3 is an unstable triatomic molecule containing only hydrogen. Since this molecule contains only three atoms of hydrogen it is the simplest triatomic molecule and it is relatively simple to numerically solve the quantum mechanics description of the particles. Being unstable the molecule breaks up in under a millionth of a second. Its fleeting lifetime makes it rare, but it is quite commonly formed and destroyed in the universe thanks to the commonness of the trihydrogen cation. The infrared spectrum of H3 due to vibration and rotation is very similar to that of the ion, H+
3. In the early universe this ability to emit infrared light allowed the primordial hydrogen and helium gas to cool down so as to form stars.
Bond softening is an effect of reducing the strength of a chemical bond by strong laser fields. To make this effect significant, the strength of the electric field in the laser light has to be comparable with the electric field the bonding electron "feels" from the nuclei of the molecule. Such fields are typically in the range of 1–10 V/Å, which corresponds to laser intensities 1013–1015 W/cm2. Nowadays, these intensities are routinely achievable from table-top Ti:Sapphire lasers.
References
- ↑ "Students create exotic state of matter". 15 November 2016.
- ↑ Šibalić, Nikola; S Adams, Charles (2018). Rydberg Physics. IOP Publishing. Bibcode:2018ryph.book.....S. doi:10.1088/978-0-7503-1635-4. ISBN 9780750316354.
- ↑ Fielding, H. H. (2005). "Rydberg wavepackets in molecules: from observation to control". Annual Review of Physical Chemistry. 56: 91–117. Bibcode:2005ARPC...56...91F. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.55.091602.094428. ISSN 0066-426X. PMID 15796697.
- ↑ Gessner, O.; Lee, M.; Shaffer, P.; Reisler, H.; Levchenko, V.; Krylov, I.; Underwood, G.; Shi, H.; East, L.; Wardlaw, D. M.; Chrysostom, E. T.; Hayden, C. C.; Stolow, A. (Jan 2006). "Femtosecond multidimensional imaging of a molecular dissociation". Science. 311 (5758): 219–222. Bibcode:2006Sci...311..219G. doi: 10.1126/science.1120779 . ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 16357226. S2CID 40024888.
- ↑ Stohr, J., "NEXAFS Spectroscopy" Springer Series in Surface Science 25, (1992), p. 86.
- Atomic Spectra and Atomic Structure, Gerhard Herzberg, Prentice-Hall, 1937.
- Atoms and Molecules, Martin Karplus and Richard N. Porter, Benjamin & Company, Inc., 1970.